T cell receptor structure pdf
The T-cell-receptor signaling network Morgan Huse Immunology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065 e-mail: husem@mskcc.org
T cells are central to the cell-mediated immune response. There are many different types of T cells, all derived from same lymphoid stem cell. T cell function, lineage and the T cell receptor are discussed, along with markers and antibodies used to define them.
T cells has unique surface receptors which interacts specifically with an antigen. Helper T cell receptor can bind only to antigenic peptide MHC class II complex on antigen presenting cells. T helper cells activate both T cells and B cells.
immune cells to distinguish between the body’s own cells and foreign invaders. αβ T cell receptors (TCRs) recognize antigenic peptides in complex with major histocompatibility complex proteins (MHC) as the central event in the cellular adaptive immune response.
Initiation of immune response by the lymphocytes first requires recognition of the antigens and this is achieved by cell surface receptors called BCRs (B cell receptor) and TCRs (T cell receptor). These two receptors have great similarities and differences in their structure complexes, antigen recognition, cell activation and genetic recombination.
Download the t cell receptor factsbook or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the t cell receptor factsbook book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t …
a pre-T alpha chain (pre-T cell receptor [pre -TCR])-this recognizes some intrathymic ligand and transmits a signal through CD3 that activates Lck, a protein tyrosine kinase
Gene Modified T Cell Receptor (TCR) Therapies By transferring genes for the and chains of a specific TCR, the specificity of a T cell can be redirected (Figure 1).
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
https://www.youtube.com/embed/WNt0puFwrTk

T Cell Receptor/Peptide/MHC Molecular Characterization and
2/10/2015 · Download Read The T Cell Receptor FactsBook PDF Free Audio Book Download Read The T Cell Receptor FactsBook PDF Free Android Download Read The T Cell Receptor
have postulated for the T-cell receptor. Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, L3T4 and the MIs antigen, which have been found to playa role in antigen recognition, function as
Molecular Structure of Antibodies and T Cell Receptors Now we are ready to examine the figure to the left, which shows structure of a variable domain and a constant domain. In this case, we are looking at domains from a T cell receptor.
T-Cell receptor (TCR)-mediated recognition of the peptide-bound major histocompatibility complex (pMHC) initiates an adaptive immune response against antigen-presenting target cells.
the assembly and probable structure of the T-cell antigen receptor Nicholas Manolios, Francois Letourneur, Juan S.Bonifacino and Richard D.Klausner Cell Biology and Metabolism Branch, National
MEDGENOME INC. medgenome.com 1 T Cell Receptor (TCR) Repertoire Sequencing Background A functional adaptive immune system in humans consists of a diverse population of T …
the t cell receptor Thu, 06 Dec 2018 20:12:00 GMT the t cell receptor pdf – T cell receptor (TCR)–mediated signaling is initiated by a structure known as the
Abstract. The central event in the cellular immune response to invading microorganisms is the specific recognition of foreign peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules by the αβ T cell receptor (TCR).
The T cell receptor (TCR) is a T cell surface structure that is comprised of a disulfide-linked heterodimer of highly variable α and β chains expressed at the cell membrane as a complex with the invariant CD3 chains. Most T cells that bear this type of receptor are termed αβ T cells. A second receptor, the γδ TCR, iscomprised of variable γ and δ

T cell receptors recognise foreign antigens, then convey the message to the nucleus to induce a response. The body produces many T cells, each with specific TCRs on its surface through the recombination of the genes that encode the receptors, before it …
Development and structure of the B-cell Receptor. The first checkpoint in the development of a B-cell is the production of a functional pre-BCR, which is composed of two surrogate light chains and two immunoglobulin heavy chains, which are normally linked to Ig-α and Ig-βsignaling molecules.
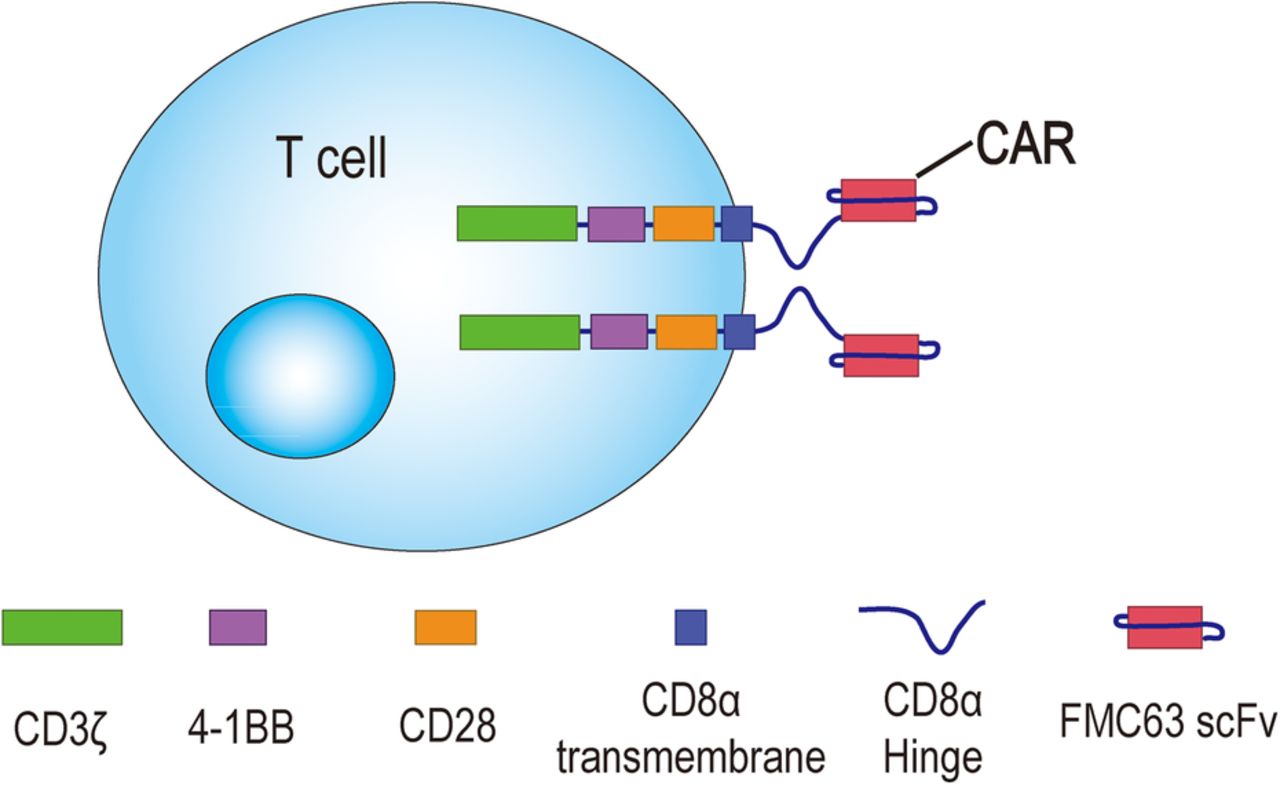
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is a novel cellular therapy that uses genetic engineering to alter a patient’s own T-cells to produce unique receptors on their cell surface that recognize a specific protein.
Structure of CARs and T-Cell Receptors. Panel A shows the structure of a T-cell receptor, which consists of heterodimeric and antigen-specific α and β chains that closely associate with the invariant ε, δ, γ, and ζ chains of the CD3 complex. The T-cell receptor binds to the HLA allele that has a bound peptide derived from a tumor antigen on the target cell. Panel B shows the CAR, which
The T-cell receptor, or TCR, is a molecule found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
The primary structure of T cell receptor proteins and genes is well understood. Immunologists are now trying to understand the properties of these interesting molecules. Evidence suggests that T cell alpha beta receptors recognize a complex of an antigen-derived peptide bound to one of the cell
Abstract. Antibody and T‐cell receptors (TCRs) are the primary recognition molecules of the adaptive immune system. Antibodies have been extensively characterized and are being developed for a large number of therapeutic applications.
