Risk analysis in financial management pdf
Credit Risk Credit Analysis Seven C’s Credit Analysis Process 2. Lending Process 8. Problem LoansObjectives Introduction Credit Process Documentation Loan Pricing and Profitability Analysis Regulations 3. Financial Statement Analysis-I Objectives Introduction Ratio Analysis Liquidity Ratios Turnover Ratios Profitability Ratios Leverage Ratios Market Ratios 4. Financial Statement Analysis …
The Risk Adjusted Discount Rate is composite of discount rate which combines .V.V: and LRX In the case of N. future cash flows should be discounted using Risk Adjusted Discount Rate and then N.P. 109 . which in turn are subject to risk attitude of management.V.P. The risk adjusted discount rate is a composite rate which combines both the time and discount factors. iv) This method of
Financial Management Act 2006. Compliance with this policy is mandatory to enhance governance and outcomes through effective and consistent risk management in and across the WA health system. 2. Scope This policy applies all Health Service Providers under the Health Services Act 20162 3. Policy statement The WA health system is committed to the management of its risks including those
KeywordS: organisational risk, risk analysis, risk management, organisational integrity, Supreme Audit Institution JeL codeS: D81, In public entities, the regulations of financial management and control systems were devel-oped in the course of a multiple-step process. After the legislative basis was created, the regulatory concept was developed under the influence of the coso model from
after-the-fact analysis of a risk failure, and many are enhancing scenario analysis and tools to better assess forward non-financial risk. This is akin to a financial-risk mindset, which aims to identify credit and market risks and anticipate their effects. To spur the change, a number of banks are moving the compliance function under the risk function. • Increased accountability of
The role of risk management in financial firms has evolved far beyond the simple insurance of identified risks, to a discipline that centres on complex econometric and financial models of uncertainty. Financial risk management has been defined by the Basel Committee (2001) as a
frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence designed to improve organizational performance and governance and to reduce the extent of fraud in organizations. COSO is a private-sector initiative jointly sponsored and funded by the following organizations: American Accounting Association (AAA) American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Financial
Effective financial risk management: Extract Against this background, ‘financial risk’ may broadly be thought of as adverse movements in financial price or other events that impair financial condition, financial performance or other financial outcomes. For example, financial risk may affect the adequacy of returns or accessibility to finance at reasonable cost. These characteristics have
reached on model risk management in financial institutions (which are elaborated on in the appropriate sections of this document). Model risk definition and regulations 1. The use of mathematical models by financial institutions in many areas is rapidly gaining ground. This brings significant benefits (objectivity, automation, efficiency, etc.) but also entails costs. 2. Among these costs is
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
In a financial institution, enterprise risk management is normally thought of as the combination of credit risk, interest rate risk or asset liability management, liquidity risk, market risk, and operational risk.
Quantitative Analysis, Risk Management, Modelling, Algo-Trading, Blockchain for Finance Financial Risk Management The most current collection of articles on Financial Risk Management and Modeling at QuantAtRisk.com:
No. 18 Public Private Partnerships Risk Management, May 2005. No. 19 Public Private Partnerships Contract Management, May 2005. iv The Financial Management Guidance series of publications Archived. Contents v Introduction 1 Section A – Overview of Cost-Benefi t Analysis 3 1. Cost-Benefi t Analysis – An Overview 4 1.1 Explanation of cost-benefi t analysis 4 1.2 What is a CBA attempting
A top risk management practitioner addresses the essential aspects of modern financial risk management. In the Second Edition of Financial Risk Management + Website, market risk expert Steve Allen offers an insider’s view of this discipline and covers the strategies, principles, and measurement techniques necessary to manage
Risk Analysis Matrix CONSEQUENCES: Insignificant No injuries, low financial loss Minor First aid treatment, on-site release immediately contained, medium
management and fiduciary risk identification, “procurement” may be referred to as a separate system from other systems involved in PFM for clarity and precision. Public Financial Management Risk Assessment Framework (PFMRAF) is USAID’s risk management
Risk Analysis Matrix Club Help
https://www.youtube.com/embed/464hlwCV2ao

RISK ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT The Center for ETH Z
management in accordance with the Financial Accountability Act 2009, Financial and Performance Management Standard 2009 and Public Sector Ethics Act 1994. 3.2 Governance The Director-General and Department Leadership Team (DLT) members shall determine and communicate the department’s risk appetite to effectively manage and prioritise risks to meet obligations and provide oversight of risk
