Eukaryotic cell organelles and their functions pdf
Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a logarithmic scale.
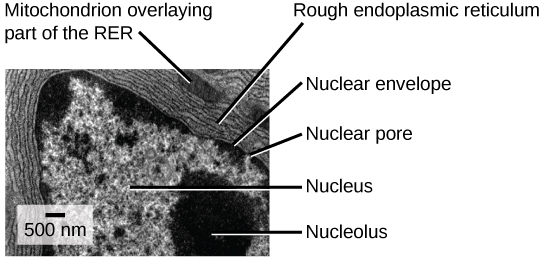
Eukaryotic cells, including all animal cells, also contain various cellular organelles. An organelle (“little organ”) is one of several different types of membrane-enclosed bodies in the cell, each performing a unique function.
5.1 A typical eukaryotic cell 1. Compare and contrast eukaryotic, bacterial, and archaeal cells in terms of their use of membranes, size, morphological diversity, and organelles.
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure and Function. Introduction to eukaryotic cells . By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts
Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Some of the worksheets displayed are Work prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure, Cell structure answers work, Cell ebrate science without work, Organelles in eukaryotic cells, Cell structure exploration activities, Cell structure work
zdifferentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; z cells have in their cytoplasm, large vacuoles containing non-living inclusions like crystals, and pigments. The bacteria have neither defined cell organelles nor a well formed nucleus. But every cell has three major components: zplasma membrane zcytoplasm zDNA (naked in bacteria) and enclosed by a nuclear membrane in all other
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
19 Doc organelles In Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet from cell organelles worksheet , source:swiftcantrellpark.org. Cell organelles Worksheet – functions of cell organelles worksheet this cool worksheet prompts young biologists to research the functions of cell organelles …
Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet as Well as Worksheet Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet Worksheet worksheet December 11, 2018 Download by size: Handphone Tablet Desktop (Original Size)
This introduction to cells will take you through the basic structure of cells, the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and you will learn about organelles. STRUCTURE OF A CELL Every cell is different but there is a basic structure that is common to all cells.
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Their Functions Questions
https://www.youtube.com/embed/7hFwLvnjfUc
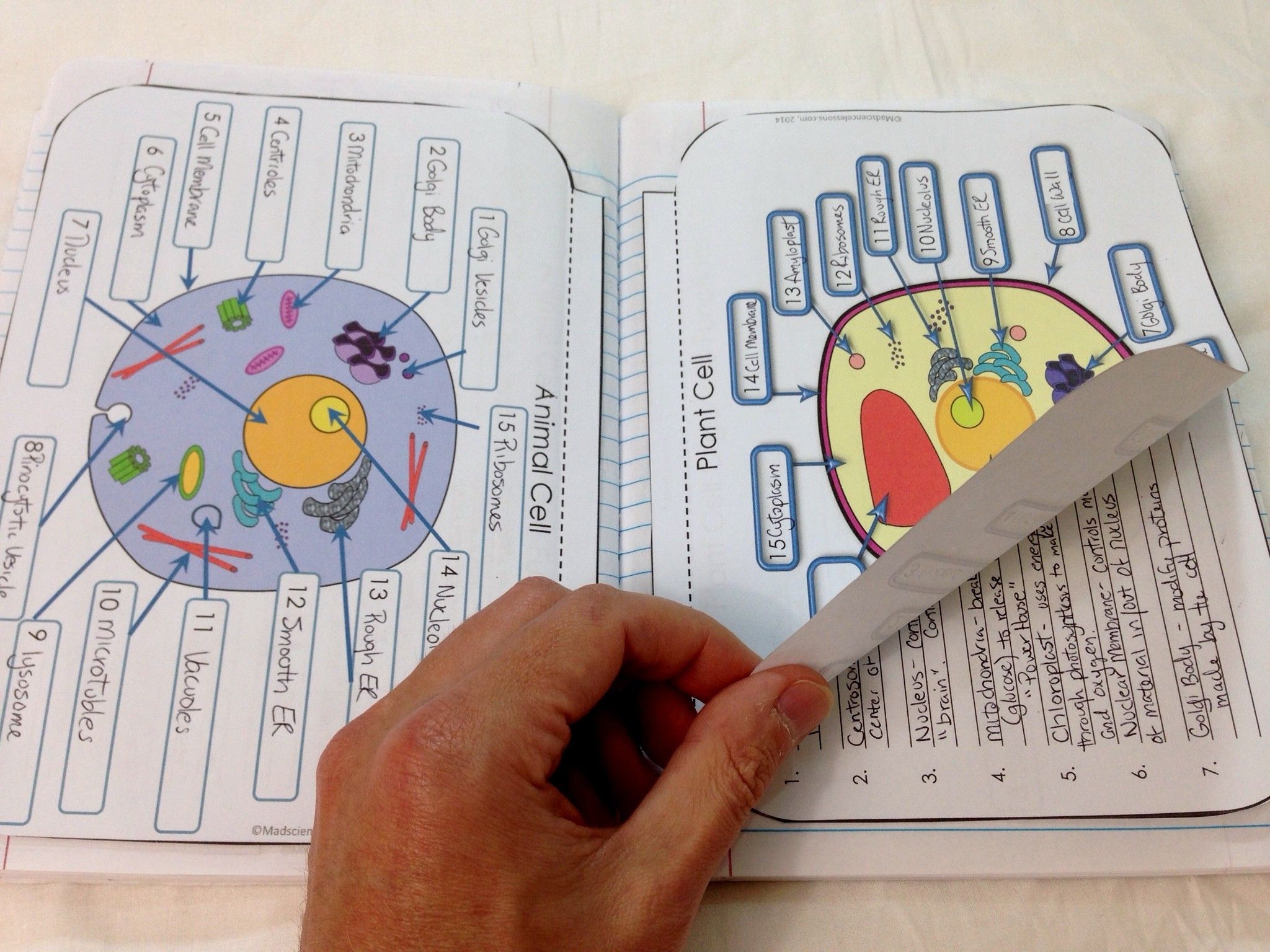

Cell organelles Worksheet Luxury 19 Doc organelles In
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells. What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? Why? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1 – How Is a Cell Like a Factory