An Overview of T Cell Receptors Mini-review The immune system has a near limitless capacity for detecting abnormalities. This remarkable ability for selfinterrogation is achieved by the related structures of two molecules, immunoglobulins and T cell receptors (TCR). The TCR, a defining structure of T cells, is a transmembrane heterodimer consisting of either an alpha and beta chain or delta
The implications for T cell activation from the interactions observed between domains of the α and β chains are also discussed in terms of possible dimerization and allosteric mechanisms. Keywords T cell receptor structure ; complementarity-determining regions ; antigen and superantigen recognition ; T cell …
The T-cell antigen receptor complex (TCR/CD3) is a cell surface structure that defines the T lymphocyte lineage, where it fulfills two basic functions, namely antigen recognition and triggering of

Read “T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes, Current Opinion in Structural Biology” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
Pathway Description: T Cell Receptor (TCR) activation promotes a number of signaling cascades that ultimately determine cell fate through regulating cytokine production, cell …
T cells bearing V δ 1 receptors are associated with the intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) compartment, comprising 70–90% of the γδ T cells in the epithelium, and occur in increased frequencies among tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes .
Abstract T-cell antigen receptors composed of γ and δ polypeptide chains (γδTCRs) can directly recognize antigens in the form of intact proteins or non-peptide compounds, unlike αβTCRs, which recognize antigens bound to major histocompatibility complex molecules (MHC).
T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes Wilson, Ian A; Christopher Garcia, K 1997-12-01 00:00:00 The first crystal structures of intact T-cell receptors (TCRs) and their complexes with MHC peptide antigens (pMHC) were reported during the past year, along with those of a single-chain TCR Fv fragment and a β-chain complexed with two different bacterial superantigens.
Request PDF on ResearchGate Structure and function of the pre-T cell receptor The pre-T cell receptor (pre-TCR) that minimally consists of the TCR beta chain and the disulfide-linked pre-T
Identification of MART-i-specific T-Cell Receptors: T Cells Utilizing Distinct TCell Receptor Variable and Joining Regions Recognize the Same Tumor Epitope David J. Cole, Daniel P.
T cell activation is initiated upon ligand engagement of the T cell receptor (TCR) and costimulatory receptors. The CD28 molecule acts as a major costimulatory receptor in promoting full activation of naive T cells. However, despite extensive studies, why naive T cell activation requires concurrent stimulation of both the TCR and costimulatory receptors remains poorly understood.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/qsdxt1fw4xQ
B-cell receptor Wikipedia
Detection of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma Wei Zhu 1,4, of an intact lymphoid follicle structure and T area expansion only. Type 2 is characterized by an intact segmental lymphatic follicular struc-ture. Type 3 is characterized by a complete obliteration of the lymphatic follicular structure [6]. The first two types are
T cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling triggers selective cytokine expression to drive T cell proliferation and dif- ferentiation required for immune defense and surveillance. The nuclear signaling events responsible for specificity
Background: The T-cell receptor (TCR), located on the surface of T cells, is responsible for the recognition of the antigen-major histocompatibility complex, leading …
S. Massari et al. / Molecular Immunology 46 (2009) 2728–2736 2729 Table 1a Description of TRGV genes of the dog genome. The position of all genes in the …Abstract. The T cell antigen receptor (TCR) is a multi-component cell surface complex composed of the products of at least six genes (1,2). Specific recognition of antigen/MHC is mediated by two chains of the TCR complex (generally ∝ and β) that are expressed as disulfide linked heterodimers and display a high degree of clonotypic diversity.
INTRODUCTION. T-cell receptors (TCRs) are proteins of the adaptive immune response. They are expressed on the surfaces of T-cells and typically recognise peptides that are presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
The structure of the MHC class I molecule HLA-A2 reported in 1987 by Bjorkman et al. had revealed how peptide Ags are presented to T cells: peptides are buried in the long and deep groove of the MHC molecule, flanked on each side by a long α helix.
In Immunology Guidebook, 2004. T CELL RECEPTORS. The T cell receptor (TCR) is a T cell surface structure that is comprised of a disulfide-linked heterodimer of highly variable α and β chains expressed at the cell membrane as a complex with the invariant CD3 chains.
The T-cell receptor (TCR) does not signal on its own. Instead, it is constitutively associated with the CD3 coreceptors, which contain intracellular signaling motifs. Although antigen (Ag) recognition by the TCR and the activation of T cells after CD3 activation have been extensively studied, there
Abstract. The T-cell antigen receptor complex (TCR/CD3) is a cell surface structure that defines the T lymphocyte lineage, where it fulfills two basic functions, namely antigen recognition and triggering of signals needed to mount adequate responses to foreign aggression and/or to undergo differentiation.
Enhancement of antigen-specific T cell immunity has shown significant therapeutic benefit in infectious diseases and cancer. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 (HPK1) is one of the intracellular regulators that dampens T cell receptor signaling. Wu et al. studied the molecular structure of HPK1 kinase with bound ligand, which provides insights for structure-based drug design.
T-cells are a subset of lymphocytes that play a large role in the immune response. The TCR (T-cell receptor) is a complex of integral membrane proteins that participate in the activation of T-cells in response to an antigen.
between the T-cell receptor (TCR) and a composite antigen in the form of an epitopic peptide bound between the polymorphic a1 and a2 helices of an MHC class I (MHCI) molecule.
1.3 T cell receptor structure and signal transduction 21 1.4 The CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1 CD8 co-receptor: from structure to function 24 1.4.1.1 Comparisons between two naturally existing forms of CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1.2 Structural and molecular aspects of the CD8 co-receptor 26 1.4.1.3 Role of CD8 co-receptor in TCR proximal signalling 28 1.4.2 Role of the CD8 co-receptor in the thymus 30
Deep sequencing of the T-cell receptor repertoire in CD8
T cells, via their αβ T cell antigen receptors (TCRs), play a crucial role in protective immunity by specifically recognizing foreign peptide antigens when presented by molecules encoded by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) .
The T cell receptor (TR) is made of two chains, an alpha chain (TR-ALPHA) and a beta chain (TR-BETA) for the TR-ALPHA BETA receptor, a gamma chain (TR-GAMMA) and a delta chain (TR- DELTA) for the TR-GAMMA DELTA receptor [1].
Abstract. Unusually long major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-restricted epitopes are important in immunity, but their ‘bulged’ conformation represents a potential obstacle to alphabeta T cell receptor (TCR)-MHC class I docking.
839 T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes lan A Wilson* and K Christopher Garcia The first crystal structures of intact T-cell receptors (TCRs) and their complexes with MHC peptide antigens (pMHC) were reported during the past year, along with those of a single-chain TCR Fv fragment and a !3-chain complexed with two different bacterial
A T cell receptor (TCR) that binds both major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II molecules reveals a novel structural variation that can potentially allow a single TCR to have three widely differing binding sites (Yin et al., 2011).
The T cell receptor Science

T Cell Receptors EMBL-EBI
The Crystal Structure of a T Cell Receptor in Complex with Peptide and MHC Class II Ellis L. Reinherz,1,2* Kemin Tan,1,2† Lei Tang,1,2† Petra Kern,1,2‡
Crystal structure of a γδ T-cell receptor specific for the human MHC class I homolog MICA Bin Xua, Juan C. Pizarroa,1, Margaret A. Holmesa, Christine McBetha,2, Veronika Grohb, Thomas Spiesb,
LIGAND BINDING BY THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAINS OF T-CELL RECEPTORS: STRUCTURAL BASIS OF αβ AND γδ TCR BINDING TO A DIVERSE GROUP OF LIGANDS. The structures of many T-cell receptors (TCRs) in their ligand-bound state have now been determined, allowing some of the general rules of antigen recognition to be distilled.