Country risk assessment is a critical foundation for disaster risk management and related financial strategies and requires clear rules and governance. Risk assessment needs to be comprehensive and well orchestrated both within government and with
The sample risk analysis template has great benefits in risk management. In fact risk management can be made possible only when a risk analysis is done properly. Therefore you must make a proper risk analysis file. As you can see that making of a risk analysis report is not an easy affair. You have to involve and consider many important points to do that, and that is why when you are doing
Analysis for Financial Management Tenth Edition ROBERT C.HIGGINS (irmiente Keimers ot Finance The University of Washington, McGraw-Hill Irwin. Contents Preface XI PART ONE ASSESSING THE FINANCIAL HEALTH OF THE FIRM 1 Chapter 1 Interpreting Financial Statements 3 The Cash Flow Cycle 3 The Balance Sheet 6 Current Assets and Liabilities 9 Shareholders’ Equity 11 The Income …
formulation of the analysis theory on the basis of financial ratios, companies and entrepreneurs to calculate and use financial ratios to analyze their own business, for comparison with others in both the same business and the economy as a whole and for assessing business risks and to refer
First, there is traditional risk management which focuses on financial risk and manages risks in individual cases. Next, there is enterprise risk management (ERM) which
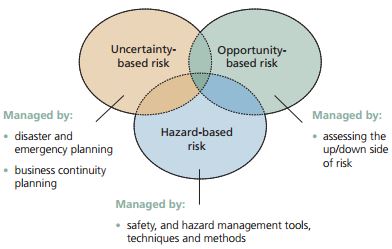
Risk Assessment – The overall process of risk identification, risk analysis and risk evaluation. Risk Management – The culture, processes and structures that are directed towards realising potential
MMU Risk Analysis toolkit (v 5) Page 2 Project Role Risk Management Role Project Sponsor Ensures that risk management structures and processes are in place for the
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66

https://www.youtube.com/embed/KOX4HW5YsWE
Risk Management Policy Queensland Health
Credit Analysis KESDEE
financial-management-risk-analysis-in-capital-budgeting
WA Health Risk Management Policy


https://www.youtube.com/embed/55af7cmyczo
financial-management-risk-analysis-in-capital-budgeting
Credit Analysis KESDEE
after-the-fact analysis of a risk failure, and many are enhancing scenario analysis and tools to better assess forward non-financial risk. This is akin to a financial-risk mindset, which aims to identify credit and market risks and anticipate their effects. To spur the change, a number of banks are moving the compliance function under the risk function. • Increased accountability of
Effective financial risk management: Extract Against this background, ‘financial risk’ may broadly be thought of as adverse movements in financial price or other events that impair financial condition, financial performance or other financial outcomes. For example, financial risk may affect the adequacy of returns or accessibility to finance at reasonable cost. These characteristics have
Analysis for Financial Management Tenth Edition ROBERT C.HIGGINS (irmiente Keimers ot Finance The University of Washington, McGraw-Hill Irwin. Contents Preface XI PART ONE ASSESSING THE FINANCIAL HEALTH OF THE FIRM 1 Chapter 1 Interpreting Financial Statements 3 The Cash Flow Cycle 3 The Balance Sheet 6 Current Assets and Liabilities 9 Shareholders’ Equity 11 The Income …
Risk Assessment – The overall process of risk identification, risk analysis and risk evaluation. Risk Management – The culture, processes and structures that are directed towards realising potential
KeywordS: organisational risk, risk analysis, risk management, organisational integrity, Supreme Audit Institution JeL codeS: D81, In public entities, the regulations of financial management and control systems were devel-oped in the course of a multiple-step process. After the legislative basis was created, the regulatory concept was developed under the influence of the coso model from
management in accordance with the Financial Accountability Act 2009, Financial and Performance Management Standard 2009 and Public Sector Ethics Act 1994. 3.2 Governance The Director-General and Department Leadership Team (DLT) members shall determine and communicate the department’s risk appetite to effectively manage and prioritise risks to meet obligations and provide oversight of risk
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
Analysis for Financial Management GBV
Risk Assessment – The overall process of risk identification, risk analysis and risk evaluation. Risk Management – The culture, processes and structures that are directed towards realising potential
management in accordance with the Financial Accountability Act 2009, Financial and Performance Management Standard 2009 and Public Sector Ethics Act 1994. 3.2 Governance The Director-General and Department Leadership Team (DLT) members shall determine and communicate the department’s risk appetite to effectively manage and prioritise risks to meet obligations and provide oversight of risk
formulation of the analysis theory on the basis of financial ratios, companies and entrepreneurs to calculate and use financial ratios to analyze their own business, for comparison with others in both the same business and the economy as a whole and for assessing business risks and to refer