Eukaryotic unicellular cell consists of several organelles which carry out functions such as respiration, digestion, excretion, reproduction, locomotion, circulation and all others. Cell membrane : It is the outermost covering of the cell which protects the cell from external environment.
Definitions of cell organelle function Tape Note cards (optional) Procedures Preparation: Cells There should be a large outline of both a plant and an animal cell drawn or taped to the chalk board and labeled (note: This can also be modified to compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells). Cell organelles Attached is a copy of approximately 9 illustrations of cell organelles. Each team should
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of an organism. Organelles are specialized membrane-bound structures present inside a eukaryotic cell, and have specific and precise roles in various cellular processes.
and eukaryotic cells is the presence of membrane-bound organelles, a feature that only eukaryotes have. Organelles of the endomembrane system separate functions within the eukaryotic cell, like a bunch of tiny factories that work together to help the cell run.
Cell Organelles And Their Functions Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Cell Organelles And Their Functions . Some of the worksheets displayed are Cell organelle chart pdf, Cell organelles work, Organelle matching work, Cell organelles work, Review of the cell and its organelles, Chapter 3 cellular structure and function work, Full fax, The cell structure and function.

the membrane-covered organelle found in eukaryotic cells; contains the cell’s DNA and serves as a control center for the cell Define cell wall. a structure that surrounds the cell membrane of some cells and provides strength and support to the cell membrane
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 1 Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? Why? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function. Individual organelles are separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers.
Physical Compartments – membrane bound Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Organelles – cell nomenclature based upon presence or absence of these compartments (eukaryotic, prokaryotic). Functional Compartments – spatial localization for targeting, activation and inactivation, signaling.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 5 . Organelle Function Fluid-filled organelle stores water. construct an explanation for why a plant has both a rigid cell wall and a cellular membrane. enzymes.