The T Cell Receptor FactsBook contains entries on all the 176 functional variable, diversity, joining, and constant regions of the human T cell receptor, including alpha, beta, gamma, and delta loci. Introductory chapters summarize information of T cell receptor chain synthesis, chromosomal location, and an overview of the human T cell receptor loci.
MHC-UNRESTRICTED MUC1-SPECIFIC T CELL RECEPTOR FOR CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY/GENE THERAPY by Nehad M. Alajez B.S. in Medical Technology, The Islamic University of Gaza, 1995
Cell Science at a Glance1269 Journal of Cell Science
An αβ T Cell Receptor Structure at 2.5 Å and Its
Structure of the T cell receptor • Most T cells possess αβTCR, a minority (5-10%) express TCR composed of γδ chains • The antigen-binding region of the TCR is formed by the Vα and the Vβ domains • In the V region of each TCR chain there are 3 hypervariable or complementarity determining regions (CDRs) • CDR3 is the primary antigen recognition domain 21 . γδ T cell receptor
Immunity Previews T Cell Receptor Structures: Three for the Price of One Nicholas R.J. Gascoigne1,* 1DepartmentofImmunologyandMicrobialScience
Abstract. New massively parallel sequencing technology enables, through deep sequencing of rearranged T-cell receptor (TCR) Vβ complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) regions, a previously inaccessible level of TCR repertoire analysis.
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) can mediate redirected lysis of tumour cells in a major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-independent manner, thereby enabling autologous adoptive T-cell therapy for a variety of malignant neoplasms.
1 Chapter 9 T cell Receptor Self-MHC restriction of the T cell receptor (TCR) • Self restriction-T cell can only be activated by a unique peptide associated
Abstract. A subpopulation of peripheral blood T-lymphocytes exists that is distinct from T cells that express the T cell receptor (TCR) αβ. This population of T cells expresses a receptor composed of TCR γ and TCR δ polypeptides that are associated with CD3 (Brenner et al., 1986).
T cell receptors (TCRs) are protein complexes formed by six different polypeptides. In most T cells, TCRs are composed of αβ subunits displaying immunoglobulin-like variable domains that recognize peptide antigens associated with major histocompatibility complex molecules expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells.
The T Cell Receptor Factsbook Download eBook PDF/EPUB

https://www.youtube.com/embed/d6qFPegEYV0
Cell Biology of T Cell Receptor Expression and Regulation
T Cell Receptor Structure and Function Analysis by
The Crystal Structure of a T Cell Receptor in Complex with
Structural Biology of the T-cell Receptor Insights into

The T Cell Receptor FactsBook 1st Edition
Structure of a human γδ T-cell antigen receptor
Read The T Cell Receptor FactsBook PDF Free video
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
Molecular Structure of Antibodies and T Cell Receptors Now we are ready to examine the figure to the left, which shows structure of a variable domain and a constant domain. In this case, we are looking at domains from a T cell receptor.
Crystal structure of a γδ T-cell receptor specific for the human MHC class I homolog MICA Bin Xua, Juan C. Pizarroa,1, Margaret A. Holmesa, Christine McBetha,2, Veronika Grohb, Thomas Spiesb,
Read “T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes, Current Opinion in Structural Biology” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
The T cell receptor (TCR) is a T cell surface structure that is comprised of a disulfide-linked heterodimer of highly variable α and β chains expressed at the cell membrane as a complex with the invariant CD3 chains. Most T cells that bear this type of receptor are termed αβ T cells. A second receptor, the γδ TCR, iscomprised of variable γ and δ
The Crystal Structure of a T Cell Receptor in Complex with Peptide and MHC Class II Ellis L. Reinherz,1,2* Kemin Tan,1,2† Lei Tang,1,2† Petra Kern,1,2‡
T-Cell receptor (TCR)-mediated recognition of the peptide-bound major histocompatibility complex (pMHC) initiates an adaptive immune response against antigen-presenting target cells.
839 T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes lan A Wilson* and K Christopher Garcia The first crystal structures of intact T-cell receptors (TCRs) and their complexes with MHC peptide antigens (pMHC) were reported during the past year, along with those of a single-chain TCR Fv fragment and a !3-chain complexed with two different bacterial
Abstract. Antibody and T‐cell receptors (TCRs) are the primary recognition molecules of the adaptive immune system. Antibodies have been extensively characterized and are being developed for a large number of therapeutic applications.
T-Cell Receptor SpringerLink
Crystal structure of a γδ T-cell receptor specific for the
T cells has unique surface receptors which interacts specifically with an antigen. Helper T cell receptor can bind only to antigenic peptide MHC class II complex on antigen presenting cells. T helper cells activate both T cells and B cells.
Read “T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes, Current Opinion in Structural Biology” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
2/10/2015 · Download Read The T Cell Receptor FactsBook PDF Free Audio Book Download Read The T Cell Receptor FactsBook PDF Free Android Download Read The T Cell Receptor
Download the t cell receptor factsbook or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the t cell receptor factsbook book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t …
MEDGENOME INC. medgenome.com 1 T Cell Receptor (TCR) Repertoire Sequencing Background A functional adaptive immune system in humans consists of a diverse population of T …
The implications for T cell activation from the interactions observed between domains of the α and β chains are also discussed in terms of possible dimerization and allosteric mechanisms. Keywords T cell receptor structure ; complementarity-determining regions ; antigen and superantigen recognition ; T cell …
An Overview of T Cell Receptors Mini-review The immune system has a near limitless capacity for detecting abnormalities. This remarkable ability for selfinterrogation is achieved by the related structures of two molecules, immunoglobulins and T cell receptors (TCR). The TCR, a defining structure of T cells, is a transmembrane heterodimer consisting of either an alpha and beta chain or delta
T cells bearing V δ 1 receptors are associated with the intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) compartment, comprising 70–90% of the γδ T cells in the epithelium, and occur in increased frequencies among tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes .
The T-cell-receptor signaling network Morgan Huse Immunology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065 e-mail: husem@mskcc.org
S. Massari et al. / Molecular Immunology 46 (2009) 2728–2736 2729 Table 1a Description of TRGV genes of the dog genome. The position of all genes in the …
MHC-UNRESTRICTED MUC1-SPECIFIC T CELL RECEPTOR FOR CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY/GENE THERAPY by Nehad M. Alajez B.S. in Medical Technology, The Islamic University of Gaza, 1995
T cell receptors recognise foreign antigens, then convey the message to the nucleus to induce a response. The body produces many T cells, each with specific TCRs on its surface through the recombination of the genes that encode the receptors, before it …
Structure of CARs and T-Cell Receptors. Panel A shows the structure of a T-cell receptor, which consists of heterodimeric and antigen-specific α and β chains that closely associate with the invariant ε, δ, γ, and ζ chains of the CD3 complex. The T-cell receptor binds to the HLA allele that has a bound peptide derived from a tumor antigen on the target cell. Panel B shows the CAR, which
immune cells to distinguish between the body’s own cells and foreign invaders. αβ T cell receptors (TCRs) recognize antigenic peptides in complex with major histocompatibility complex proteins (MHC) as the central event in the cellular adaptive immune response.