The sample risk analysis template has great benefits in risk management. In fact risk management can be made possible only when a risk analysis is done properly. Therefore you must make a proper risk analysis file. As you can see that making of a risk analysis report is not an easy affair. You have to involve and consider many important points to do that, and that is why when you are doing
MMU Risk Analysis toolkit (v 5) Page 2 Project Role Risk Management Role Project Sponsor Ensures that risk management structures and processes are in place for the
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
Country risk assessment is a critical foundation for disaster risk management and related financial strategies and requires clear rules and governance. Risk assessment needs to be comprehensive and well orchestrated both within government and with
financial-management-risk-analysis-in-capital-budgeting
Analysis for Financial Management GBV
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
after-the-fact analysis of a risk failure, and many are enhancing scenario analysis and tools to better assess forward non-financial risk. This is akin to a financial-risk mindset, which aims to identify credit and market risks and anticipate their effects. To spur the change, a number of banks are moving the compliance function under the risk function. • Increased accountability of
Country risk assessment is a critical foundation for disaster risk management and related financial strategies and requires clear rules and governance. Risk assessment needs to be comprehensive and well orchestrated both within government and with
Risk Analysis Matrix CONSEQUENCES: Insignificant No injuries, low financial loss Minor First aid treatment, on-site release immediately contained, medium
frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence designed to improve organizational performance and governance and to reduce the extent of fraud in organizations. COSO is a private-sector initiative jointly sponsored and funded by the following organizations: American Accounting Association (AAA) American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Financial
Analysis for Financial Management GBV
Credit Analysis KESDEE
Risk Assessment – The overall process of risk identification, risk analysis and risk evaluation. Risk Management – The culture, processes and structures that are directed towards realising potential
frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence designed to improve organizational performance and governance and to reduce the extent of fraud in organizations. COSO is a private-sector initiative jointly sponsored and funded by the following organizations: American Accounting Association (AAA) American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Financial
reached on model risk management in financial institutions (which are elaborated on in the appropriate sections of this document). Model risk definition and regulations 1. The use of mathematical models by financial institutions in many areas is rapidly gaining ground. This brings significant benefits (objectivity, automation, efficiency, etc.) but also entails costs. 2. Among these costs is
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
management and fiduciary risk identification, “procurement” may be referred to as a separate system from other systems involved in PFM for clarity and precision. Public Financial Management Risk Assessment Framework (PFMRAF) is USAID’s risk management
RISK ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT The Center for ETH Z
Financial Risk Management and Modeling QuantAtRisk
No. 18 Public Private Partnerships Risk Management, May 2005. No. 19 Public Private Partnerships Contract Management, May 2005. iv The Financial Management Guidance series of publications Archived. Contents v Introduction 1 Section A – Overview of Cost-Benefi t Analysis 3 1. Cost-Benefi t Analysis – An Overview 4 1.1 Explanation of cost-benefi t analysis 4 1.2 What is a CBA attempting
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
MMU Risk Analysis toolkit (v 5) Page 2 Project Role Risk Management Role Project Sponsor Ensures that risk management structures and processes are in place for the
Analysis for Financial Management Tenth Edition ROBERT C.HIGGINS (irmiente Keimers ot Finance The University of Washington, McGraw-Hill Irwin. Contents Preface XI PART ONE ASSESSING THE FINANCIAL HEALTH OF THE FIRM 1 Chapter 1 Interpreting Financial Statements 3 The Cash Flow Cycle 3 The Balance Sheet 6 Current Assets and Liabilities 9 Shareholders’ Equity 11 The Income …
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
Credit Analysis KESDEE
RISK ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT The Center for ETH Z
Risk Analysis Matrix CONSEQUENCES: Insignificant No injuries, low financial loss Minor First aid treatment, on-site release immediately contained, medium
frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence designed to improve organizational performance and governance and to reduce the extent of fraud in organizations. COSO is a private-sector initiative jointly sponsored and funded by the following organizations: American Accounting Association (AAA) American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Financial
MMU Risk Analysis toolkit (v 5) Page 2 Project Role Risk Management Role Project Sponsor Ensures that risk management structures and processes are in place for the
In a financial institution, enterprise risk management is normally thought of as the combination of credit risk, interest rate risk or asset liability management, liquidity risk, market risk, and operational risk.