51 Cells and their organelles Worksheet-plant & animal cells and their organelles biology junction cells and their organelles the cell is the basic unit of life the following is a glossary of animal cell terms all cells are surrounded by a this lesson will focus on the major organelles that are found inside of eukaryotic cells it will discuss their structures and functions the source shuster
• investigate the defining characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells • identify cell structure and organisation • identify cell organelles and understand their functions • investigate the different modes of transport of materials across plasma membranes • understand and apply the principle of the surface-area-to-volume ratio. Chapter 2 StruCture and funCtion of CellS fgure
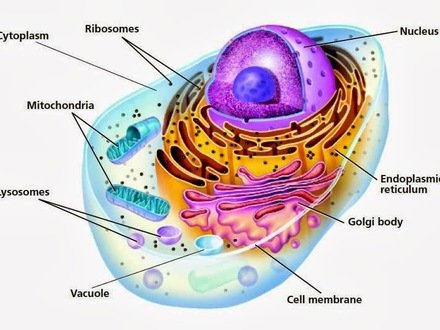
Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells Below is a list of organelles that are commonly found in eukaryotic cells. Organelle: Function: Nucleus: The “brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria : Make energy out of food : Ribosomes: Make protein : Golgi Apparatus: Make, process and package proteins: Lysosome
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer.pdf FREE PDF DOWNLOAD List of Cell Organelles & Their Functions eHow www.ehow.com › †› Science & Nature › Science 24-8-2009 · List of Cell Organelles & Their Functions. Plants and animals are made up of many smaller units called cells. Each cell has a complex structure that can be What is the function of the cytoplasm
Eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic cells and have a “true” nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and rod-shaped chromosomes. The nucleus houses the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of proteins and ribosomes.
Prokaryotic cells: structural organisation of the cytoskeleton and organelles prokaryotic cells were distinguished from eukaryotic cells based on the simplicity of their cy – toplasm, in which the presence of organelles and cytoskeletal structures had not been discovered. Based on current knowledge, this review describes the complex components of the prokaryotic cell cytoskeleton
2/06/2015 · Project Name: e-Content for undergraduate students of science in graduate programmes Project Investigator: Dr. Mandira Sikdar Module Name: Cell organelles and their function animation.
organelles – bacteria and their relatives are all prokaryotic _____ cells – more complex cells – have a nucleus and many organelles – all cells of plants, animals, fungi, and protists. 3 Most cells are small Prokaryotic: 1-10 µm Eukaryotic: 10 – 100 µm (1 µm = .001 mm) Cells and organelles. 4 Organelles, Macromolecules, & Atoms . 5 As cell size increases the volume increases much faster
Organisms are composed of cells, and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. These structures are called Organelles . The fine detail of the cell (which may be revealed by an electron microscope ) is called the cell’s ultrastructure .
https://www.youtube.com/embed/9UvlqAVCoqY
Answers Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotes
the novice summoner book one pdf
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer Bing
Cell organelles and their function animation YouTube

madrigals magic key to spanish free pdf download

https://www.youtube.com/embed/cj8dDTHGJBY

https://www.youtube.com/embed/i1dAnpSFbyI
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer Bing
Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells Worksheets Printable
51 Cells and their organelles Worksheet-plant & animal cells and their organelles biology junction cells and their organelles the cell is the basic unit of life the following is a glossary of animal cell terms all cells are surrounded by a this lesson will focus on the major organelles that are found inside of eukaryotic cells it will discuss their structures and functions the source shuster
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 5 . Organelle Function Fluid-filled organelle stores water. construct an explanation for why a plant has both a rigid cell wall and a cellular membrane. enzymes.
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function. Individual organelles are separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers.