Cell Biology of T Cell Receptor Expression and Regulation
T cell Receptor Northern Arizona University
Download the t cell receptor factsbook or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the t cell receptor factsbook book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t …
T cell receptors (TCRs) are protein complexes formed by six different polypeptides. In most T cells, TCRs are composed of αβ subunits displaying immunoglobulin-like variable domains that recognize peptide antigens associated with major histocompatibility complex molecules expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells.
The T-cell receptor (TCR) does not signal on its own. Instead, it is constitutively associated with the CD3 coreceptors, which contain intracellular signaling motifs. Although antigen (Ag) recognition by the TCR and the activation of T cells after CD3 activation have been extensively studied, there
Initiation of immune response by the lymphocytes first requires recognition of the antigens and this is achieved by cell surface receptors called BCRs (B cell receptor) and TCRs (T cell receptor). These two receptors have great similarities and differences in their structure complexes, antigen recognition, cell activation and genetic recombination.
The Crystal Structure of a T Cell Receptor in Complex with Peptide and MHC Class II Ellis L. Reinherz,1,2* Kemin Tan,1,2† Lei Tang,1,2† Petra Kern,1,2‡
Crystal structure of a γδ T-cell receptor specific for the human MHC class I homolog MICA Bin Xua, Juan C. Pizarroa,1, Margaret A. Holmesa, Christine McBetha,2, Veronika Grohb, Thomas Spiesb,
T cells bearing V δ 1 receptors are associated with the intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) compartment, comprising 70–90% of the γδ T cells in the epithelium, and occur in increased frequencies among tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes .
Abstract. New massively parallel sequencing technology enables, through deep sequencing of rearranged T-cell receptor (TCR) Vβ complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) regions, a previously inaccessible level of TCR repertoire analysis.
The T-cell antigen receptor complex (TCR/CD3) is a cell surface structure that defines the T lymphocyte lineage, where it fulfills two basic functions, namely antigen recognition and triggering of
Abstract. Antibody and T‐cell receptors (TCRs) are the primary recognition molecules of the adaptive immune system. Antibodies have been extensively characterized and are being developed for a large number of therapeutic applications.
The T cell receptor (TR) is made of two chains, an alpha chain (TR-ALPHA) and a beta chain (TR-BETA) for the TR-ALPHA BETA receptor, a gamma chain (TR-GAMMA) and a delta chain (TR- DELTA) for the TR-GAMMA DELTA receptor [1].
LIGAND BINDING BY THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAINS OF T-CELL RECEPTORS: STRUCTURAL BASIS OF αβ AND γδ TCR BINDING TO A DIVERSE GROUP OF LIGANDS. The structures of many T-cell receptors (TCRs) in their ligand-bound state have now been determined, allowing some of the general rules of antigen recognition to be distilled.
The T-Cell Receptor Can Bind to the Peptide-Bound Major
Structural Biology of the T-cell Receptor Insights into
1.3 T cell receptor structure and signal transduction 21 1.4 The CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1 CD8 co-receptor: from structure to function 24 1.4.1.1 Comparisons between two naturally existing forms of CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1.2 Structural and molecular aspects of the CD8 co-receptor 26 1.4.1.3 Role of CD8 co-receptor in TCR proximal signalling 28 1.4.2 Role of the CD8 co-receptor in the thymus 30
Background: The T-cell receptor (TCR), located on the surface of T cells, is responsible for the recognition of the antigen-major histocompatibility complex, leading …
the assembly and probable structure of the T-cell antigen receptor Nicholas Manolios, Francois Letourneur, Juan S.Bonifacino and Richard D.Klausner Cell Biology and Metabolism Branch, National
An Overview of T Cell Receptors Mini-review The immune system has a near limitless capacity for detecting abnormalities. This remarkable ability for selfinterrogation is achieved by the related structures of two molecules, immunoglobulins and T cell receptors (TCR). The TCR, a defining structure of T cells, is a transmembrane heterodimer consisting of either an alpha and beta chain or delta
Read “T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes, Current Opinion in Structural Biology” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
Abstract. The T cell antigen receptor (TCR) is a multi-component cell surface complex composed of the products of at least six genes (1,2). Specific recognition of antigen/MHC is mediated by two chains of the TCR complex (generally ∝ and β) that are expressed as disulfide linked heterodimers and display a high degree of clonotypic diversity.
a pre-T alpha chain (pre-T cell receptor [pre -TCR])-this recognizes some intrathymic ligand and transmits a signal through CD3 that activates Lck, a protein tyrosine kinase
1 Chapter 9 T cell Receptor Self-MHC restriction of the T cell receptor (TCR) • Self restriction-T cell can only be activated by a unique peptide associated
Download the t cell receptor factsbook or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the t cell receptor factsbook book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t …
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
The First Structures of T Cell Receptors Bound to Peptide
Structure of the T cell receptor • Most T cells possess αβTCR, a minority (5-10%) express TCR composed of γδ chains • The antigen-binding region of the TCR is formed by the Vα and the Vβ domains • In the V region of each TCR chain there are 3 hypervariable or complementarity determining regions (CDRs) • CDR3 is the primary antigen recognition domain 21 . γδ T cell receptor
T cells, via their αβ T cell antigen receptors (TCRs), play a crucial role in protective immunity by specifically recognizing foreign peptide antigens when presented by molecules encoded by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) .
1.3 T cell receptor structure and signal transduction 21 1.4 The CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1 CD8 co-receptor: from structure to function 24 1.4.1.1 Comparisons between two naturally existing forms of CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1.2 Structural and molecular aspects of the CD8 co-receptor 26 1.4.1.3 Role of CD8 co-receptor in TCR proximal signalling 28 1.4.2 Role of the CD8 co-receptor in the thymus 30
The implications for T cell activation from the interactions observed between domains of the α and β chains are also discussed in terms of possible dimerization and allosteric mechanisms. Keywords T cell receptor structure ; complementarity-determining regions ; antigen and superantigen recognition ; T cell …
839 T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes lan A Wilson* and K Christopher Garcia The first crystal structures of intact T-cell receptors (TCRs) and their complexes with MHC peptide antigens (pMHC) were reported during the past year, along with those of a single-chain TCR Fv fragment and a !3-chain complexed with two different bacterial
1 Chapter 9 T cell Receptor Self-MHC restriction of the T cell receptor (TCR) • Self restriction-T cell can only be activated by a unique peptide associated
The Crystal Structure of a T Cell Receptor in Complex with Peptide and MHC Class II Ellis L. Reinherz,1,2* Kemin Tan,1,2† Lei Tang,1,2† Petra Kern,1,2‡
Download the t cell receptor factsbook or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the t cell receptor factsbook book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t …
T cell activation is initiated upon ligand engagement of the T cell receptor (TCR) and costimulatory receptors. The CD28 molecule acts as a major costimulatory receptor in promoting full activation of naive T cells. However, despite extensive studies, why naive T cell activation requires concurrent stimulation of both the TCR and costimulatory receptors remains poorly understood.
Development and structure of the B-cell Receptor. The first checkpoint in the development of a B-cell is the production of a functional pre-BCR, which is composed of two surrogate light chains and two immunoglobulin heavy chains, which are normally linked to Ig-α and Ig-βsignaling molecules.
The First Structures of T Cell Receptors Bound to Peptide
T Cell Receptor (TCR) Repertoire Sequencing
Pathway Description: T Cell Receptor (TCR) activation promotes a number of signaling cascades that ultimately determine cell fate through regulating cytokine production, cell …
MEDGENOME INC. medgenome.com 1 T Cell Receptor (TCR) Repertoire Sequencing Background A functional adaptive immune system in humans consists of a diverse population of T …
Structure of the T cell receptor • Most T cells possess αβTCR, a minority (5-10%) express TCR composed of γδ chains • The antigen-binding region of the TCR is formed by the Vα and the Vβ domains • In the V region of each TCR chain there are 3 hypervariable or complementarity determining regions (CDRs) • CDR3 is the primary antigen recognition domain 21 . γδ T cell receptor
In Immunology Guidebook, 2004. T CELL RECEPTORS. The T cell receptor (TCR) is a T cell surface structure that is comprised of a disulfide-linked heterodimer of highly variable α and β chains expressed at the cell membrane as a complex with the invariant CD3 chains.