after-the-fact analysis of a risk failure, and many are enhancing scenario analysis and tools to better assess forward non-financial risk. This is akin to a financial-risk mindset, which aims to identify credit and market risks and anticipate their effects. To spur the change, a number of banks are moving the compliance function under the risk function. • Increased accountability of
KeywordS: organisational risk, risk analysis, risk management, organisational integrity, Supreme Audit Institution JeL codeS: D81, In public entities, the regulations of financial management and control systems were devel-oped in the course of a multiple-step process. After the legislative basis was created, the regulatory concept was developed under the influence of the coso model from
Effective financial risk management: Extract Against this background, ‘financial risk’ may broadly be thought of as adverse movements in financial price or other events that impair financial condition, financial performance or other financial outcomes. For example, financial risk may affect the adequacy of returns or accessibility to finance at reasonable cost. These characteristics have
No. 18 Public Private Partnerships Risk Management, May 2005. No. 19 Public Private Partnerships Contract Management, May 2005. iv The Financial Management Guidance series of publications Archived. Contents v Introduction 1 Section A – Overview of Cost-Benefi t Analysis 3 1. Cost-Benefi t Analysis – An Overview 4 1.1 Explanation of cost-benefi t analysis 4 1.2 What is a CBA attempting
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
Analysis for Financial Management Tenth Edition ROBERT C.HIGGINS (irmiente Keimers ot Finance The University of Washington, McGraw-Hill Irwin. Contents Preface XI PART ONE ASSESSING THE FINANCIAL HEALTH OF THE FIRM 1 Chapter 1 Interpreting Financial Statements 3 The Cash Flow Cycle 3 The Balance Sheet 6 Current Assets and Liabilities 9 Shareholders’ Equity 11 The Income …
First, there is traditional risk management which focuses on financial risk and manages risks in individual cases. Next, there is enterprise risk management (ERM) which
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
management and fiduciary risk identification, “procurement” may be referred to as a separate system from other systems involved in PFM for clarity and precision. Public Financial Management Risk Assessment Framework (PFMRAF) is USAID’s risk management
Analysis for Financial Management GBV
Credit Analysis KESDEE
MMU Risk Analysis toolkit (v 5) Page 2 Project Role Risk Management Role Project Sponsor Ensures that risk management structures and processes are in place for the
A top risk management practitioner addresses the essential aspects of modern financial risk management. In the Second Edition of Financial Risk Management Website, market risk expert Steve Allen offers an insider’s view of this discipline and covers the strategies, principles, and measurement techniques necessary to manage
Financial Management Act 2006. Compliance with this policy is mandatory to enhance governance and outcomes through effective and consistent risk management in and across the WA health system. 2. Scope This policy applies all Health Service Providers under the Health Services Act 20162 3. Policy statement The WA health system is committed to the management of its risks including those
KeywordS: organisational risk, risk analysis, risk management, organisational integrity, Supreme Audit Institution JeL codeS: D81, In public entities, the regulations of financial management and control systems were devel-oped in the course of a multiple-step process. After the legislative basis was created, the regulatory concept was developed under the influence of the coso model from
Quantitative Analysis, Risk Management, Modelling, Algo-Trading, Blockchain for Finance Financial Risk Management The most current collection of articles on Financial Risk Management and Modeling at QuantAtRisk.com:
No. 18 Public Private Partnerships Risk Management, May 2005. No. 19 Public Private Partnerships Contract Management, May 2005. iv The Financial Management Guidance series of publications Archived. Contents v Introduction 1 Section A – Overview of Cost-Benefi t Analysis 3 1. Cost-Benefi t Analysis – An Overview 4 1.1 Explanation of cost-benefi t analysis 4 1.2 What is a CBA attempting
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
reached on model risk management in financial institutions (which are elaborated on in the appropriate sections of this document). Model risk definition and regulations 1. The use of mathematical models by financial institutions in many areas is rapidly gaining ground. This brings significant benefits (objectivity, automation, efficiency, etc.) but also entails costs. 2. Among these costs is