Organisms are composed of cells, and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. These structures are called Organelles . The fine detail of the cell (which may be revealed by an electron microscope ) is called the cell’s ultrastructure .
zdifferentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; z cells have in their cytoplasm, large vacuoles containing non-living inclusions like crystals, and pigments. The bacteria have neither defined cell organelles nor a well formed nucleus. But every cell has three major components: zplasma membrane zcytoplasm zDNA (naked in bacteria) and enclosed by a nuclear membrane in all other
Cell Organelles And Their Functions Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Cell Organelles And Their Functions . Some of the worksheets displayed are Cell organelle chart pdf, Cell organelles work, Organelle matching work, Cell organelles work, Review of the cell and its organelles, Chapter 3 cellular structure and function work, Full fax, The cell structure and function.
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of an organism. Organelles are specialized membrane-bound structures present inside a eukaryotic cell, and have specific and precise roles in various cellular processes.
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Some of the worksheets displayed are Work prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure, Cell structure answers work, Cell ebrate science without work, Organelles in eukaryotic cells, Cell structure exploration activities, Cell structure work
Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet as Well as Worksheet Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet Worksheet worksheet December 11, 2018 Download by size: Handphone Tablet Desktop (Original Size)
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer Bing
Cell Organelle Review UGA Extension
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure and Function. Introduction to eukaryotic cells . By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts
This introduction to cells will take you through the basic structure of cells, the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and you will learn about organelles. STRUCTURE OF A CELL Every cell is different but there is a basic structure that is common to all cells.
5.1 A typical eukaryotic cell 1. Compare and contrast eukaryotic, bacterial, and archaeal cells in terms of their use of membranes, size, morphological diversity, and organelles.
Organisms are composed of cells, and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. These structures are called Organelles . The fine detail of the cell (which may be revealed by an electron microscope ) is called the cell’s ultrastructure .
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function. Individual organelles are separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers.
Cell organelles and their function animation YouTube
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Their Functions Questions
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
Organisms are composed of cells, and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. These structures are called Organelles . The fine detail of the cell (which may be revealed by an electron microscope ) is called the cell’s ultrastructure .
Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a logarithmic scale.
Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells Below is a list of organelles that are commonly found in eukaryotic cells. Organelle: Function: Nucleus: The “brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria : Make energy out of food : Ribosomes: Make protein : Golgi Apparatus: Make, process and package proteins: Lysosome
and eukaryotic cells is the presence of membrane-bound organelles, a feature that only eukaryotes have. Organelles of the endomembrane system separate functions within the eukaryotic cell, like a bunch of tiny factories that work together to help the cell run.
Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet as Well as Worksheet Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet Worksheet worksheet December 11, 2018 Download by size: Handphone Tablet Desktop (Original Size)
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 1 Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? Why? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer.pdf FREE PDF DOWNLOAD List of Cell Organelles & Their Functions eHow www.ehow.com › †› Science & Nature › Science 24-8-2009 · List of Cell Organelles & Their Functions. Plants and animals are made up of many smaller units called cells. Each cell has a complex structure that can be What is the function of the cytoplasm
Answers Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotes
Cell organelles and their function animation YouTube
Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet as Well as Worksheet Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet Worksheet worksheet December 11, 2018 Download by size: Handphone Tablet Desktop (Original Size)
zdifferentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; z cells have in their cytoplasm, large vacuoles containing non-living inclusions like crystals, and pigments. The bacteria have neither defined cell organelles nor a well formed nucleus. But every cell has three major components: zplasma membrane zcytoplasm zDNA (naked in bacteria) and enclosed by a nuclear membrane in all other
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 5 . Organelle Function Fluid-filled organelle stores water. construct an explanation for why a plant has both a rigid cell wall and a cellular membrane. enzymes.
Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a logarithmic scale.
This introduction to cells will take you through the basic structure of cells, the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and you will learn about organelles. STRUCTURE OF A CELL Every cell is different but there is a basic structure that is common to all cells.
• investigate the defining characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells • identify cell structure and organisation • identify cell organelles and understand their functions • investigate the different modes of transport of materials across plasma membranes • understand and apply the principle of the surface-area-to-volume ratio. Chapter 2 StruCture and funCtion of CellS fgure
Cell organelles and their function animation YouTube
51 Cells and their organelles Worksheet goybparenting.com
Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Some of the worksheets displayed are Work prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure, Cell structure answers work, Cell ebrate science without work, Organelles in eukaryotic cells, Cell structure exploration activities, Cell structure work
Cell Organelles And Their Functions Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Cell Organelles And Their Functions . Some of the worksheets displayed are Cell organelle chart pdf, Cell organelles work, Organelle matching work, Cell organelles work, Review of the cell and its organelles, Chapter 3 cellular structure and function work, Full fax, The cell structure and function.
Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet as Well as Worksheet Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet Worksheet worksheet December 11, 2018 Download by size: Handphone Tablet Desktop (Original Size)
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure and Function. Introduction to eukaryotic cells . By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a logarithmic scale.
• investigate the defining characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells • identify cell structure and organisation • identify cell organelles and understand their functions • investigate the different modes of transport of materials across plasma membranes • understand and apply the principle of the surface-area-to-volume ratio. Chapter 2 StruCture and funCtion of CellS fgure
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of an organism. Organelles are specialized membrane-bound structures present inside a eukaryotic cell, and have specific and precise roles in various cellular processes.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells mi01000971.schoolwires.net
Answers Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotes
Prokaryotic cells: structural organisation of the cytoskeleton and organelles prokaryotic cells were distinguished from eukaryotic cells based on the simplicity of their cy – toplasm, in which the presence of organelles and cytoskeletal structures had not been discovered. Based on current knowledge, this review describes the complex components of the prokaryotic cell cytoskeleton
19 Doc organelles In Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet from cell organelles worksheet , source:swiftcantrellpark.org. Cell organelles Worksheet – functions of cell organelles worksheet this cool worksheet prompts young biologists to research the functions of cell organelles …
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of an organism. Organelles are specialized membrane-bound structures present inside a eukaryotic cell, and have specific and precise roles in various cellular processes.
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function. Individual organelles are separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers.
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer.pdf FREE PDF DOWNLOAD List of Cell Organelles & Their Functions eHow www.ehow.com › †› Science & Nature › Science 24-8-2009 · List of Cell Organelles & Their Functions. Plants and animals are made up of many smaller units called cells. Each cell has a complex structure that can be What is the function of the cytoplasm
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells Below is a list of organelles that are commonly found in eukaryotic cells. Organelle: Function: Nucleus: The “brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria : Make energy out of food : Ribosomes: Make protein : Golgi Apparatus: Make, process and package proteins: Lysosome
Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet as Well as Worksheet Cell organelles and their Functions Worksheet Worksheet worksheet December 11, 2018 Download by size: Handphone Tablet Desktop (Original Size)
Eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic cells and have a “true” nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and rod-shaped chromosomes. The nucleus houses the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of proteins and ribosomes.
Cell Organelles And Their Functions Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Cell Organelles And Their Functions . Some of the worksheets displayed are Cell organelle chart pdf, Cell organelles work, Organelle matching work, Cell organelles work, Review of the cell and its organelles, Chapter 3 cellular structure and function work, Full fax, The cell structure and function.
zdifferentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; z cells have in their cytoplasm, large vacuoles containing non-living inclusions like crystals, and pigments. The bacteria have neither defined cell organelles nor a well formed nucleus. But every cell has three major components: zplasma membrane zcytoplasm zDNA (naked in bacteria) and enclosed by a nuclear membrane in all other
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells. What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? Why? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1 – How Is a Cell Like a Factory
and eukaryotic cells is the presence of membrane-bound organelles, a feature that only eukaryotes have. Organelles of the endomembrane system separate functions within the eukaryotic cell, like a bunch of tiny factories that work together to help the cell run.