The T-Cell Receptor Can Bind to the Peptide-Bound Major
A molecular basis of human T cell receptor autoreactivity
Gene Modified T Cell Receptor (TCR) Therapies By transferring genes for the and chains of a specific TCR, the specificity of a T cell can be redirected (Figure 1).
LIGAND BINDING BY THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAINS OF T-CELL RECEPTORS: STRUCTURAL BASIS OF αβ AND γδ TCR BINDING TO A DIVERSE GROUP OF LIGANDS. The structures of many T-cell receptors (TCRs) in their ligand-bound state have now been determined, allowing some of the general rules of antigen recognition to be distilled.
between the T-cell receptor (TCR) and a composite antigen in the form of an epitopic peptide bound between the polymorphic a1 and a2 helices of an MHC class I (MHCI) molecule.
An Overview of T Cell Receptors Mini-review The immune system has a near limitless capacity for detecting abnormalities. This remarkable ability for selfinterrogation is achieved by the related structures of two molecules, immunoglobulins and T cell receptors (TCR). The TCR, a defining structure of T cells, is a transmembrane heterodimer consisting of either an alpha and beta chain or delta
The T cell receptor (TR) is made of two chains, an alpha chain (TR-ALPHA) and a beta chain (TR-BETA) for the TR-ALPHA BETA receptor, a gamma chain (TR-GAMMA) and a delta chain (TR- DELTA) for the TR-GAMMA DELTA receptor [1].
T cells bearing V δ 1 receptors are associated with the intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) compartment, comprising 70–90% of the γδ T cells in the epithelium, and occur in increased frequencies among tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes .
Abstract. A subpopulation of peripheral blood T-lymphocytes exists that is distinct from T cells that express the T cell receptor (TCR) αβ. This population of T cells expresses a receptor composed of TCR γ and TCR δ polypeptides that are associated with CD3 (Brenner et al., 1986).
have postulated for the T-cell receptor. Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, L3T4 and the MIs antigen, which have been found to playa role in antigen recognition, function as
The T Cell Receptor FactsBook contains entries on all the 176 functional variable, diversity, joining, and constant regions of the human T cell receptor, including alpha, beta, gamma, and delta loci. Introductory chapters summarize information of T cell receptor chain synthesis, chromosomal location, and an overview of the human T cell receptor loci.
T cell receptors (TCRs) are protein complexes formed by six different polypeptides. In most T cells, TCRs are composed of αβ subunits displaying immunoglobulin-like variable domains that recognize peptide antigens associated with major histocompatibility complex molecules expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells.
The T Cell Receptor apdst.org
T cells Function receptor lineage and markers
The structure of the MHC class I molecule HLA-A2 reported in 1987 by Bjorkman et al. had revealed how peptide Ags are presented to T cells: peptides are buried in the long and deep groove of the MHC molecule, flanked on each side by a long α helix.
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is a novel cellular therapy that uses genetic engineering to alter a patient’s own T-cells to produce unique receptors on their cell surface that recognize a specific protein.
T cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling triggers selective cytokine expression to drive T cell proliferation and dif- ferentiation required for immune defense and surveillance. The nuclear signaling events responsible for specificity
Development and structure of the B-cell Receptor. The first checkpoint in the development of a B-cell is the production of a functional pre-BCR, which is composed of two surrogate light chains and two immunoglobulin heavy chains, which are normally linked to Ig-α and Ig-βsignaling molecules.
Background: The T-cell receptor (TCR), located on the surface of T cells, is responsible for the recognition of the antigen-major histocompatibility complex, leading …
Download the t cell receptor factsbook or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the t cell receptor factsbook book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t …
The T Cell Receptor FactsBook contains entries on all the 176 functional variable, diversity, joining, and constant regions of the human T cell receptor, including alpha, beta, gamma, and delta loci. Introductory chapters summarize information of T cell receptor chain synthesis, chromosomal location, and an overview of the human T cell receptor loci.
T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes ScienceDirect
Read The T Cell Receptor FactsBook PDF Free video
The T-cell-receptor signaling network Morgan Huse Immunology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065 e-mail: husem@mskcc.org
T-cells are a subset of lymphocytes that play a large role in the immune response. The TCR (T-cell receptor) is a complex of integral membrane proteins that participate in the activation of T-cells in response to an antigen.
A T cell receptor (TCR) that binds both major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II molecules reveals a novel structural variation that can potentially allow a single TCR to have three widely differing binding sites (Yin et al., 2011).
Background: The T-cell receptor (TCR), located on the surface of T cells, is responsible for the recognition of the antigen-major histocompatibility complex, leading …
An Overview of T Cell Receptors Mini-review The immune system has a near limitless capacity for detecting abnormalities. This remarkable ability for selfinterrogation is achieved by the related structures of two molecules, immunoglobulins and T cell receptors (TCR). The TCR, a defining structure of T cells, is a transmembrane heterodimer consisting of either an alpha and beta chain or delta
Abstract. The T-cell antigen receptor complex (TCR/CD3) is a cell surface structure that defines the T lymphocyte lineage, where it fulfills two basic functions, namely antigen recognition and triggering of signals needed to mount adequate responses to foreign aggression and/or to undergo differentiation.
INTRODUCTION. T-cell receptors (TCRs) are proteins of the adaptive immune response. They are expressed on the surfaces of T-cells and typically recognise peptides that are presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
The T-cell antigen receptor complex (TCR/CD3) is a cell surface structure that defines the T lymphocyte lineage, where it fulfills two basic functions, namely antigen recognition and triggering of
839 T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes lan A Wilson* and K Christopher Garcia The first crystal structures of intact T-cell receptors (TCRs) and their complexes with MHC peptide antigens (pMHC) were reported during the past year, along with those of a single-chain TCR Fv fragment and a !3-chain complexed with two different bacterial
T Cell Receptor (TCR) Repertoire Sequencing
T Cell Receptor Structure and Function Analysis by
T cells, via their αβ T cell antigen receptors (TCRs), play a crucial role in protective immunity by specifically recognizing foreign peptide antigens when presented by molecules encoded by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) .
Abstract. The T-cell antigen receptor complex (TCR/CD3) is a cell surface structure that defines the T lymphocyte lineage, where it fulfills two basic functions, namely antigen recognition and triggering of signals needed to mount adequate responses to foreign aggression and/or to undergo differentiation.
The T-cell antigen receptor complex (TCR/CD3) is a cell surface structure that defines the T lymphocyte lineage, where it fulfills two basic functions, namely antigen recognition and triggering of
Identification of MART-i-specific T-Cell Receptors: T Cells Utilizing Distinct TCell Receptor Variable and Joining Regions Recognize the Same Tumor Epitope David J. Cole, Daniel P.
An Overview of T Cell Receptors Mini-review The immune system has a near limitless capacity for detecting abnormalities. This remarkable ability for selfinterrogation is achieved by the related structures of two molecules, immunoglobulins and T cell receptors (TCR). The TCR, a defining structure of T cells, is a transmembrane heterodimer consisting of either an alpha and beta chain or delta
Abstract. The central event in the cellular immune response to invading microorganisms is the specific recognition of foreign peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules by the αβ T cell receptor (TCR).
T-cells are a subset of lymphocytes that play a large role in the immune response. The TCR (T-cell receptor) is a complex of integral membrane proteins that participate in the activation of T-cells in response to an antigen.