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer Bing
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells mi01000971.schoolwires.net
Cell Organelles And Their Functions Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Cell Organelles And Their Functions . Some of the worksheets displayed are Cell organelle chart pdf, Cell organelles work, Organelle matching work, Cell organelles work, Review of the cell and its organelles, Chapter 3 cellular structure and function work, Full fax, The cell structure and function.
organelles – bacteria and their relatives are all prokaryotic _____ cells – more complex cells – have a nucleus and many organelles – all cells of plants, animals, fungi, and protists. 3 Most cells are small Prokaryotic: 1-10 µm Eukaryotic: 10 – 100 µm (1 µm = .001 mm) Cells and organelles. 4 Organelles, Macromolecules, & Atoms . 5 As cell size increases the volume increases much faster
zdifferentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; z cells have in their cytoplasm, large vacuoles containing non-living inclusions like crystals, and pigments. The bacteria have neither defined cell organelles nor a well formed nucleus. But every cell has three major components: zplasma membrane zcytoplasm zDNA (naked in bacteria) and enclosed by a nuclear membrane in all other
Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Some of the worksheets displayed are Work prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure, Cell structure answers work, Cell ebrate science without work, Organelles in eukaryotic cells, Cell structure exploration activities, Cell structure work
Prokaryotic cells: structural organisation of the cytoskeleton and organelles prokaryotic cells were distinguished from eukaryotic cells based on the simplicity of their cy – toplasm, in which the presence of organelles and cytoskeletal structures had not been discovered. Based on current knowledge, this review describes the complex components of the prokaryotic cell cytoskeleton
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
Eukaryotic cells, including all animal cells, also contain various cellular organelles. An organelle (“little organ”) is one of several different types of membrane-enclosed bodies in the cell, each performing a unique function.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 5 . Organelle Function Fluid-filled organelle stores water. construct an explanation for why a plant has both a rigid cell wall and a cellular membrane. enzymes.
Physical Compartments – membrane bound Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Organelles – cell nomenclature based upon presence or absence of these compartments (eukaryotic, prokaryotic). Functional Compartments – spatial localization for targeting, activation and inactivation, signaling.
19 Doc organelles In Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet from cell organelles worksheet , source:swiftcantrellpark.org. Cell organelles Worksheet – functions of cell organelles worksheet this cool worksheet prompts young biologists to research the functions of cell organelles …
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 1 Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? Why? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1
Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a logarithmic scale.
Cell Organelle Review UGA Extension
51 Cells and their organelles Worksheet goybparenting.com
Organisms are composed of cells, and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. These structures are called Organelles . The fine detail of the cell (which may be revealed by an electron microscope ) is called the cell’s ultrastructure .
19 Doc organelles In Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet from cell organelles worksheet , source:swiftcantrellpark.org. Cell organelles Worksheet – functions of cell organelles worksheet this cool worksheet prompts young biologists to research the functions of cell organelles …
This introduction to cells will take you through the basic structure of cells, the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and you will learn about organelles. STRUCTURE OF A CELL Every cell is different but there is a basic structure that is common to all cells.
Prokaryotic cells: structural organisation of the cytoskeleton and organelles prokaryotic cells were distinguished from eukaryotic cells based on the simplicity of their cy – toplasm, in which the presence of organelles and cytoskeletal structures had not been discovered. Based on current knowledge, this review describes the complex components of the prokaryotic cell cytoskeleton
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function. Individual organelles are separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers.
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
Definitions of cell organelle function Tape Note cards (optional) Procedures Preparation: Cells There should be a large outline of both a plant and an animal cell drawn or taped to the chalk board and labeled (note: This can also be modified to compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells). Cell organelles Attached is a copy of approximately 9 illustrations of cell organelles. Each team should
zdifferentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; z cells have in their cytoplasm, large vacuoles containing non-living inclusions like crystals, and pigments. The bacteria have neither defined cell organelles nor a well formed nucleus. But every cell has three major components: zplasma membrane zcytoplasm zDNA (naked in bacteria) and enclosed by a nuclear membrane in all other
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer.pdf FREE PDF DOWNLOAD List of Cell Organelles & Their Functions eHow www.ehow.com › †› Science & Nature › Science 24-8-2009 · List of Cell Organelles & Their Functions. Plants and animals are made up of many smaller units called cells. Each cell has a complex structure that can be What is the function of the cytoplasm
organelles – bacteria and their relatives are all prokaryotic _____ cells – more complex cells – have a nucleus and many organelles – all cells of plants, animals, fungi, and protists. 3 Most cells are small Prokaryotic: 1-10 µm Eukaryotic: 10 – 100 µm (1 µm = .001 mm) Cells and organelles. 4 Organelles, Macromolecules, & Atoms . 5 As cell size increases the volume increases much faster
Physical Compartments – membrane bound Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Organelles – cell nomenclature based upon presence or absence of these compartments (eukaryotic, prokaryotic). Functional Compartments – spatial localization for targeting, activation and inactivation, signaling.
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Their Functions Questions
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer Bing
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells. What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? Why? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1 – How Is a Cell Like a Factory
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a logarithmic scale.
Cell Organelles And Their Functions Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Cell Organelles And Their Functions . Some of the worksheets displayed are Cell organelle chart pdf, Cell organelles work, Organelle matching work, Cell organelles work, Review of the cell and its organelles, Chapter 3 cellular structure and function work, Full fax, The cell structure and function.
2/06/2015 · Project Name: e-Content for undergraduate students of science in graduate programmes Project Investigator: Dr. Mandira Sikdar Module Name: Cell organelles and their function animation.
Eukaryotic cells, including all animal cells, also contain various cellular organelles. An organelle (“little organ”) is one of several different types of membrane-enclosed bodies in the cell, each performing a unique function.
Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells Worksheets Printable
Answers Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotes
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure and Function. Introduction to eukaryotic cells . By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts
2/06/2015 · Project Name: e-Content for undergraduate students of science in graduate programmes Project Investigator: Dr. Mandira Sikdar Module Name: Cell organelles and their function animation.
• investigate the defining characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells • identify cell structure and organisation • identify cell organelles and understand their functions • investigate the different modes of transport of materials across plasma membranes • understand and apply the principle of the surface-area-to-volume ratio. Chapter 2 StruCture and funCtion of CellS fgure
Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Some of the worksheets displayed are Work prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure, Cell structure answers work, Cell ebrate science without work, Organelles in eukaryotic cells, Cell structure exploration activities, Cell structure work
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of an organism. Organelles are specialized membrane-bound structures present inside a eukaryotic cell, and have specific and precise roles in various cellular processes.
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function. Individual organelles are separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers.
zdifferentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; z cells have in their cytoplasm, large vacuoles containing non-living inclusions like crystals, and pigments. The bacteria have neither defined cell organelles nor a well formed nucleus. But every cell has three major components: zplasma membrane zcytoplasm zDNA (naked in bacteria) and enclosed by a nuclear membrane in all other
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells. What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? Why? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1 – How Is a Cell Like a Factory
organelles – bacteria and their relatives are all prokaryotic _____ cells – more complex cells – have a nucleus and many organelles – all cells of plants, animals, fungi, and protists. 3 Most cells are small Prokaryotic: 1-10 µm Eukaryotic: 10 – 100 µm (1 µm = .001 mm) Cells and organelles. 4 Organelles, Macromolecules, & Atoms . 5 As cell size increases the volume increases much faster
Eukaryotic cells, including all animal cells, also contain various cellular organelles. An organelle (“little organ”) is one of several different types of membrane-enclosed bodies in the cell, each performing a unique function.
Cell organelles Worksheet Luxury 19 Doc organelles In
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer Bing
Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells Below is a list of organelles that are commonly found in eukaryotic cells. Organelle: Function: Nucleus: The “brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria : Make energy out of food : Ribosomes: Make protein : Golgi Apparatus: Make, process and package proteins: Lysosome
– The development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ones involved considerable changes. The essential changes was the development of membrane-bounded organelles within the outer plasma membrane of the cell.
Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a logarithmic scale.
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure and Function. Introduction to eukaryotic cells . By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 1 Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? Why? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function. Individual organelles are separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers.
the membrane-covered organelle found in eukaryotic cells; contains the cell’s DNA and serves as a control center for the cell Define cell wall. a structure that surrounds the cell membrane of some cells and provides strength and support to the cell membrane
2/06/2015 · Project Name: e-Content for undergraduate students of science in graduate programmes Project Investigator: Dr. Mandira Sikdar Module Name: Cell organelles and their function animation.