T cell receptors (TCRs) are protein complexes formed by six different polypeptides. In most T cells, TCRs are composed of αβ subunits displaying immunoglobulin-like variable domains that recognize peptide antigens associated with major histocompatibility complex molecules expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells.
1 Chapter 9 T cell Receptor Self-MHC restriction of the T cell receptor (TCR) • Self restriction-T cell can only be activated by a unique peptide associated
The Crystal Structure of a T Cell Receptor in Complex with Peptide and MHC Class II Ellis L. Reinherz,1,2* Kemin Tan,1,2† Lei Tang,1,2† Petra Kern,1,2‡
T-Cell Receptor SpringerLink
T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes Current
have postulated for the T-cell receptor. Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, L3T4 and the MIs antigen, which have been found to playa role in antigen recognition, function as
The T-cell receptor, or TCR, is a molecule found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
The T cell receptor (TR) is made of two chains, an alpha chain (TR-ALPHA) and a beta chain (TR-BETA) for the TR-ALPHA BETA receptor, a gamma chain (TR-GAMMA) and a delta chain (TR- DELTA) for the TR-GAMMA DELTA receptor [1].
A T cell receptor (TCR) that binds both major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II molecules reveals a novel structural variation that can potentially allow a single TCR to have three widely differing binding sites (Yin et al., 2011).
Abstract. The T cell antigen receptor (TCR) is a multi-component cell surface complex composed of the products of at least six genes (1,2). Specific recognition of antigen/MHC is mediated by two chains of the TCR complex (generally ∝ and β) that are expressed as disulfide linked heterodimers and display a high degree of clonotypic diversity.
Identification of MART-i-specific T-Cell Receptors: T Cells Utilizing Distinct TCell Receptor Variable and Joining Regions Recognize the Same Tumor Epitope David J. Cole, Daniel P.
Detection of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma Wei Zhu 1,4, of an intact lymphoid follicle structure and T area expansion only. Type 2 is characterized by an intact segmental lymphatic follicular struc-ture. Type 3 is characterized by a complete obliteration of the lymphatic follicular structure [6]. The first two types are
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is a novel cellular therapy that uses genetic engineering to alter a patient’s own T-cells to produce unique receptors on their cell surface that recognize a specific protein.
Abstract. A subpopulation of peripheral blood T-lymphocytes exists that is distinct from T cells that express the T cell receptor (TCR) αβ. This population of T cells expresses a receptor composed of TCR γ and TCR δ polypeptides that are associated with CD3 (Brenner et al., 1986).
Gene Modified T Cell Receptor (TCR) Therapies By transferring genes for the and chains of a specific TCR, the specificity of a T cell can be redirected (Figure 1).
MEDGENOME INC. medgenome.com 1 T Cell Receptor (TCR) Repertoire Sequencing Background A functional adaptive immune system in humans consists of a diverse population of T …
2/10/2015 · Download Read The T Cell Receptor FactsBook PDF Free Audio Book Download Read The T Cell Receptor FactsBook PDF Free Android Download Read The T Cell Receptor
T cell activation is initiated upon ligand engagement of the T cell receptor (TCR) and costimulatory receptors. The CD28 molecule acts as a major costimulatory receptor in promoting full activation of naive T cells. However, despite extensive studies, why naive T cell activation requires concurrent stimulation of both the TCR and costimulatory receptors remains poorly understood.
Crystal structure of a γδ T-cell receptor specific for the human MHC class I homolog MICA Bin Xua, Juan C. Pizarroa,1, Margaret A. Holmesa, Christine McBetha,2, Veronika Grohb, Thomas Spiesb,
T Cell Receptors EMBL-EBI
A molecular basis of human T cell receptor autoreactivity
Abstract. The T cell antigen receptor (TCR) is a multi-component cell surface complex composed of the products of at least six genes (1,2). Specific recognition of antigen/MHC is mediated by two chains of the TCR complex (generally ∝ and β) that are expressed as disulfide linked heterodimers and display a high degree of clonotypic diversity.
immune cells to distinguish between the body’s own cells and foreign invaders. αβ T cell receptors (TCRs) recognize antigenic peptides in complex with major histocompatibility complex proteins (MHC) as the central event in the cellular adaptive immune response.
Abstract. New massively parallel sequencing technology enables, through deep sequencing of rearranged T-cell receptor (TCR) Vβ complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) regions, a previously inaccessible level of TCR repertoire analysis.
The T-cell antigen receptor complex (TCR/CD3) is a cell surface structure that defines the T lymphocyte lineage, where it fulfills two basic functions, namely antigen recognition and triggering of
The T Cell Receptor FactsBook 1st Edition
Mini-review An overview of T cell receptors Bio-Rad
In Immunology Guidebook, 2004. T CELL RECEPTORS. The T cell receptor (TCR) is a T cell surface structure that is comprised of a disulfide-linked heterodimer of highly variable α and β chains expressed at the cell membrane as a complex with the invariant CD3 chains.
1.3 T cell receptor structure and signal transduction 21 1.4 The CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1 CD8 co-receptor: from structure to function 24 1.4.1.1 Comparisons between two naturally existing forms of CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1.2 Structural and molecular aspects of the CD8 co-receptor 26 1.4.1.3 Role of CD8 co-receptor in TCR proximal signalling 28 1.4.2 Role of the CD8 co-receptor in the thymus 30
MHC-UNRESTRICTED MUC1-SPECIFIC T CELL RECEPTOR FOR CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY/GENE THERAPY by Nehad M. Alajez B.S. in Medical Technology, The Islamic University of Gaza, 1995
have postulated for the T-cell receptor. Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, L3T4 and the MIs antigen, which have been found to playa role in antigen recognition, function as
The T-cell antigen receptor complex (TCR/CD3) is a cell surface structure that defines the T lymphocyte lineage, where it fulfills two basic functions, namely antigen recognition and triggering of
Immunity Previews T Cell Receptor Structures: Three for the Price of One Nicholas R.J. Gascoigne1,* 1DepartmentofImmunologyandMicrobialScience
The primary structure of T cell receptor proteins and genes is well understood. Immunologists are now trying to understand the properties of these interesting molecules. Evidence suggests that T cell alpha beta receptors recognize a complex of an antigen-derived peptide bound to one of the cell
T cells, via their αβ T cell antigen receptors (TCRs), play a crucial role in protective immunity by specifically recognizing foreign peptide antigens when presented by molecules encoded by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) .
1 Chapter 9 T cell Receptor Self-MHC restriction of the T cell receptor (TCR) • Self restriction-T cell can only be activated by a unique peptide associated
T cells has unique surface receptors which interacts specifically with an antigen. Helper T cell receptor can bind only to antigenic peptide MHC class II complex on antigen presenting cells. T helper cells activate both T cells and B cells.
Abstract. The T cell antigen receptor (TCR) is a multi-component cell surface complex composed of the products of at least six genes (1,2). Specific recognition of antigen/MHC is mediated by two chains of the TCR complex (generally ∝ and β) that are expressed as disulfide linked heterodimers and display a high degree of clonotypic diversity.
T cell receptors (TCRs) are protein complexes formed by six different polypeptides. In most T cells, TCRs are composed of αβ subunits displaying immunoglobulin-like variable domains that recognize peptide antigens associated with major histocompatibility complex molecules expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for Ovarian
T Cell Receptor an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Abstract. The central event in the cellular immune response to invading microorganisms is the specific recognition of foreign peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules by the αβ T cell receptor (TCR).
T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes Wilson, Ian A; Christopher Garcia, K 1997-12-01 00:00:00 The first crystal structures of intact T-cell receptors (TCRs) and their complexes with MHC peptide antigens (pMHC) were reported during the past year, along with those of a single-chain TCR Fv fragment and a β-chain complexed with two different bacterial superantigens.
the assembly and probable structure of the T-cell antigen receptor Nicholas Manolios, Francois Letourneur, Juan S.Bonifacino and Richard D.Klausner Cell Biology and Metabolism Branch, National
immune cells to distinguish between the body’s own cells and foreign invaders. αβ T cell receptors (TCRs) recognize antigenic peptides in complex with major histocompatibility complex proteins (MHC) as the central event in the cellular adaptive immune response.
MHC-UNRESTRICTED MUC1-SPECIFIC T CELL RECEPTOR FOR CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY/GENE THERAPY by Nehad M. Alajez B.S. in Medical Technology, The Islamic University of Gaza, 1995
T cells has unique surface receptors which interacts specifically with an antigen. Helper T cell receptor can bind only to antigenic peptide MHC class II complex on antigen presenting cells. T helper cells activate both T cells and B cells.
INTRODUCTION. T-cell receptors (TCRs) are proteins of the adaptive immune response. They are expressed on the surfaces of T-cells and typically recognise peptides that are presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
T cell activation is initiated upon ligand engagement of the T cell receptor (TCR) and costimulatory receptors. The CD28 molecule acts as a major costimulatory receptor in promoting full activation of naive T cells. However, despite extensive studies, why naive T cell activation requires concurrent stimulation of both the TCR and costimulatory receptors remains poorly understood.
A molecular basis of human T cell receptor autoreactivity
MHC-UNRESTRICTED MUC1-SPECIFIC T CELL RECEPTOR FOR
Structure of the T cell receptor • Most T cells possess αβTCR, a minority (5-10%) express TCR composed of γδ chains • The antigen-binding region of the TCR is formed by the Vα and the Vβ domains • In the V region of each TCR chain there are 3 hypervariable or complementarity determining regions (CDRs) • CDR3 is the primary antigen recognition domain 21 . γδ T cell receptor
Abstract. A subpopulation of peripheral blood T-lymphocytes exists that is distinct from T cells that express the T cell receptor (TCR) αβ. This population of T cells expresses a receptor composed of TCR γ and TCR δ polypeptides that are associated with CD3 (Brenner et al., 1986).
The T Cell Receptor FactsBook contains entries on all the 176 functional variable, diversity, joining, and constant regions of the human T cell receptor, including alpha, beta, gamma, and delta loci. Introductory chapters summarize information of T cell receptor chain synthesis, chromosomal location, and an overview of the human T cell receptor loci.
A T cell receptor (TCR) that binds both major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II molecules reveals a novel structural variation that can potentially allow a single TCR to have three widely differing binding sites (Yin et al., 2011).
The structure of the MHC class I molecule HLA-A2 reported in 1987 by Bjorkman et al. had revealed how peptide Ags are presented to T cells: peptides are buried in the long and deep groove of the MHC molecule, flanked on each side by a long α helix.
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) can mediate redirected lysis of tumour cells in a major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-independent manner, thereby enabling autologous adoptive T-cell therapy for a variety of malignant neoplasms.
the assembly and probable structure of the T-cell antigen receptor Nicholas Manolios, Francois Letourneur, Juan S.Bonifacino and Richard D.Klausner Cell Biology and Metabolism Branch, National
Pathway Description: T Cell Receptor (TCR) activation promotes a number of signaling cascades that ultimately determine cell fate through regulating cytokine production, cell …
MHC-UNRESTRICTED MUC1-SPECIFIC T CELL RECEPTOR FOR CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY/GENE THERAPY by Nehad M. Alajez B.S. in Medical Technology, The Islamic University of Gaza, 1995
between the T-cell receptor (TCR) and a composite antigen in the form of an epitopic peptide bound between the polymorphic a1 and a2 helices of an MHC class I (MHCI) molecule.
839 T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes lan A Wilson* and K Christopher Garcia The first crystal structures of intact T-cell receptors (TCRs) and their complexes with MHC peptide antigens (pMHC) were reported during the past year, along with those of a single-chain TCR Fv fragment and a !3-chain complexed with two different bacterial
T cells are central to the cell-mediated immune response. There are many different types of T cells, all derived from same lymphoid stem cell. T cell function, lineage and the T cell receptor are discussed, along with markers and antibodies used to define them.
Enhancement of antigen-specific T cell immunity has shown significant therapeutic benefit in infectious diseases and cancer. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 (HPK1) is one of the intracellular regulators that dampens T cell receptor signaling. Wu et al. studied the molecular structure of HPK1 kinase with bound ligand, which provides insights for structure-based drug design.
T-cells are a subset of lymphocytes that play a large role in the immune response. The TCR (T-cell receptor) is a complex of integral membrane proteins that participate in the activation of T-cells in response to an antigen.
Abstract. Unusually long major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-restricted epitopes are important in immunity, but their ‘bulged’ conformation represents a potential obstacle to alphabeta T cell receptor (TCR)-MHC class I docking.
The T Cell Receptor Factsbook Download eBook PDF/EPUB
The T Cell Receptor FactsBook 1st Edition
The T Cell Receptor FactsBook contains entries on all the 176 functional variable, diversity, joining, and constant regions of the human T cell receptor, including alpha, beta, gamma, and delta loci. Introductory chapters summarize information of T cell receptor chain synthesis, chromosomal location, and an overview of the human T cell receptor loci.
S. Massari et al. / Molecular Immunology 46 (2009) 2728–2736 2729 Table 1a Description of TRGV genes of the dog genome. The position of all genes in the …
have postulated for the T-cell receptor. Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, Also discussed is the possibility that molecules such as Ly2, L3T4 and the MIs antigen, which have been found to playa role in antigen recognition, function as
Background: The T-cell receptor (TCR), located on the surface of T cells, is responsible for the recognition of the antigen-major histocompatibility complex, leading …
Pathway Description: T Cell Receptor (TCR) activation promotes a number of signaling cascades that ultimately determine cell fate through regulating cytokine production, cell …
the t cell receptor Thu, 06 Dec 2018 20:12:00 GMT the t cell receptor pdf – T cell receptor (TCR)–mediated signaling is initiated by a structure known as the
Abstract. New massively parallel sequencing technology enables, through deep sequencing of rearranged T-cell receptor (TCR) Vβ complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) regions, a previously inaccessible level of TCR repertoire analysis.
immune cells to distinguish between the body’s own cells and foreign invaders. αβ T cell receptors (TCRs) recognize antigenic peptides in complex with major histocompatibility complex proteins (MHC) as the central event in the cellular adaptive immune response.
MHC-UNRESTRICTED MUC1-SPECIFIC T CELL RECEPTOR FOR CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY/GENE THERAPY by Nehad M. Alajez B.S. in Medical Technology, The Islamic University of Gaza, 1995
Abstract. Antibody and T‐cell receptors (TCRs) are the primary recognition molecules of the adaptive immune system. Antibodies have been extensively characterized and are being developed for a large number of therapeutic applications.
Abstract T-cell antigen receptors composed of γ and δ polypeptide chains (γδTCRs) can directly recognize antigens in the form of intact proteins or non-peptide compounds, unlike αβTCRs, which recognize antigens bound to major histocompatibility complex molecules (MHC).
Enhancement of antigen-specific T cell immunity has shown significant therapeutic benefit in infectious diseases and cancer. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 (HPK1) is one of the intracellular regulators that dampens T cell receptor signaling. Wu et al. studied the molecular structure of HPK1 kinase with bound ligand, which provides insights for structure-based drug design.