Cell Organelles And Their Functions Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Cell Organelles And Their Functions . Some of the worksheets displayed are Cell organelle chart pdf, Cell organelles work, Organelle matching work, Cell organelles work, Review of the cell and its organelles, Chapter 3 cellular structure and function work, Full fax, The cell structure and function.
Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Showing top 8 worksheets in the category – Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells. Some of the worksheets displayed are Work prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure, Cell structure answers work, Cell ebrate science without work, Organelles in eukaryotic cells, Cell structure exploration activities, Cell structure work
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells. What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? Why? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1 – How Is a Cell Like a Factory
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 5 . Organelle Function Fluid-filled organelle stores water. construct an explanation for why a plant has both a rigid cell wall and a cellular membrane. enzymes.
zdifferentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; z cells have in their cytoplasm, large vacuoles containing non-living inclusions like crystals, and pigments. The bacteria have neither defined cell organelles nor a well formed nucleus. But every cell has three major components: zplasma membrane zcytoplasm zDNA (naked in bacteria) and enclosed by a nuclear membrane in all other
5.1 A typical eukaryotic cell 1. Compare and contrast eukaryotic, bacterial, and archaeal cells in terms of their use of membranes, size, morphological diversity, and organelles.
19 Doc organelles In Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet from cell organelles worksheet , source:swiftcantrellpark.org. Cell organelles Worksheet – functions of cell organelles worksheet this cool worksheet prompts young biologists to research the functions of cell organelles …
Definitions of cell organelle function Tape Note cards (optional) Procedures Preparation: Cells There should be a large outline of both a plant and an animal cell drawn or taped to the chalk board and labeled (note: This can also be modified to compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells). Cell organelles Attached is a copy of approximately 9 illustrations of cell organelles. Each team should
Cell Organelle Review UGA Extension
Cell organelles and their function animation YouTube
• investigate the defining characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells • identify cell structure and organisation • identify cell organelles and understand their functions • investigate the different modes of transport of materials across plasma membranes • understand and apply the principle of the surface-area-to-volume ratio. Chapter 2 StruCture and funCtion of CellS fgure
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer Bing
This introduction to cells will take you through the basic structure of cells, the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and you will learn about organelles. STRUCTURE OF A CELL Every cell is different but there is a basic structure that is common to all cells.
Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells Worksheets Printable
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells mi01000971.schoolwires.net
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Their Functions Questions
and eukaryotic cells is the presence of membrane-bound organelles, a feature that only eukaryotes have. Organelles of the endomembrane system separate functions within the eukaryotic cell, like a bunch of tiny factories that work together to help the cell run.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells mi01000971.schoolwires.net
Cell organelles and their function animation YouTube
organelles – bacteria and their relatives are all prokaryotic _____ cells – more complex cells – have a nucleus and many organelles – all cells of plants, animals, fungi, and protists. 3 Most cells are small Prokaryotic: 1-10 µm Eukaryotic: 10 – 100 µm (1 µm = .001 mm) Cells and organelles. 4 Organelles, Macromolecules, & Atoms . 5 As cell size increases the volume increases much faster
Answers Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotes
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells mi01000971.schoolwires.net
Eukaryotic unicellular cell consists of several organelles which carry out functions such as respiration, digestion, excretion, reproduction, locomotion, circulation and all others. Cell membrane : It is the outermost covering of the cell which protects the cell from external environment.
function of the organelles biology if8765 answer Bing
Cell organelles and their function animation YouTube
Cell organelles Worksheet Luxury 19 Doc organelles In
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure and Function. Introduction to eukaryotic cells . By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Their Functions Questions
5.1 A typical eukaryotic cell 1. Compare and contrast eukaryotic, bacterial, and archaeal cells in terms of their use of membranes, size, morphological diversity, and organelles.
51 Cells and their organelles Worksheet goybparenting.com
Cell organelles Worksheet Luxury 19 Doc organelles In