Deep sequencing of the T-cell receptor repertoire in CD8
The T cell receptor Science
839 T-cell receptor structure and TCR complexes lan A Wilson* and K Christopher Garcia The first crystal structures of intact T-cell receptors (TCRs) and their complexes with MHC peptide antigens (pMHC) were reported during the past year, along with those of a single-chain TCR Fv fragment and a !3-chain complexed with two different bacterial
Structure of the T cell receptor • Most T cells possess αβTCR, a minority (5-10%) express TCR composed of γδ chains • The antigen-binding region of the TCR is formed by the Vα and the Vβ domains • In the V region of each TCR chain there are 3 hypervariable or complementarity determining regions (CDRs) • CDR3 is the primary antigen recognition domain 21 . γδ T cell receptor
MEDGENOME INC. medgenome.com 1 T Cell Receptor (TCR) Repertoire Sequencing Background A functional adaptive immune system in humans consists of a diverse population of T …
1 Chapter 9 T cell Receptor Self-MHC restriction of the T cell receptor (TCR) • Self restriction-T cell can only be activated by a unique peptide associated
Abstract. New massively parallel sequencing technology enables, through deep sequencing of rearranged T-cell receptor (TCR) Vβ complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) regions, a previously inaccessible level of TCR repertoire analysis.
Enhancement of antigen-specific T cell immunity has shown significant therapeutic benefit in infectious diseases and cancer. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 (HPK1) is one of the intracellular regulators that dampens T cell receptor signaling. Wu et al. studied the molecular structure of HPK1 kinase with bound ligand, which provides insights for structure-based drug design.
T cell receptors (TCRs) are protein complexes formed by six different polypeptides. In most T cells, TCRs are composed of αβ subunits displaying immunoglobulin-like variable domains that recognize peptide antigens associated with major histocompatibility complex molecules expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells.
Immunity Previews T Cell Receptor Structures: Three for the Price of One Nicholas R.J. Gascoigne1,* 1DepartmentofImmunologyandMicrobialScience
Abstract. Unusually long major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-restricted epitopes are important in immunity, but their ‘bulged’ conformation represents a potential obstacle to alphabeta T cell receptor (TCR)-MHC class I docking.
T-cells are a subset of lymphocytes that play a large role in the immune response. The TCR (T-cell receptor) is a complex of integral membrane proteins that participate in the activation of T-cells in response to an antigen.
The structure of the MHC class I molecule HLA-A2 reported in 1987 by Bjorkman et al. had revealed how peptide Ags are presented to T cells: peptides are buried in the long and deep groove of the MHC molecule, flanked on each side by a long α helix.
INTRODUCTION. T-cell receptors (TCRs) are proteins of the adaptive immune response. They are expressed on the surfaces of T-cells and typically recognise peptides that are presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
T cells has unique surface receptors which interacts specifically with an antigen. Helper T cell receptor can bind only to antigenic peptide MHC class II complex on antigen presenting cells. T helper cells activate both T cells and B cells.
Background: The T-cell receptor (TCR), located on the surface of T cells, is responsible for the recognition of the antigen-major histocompatibility complex, leading …
Download the t cell receptor factsbook or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the t cell receptor factsbook book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t …
STCRDab the structural T-cell receptor database Nucleic
Overview of methodologies for T-cell receptor repertoire
Abstract. Unusually long major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-restricted epitopes are important in immunity, but their ‘bulged’ conformation represents a potential obstacle to alphabeta T cell receptor (TCR)-MHC class I docking.
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is a novel cellular therapy that uses genetic engineering to alter a patient’s own T-cells to produce unique receptors on their cell surface that recognize a specific protein.
Abstract. New massively parallel sequencing technology enables, through deep sequencing of rearranged T-cell receptor (TCR) Vβ complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) regions, a previously inaccessible level of TCR repertoire analysis.
between the T-cell receptor (TCR) and a composite antigen in the form of an epitopic peptide bound between the polymorphic a1 and a2 helices of an MHC class I (MHCI) molecule.
The T-cell receptor, or TCR, is a molecule found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
1.3 T cell receptor structure and signal transduction 21 1.4 The CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1 CD8 co-receptor: from structure to function 24 1.4.1.1 Comparisons between two naturally existing forms of CD8 co-receptor 24 1.4.1.2 Structural and molecular aspects of the CD8 co-receptor 26 1.4.1.3 Role of CD8 co-receptor in TCR proximal signalling 28 1.4.2 Role of the CD8 co-receptor in the thymus 30
Crystal structure of a γδ T-cell receptor specific for the human MHC class I homolog MICA Bin Xua, Juan C. Pizarroa,1, Margaret A. Holmesa, Christine McBetha,2, Veronika Grohb, Thomas Spiesb,
The T cell receptor (TR) is made of two chains, an alpha chain (TR-ALPHA) and a beta chain (TR-BETA) for the TR-ALPHA BETA receptor, a gamma chain (TR-GAMMA) and a delta chain (TR- DELTA) for the TR-GAMMA DELTA receptor [1].
B-cell receptor Wikipedia
The T cell receptor Science
The structure of the MHC class I molecule HLA-A2 reported in 1987 by Bjorkman et al. had revealed how peptide Ags are presented to T cells: peptides are buried in the long and deep groove of the MHC molecule, flanked on each side by a long α helix.
T cells Function receptor lineage and markers
The T cell receptor (TR) is made of two chains, an alpha chain (TR-ALPHA) and a beta chain (TR-BETA) for the TR-ALPHA BETA receptor, a gamma chain (TR-GAMMA) and a delta chain (TR- DELTA) for the TR-GAMMA DELTA receptor [1].
T Cell Receptor an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Abstract. The T cell antigen receptor (TCR) is a multi-component cell surface complex composed of the products of at least six genes (1,2). Specific recognition of antigen/MHC is mediated by two chains of the TCR complex (generally ∝ and β) that are expressed as disulfide linked heterodimers and display a high degree of clonotypic diversity.
Original Article Detection of immunoglobulin and T-cell
Human T Cell Receptor γδ Structure SpringerLink
Mini-review An overview of T cell receptors Bio-Rad
The T-cell-receptor signaling network Morgan Huse Immunology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065 e-mail: husem@mskcc.org
T Cell Receptor and the B Cell Receptor Comparison
The First Structures of T Cell Receptors Bound to Peptide
S. Massari et al. / Molecular Immunology 46 (2009) 2728–2736 2729 Table 1a Description of TRGV genes of the dog genome. The position of all genes in the …
STCRDab the structural T-cell receptor database Nucleic
Molecular architecture of the αβ T cell receptor–CD3
Development and structure of the B-cell Receptor. The first checkpoint in the development of a B-cell is the production of a functional pre-BCR, which is composed of two surrogate light chains and two immunoglobulin heavy chains, which are normally linked to Ig-α and Ig-βsignaling molecules.
T-Cell Receptor SpringerLink
T-Cell Receptor (TCR) Overview Thermo Fisher Scientific US
Original Article Detection of immunoglobulin and T-cell
The T-cell-receptor signaling network Morgan Huse Immunology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065 e-mail: husem@mskcc.org
T-Cell Receptor SpringerLink
Issue Structure cell.com
An αβ T Cell Receptor Structure at 2.5 Å and Its
Structure of CARs and T-Cell Receptors. Panel A shows the structure of a T-cell receptor, which consists of heterodimeric and antigen-specific α and β chains that closely associate with the invariant ε, δ, γ, and ζ chains of the CD3 complex. The T-cell receptor binds to the HLA allele that has a bound peptide derived from a tumor antigen on the target cell. Panel B shows the CAR, which
CD3ζ-based chimeric antigen receptors mediate T cell
T cell Receptor Northern Arizona University
T-Cell Receptor SpringerLink