The sample risk analysis template has great benefits in risk management. In fact risk management can be made possible only when a risk analysis is done properly. Therefore you must make a proper risk analysis file. As you can see that making of a risk analysis report is not an easy affair. You have to involve and consider many important points to do that, and that is why when you are doing
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
Analysis for Financial Management Tenth Edition ROBERT C.HIGGINS (irmiente Keimers ot Finance The University of Washington, McGraw-Hill Irwin. Contents Preface XI PART ONE ASSESSING THE FINANCIAL HEALTH OF THE FIRM 1 Chapter 1 Interpreting Financial Statements 3 The Cash Flow Cycle 3 The Balance Sheet 6 Current Assets and Liabilities 9 Shareholders’ Equity 11 The Income …
formulation of the analysis theory on the basis of financial ratios, companies and entrepreneurs to calculate and use financial ratios to analyze their own business, for comparison with others in both the same business and the economy as a whole and for assessing business risks and to refer
management and fiduciary risk identification, “procurement” may be referred to as a separate system from other systems involved in PFM for clarity and precision. Public Financial Management Risk Assessment Framework (PFMRAF) is USAID’s risk management
Risk Analysis Matrix Club Help
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
MMU Risk Analysis toolkit (v 5) Page 2 Project Role Risk Management Role Project Sponsor Ensures that risk management structures and processes are in place for the
after-the-fact analysis of a risk failure, and many are enhancing scenario analysis and tools to better assess forward non-financial risk. This is akin to a financial-risk mindset, which aims to identify credit and market risks and anticipate their effects. To spur the change, a number of banks are moving the compliance function under the risk function. • Increased accountability of
In a financial institution, enterprise risk management is normally thought of as the combination of credit risk, interest rate risk or asset liability management, liquidity risk, market risk, and operational risk.
Financial Management Act 2006. Compliance with this policy is mandatory to enhance governance and outcomes through effective and consistent risk management in and across the WA health system. 2. Scope This policy applies all Health Service Providers under the Health Services Act 20162 3. Policy statement The WA health system is committed to the management of its risks including those
Analysis for Financial Management Tenth Edition ROBERT C.HIGGINS (irmiente Keimers ot Finance The University of Washington, McGraw-Hill Irwin. Contents Preface XI PART ONE ASSESSING THE FINANCIAL HEALTH OF THE FIRM 1 Chapter 1 Interpreting Financial Statements 3 The Cash Flow Cycle 3 The Balance Sheet 6 Current Assets and Liabilities 9 Shareholders’ Equity 11 The Income …
management and fiduciary risk identification, “procurement” may be referred to as a separate system from other systems involved in PFM for clarity and precision. Public Financial Management Risk Assessment Framework (PFMRAF) is USAID’s risk management
No. 18 Public Private Partnerships Risk Management, May 2005. No. 19 Public Private Partnerships Contract Management, May 2005. iv The Financial Management Guidance series of publications Archived. Contents v Introduction 1 Section A – Overview of Cost-Benefi t Analysis 3 1. Cost-Benefi t Analysis – An Overview 4 1.1 Explanation of cost-benefi t analysis 4 1.2 What is a CBA attempting
reached on model risk management in financial institutions (which are elaborated on in the appropriate sections of this document). Model risk definition and regulations 1. The use of mathematical models by financial institutions in many areas is rapidly gaining ground. This brings significant benefits (objectivity, automation, efficiency, etc.) but also entails costs. 2. Among these costs is
First, there is traditional risk management which focuses on financial risk and manages risks in individual cases. Next, there is enterprise risk management (ERM) which
The Risk Adjusted Discount Rate is composite of discount rate which combines .V.V: and LRX In the case of N. future cash flows should be discounted using Risk Adjusted Discount Rate and then N.P. 109 . which in turn are subject to risk attitude of management.V.P. The risk adjusted discount rate is a composite rate which combines both the time and discount factors. iv) This method of
management in accordance with the Financial Accountability Act 2009, Financial and Performance Management Standard 2009 and Public Sector Ethics Act 1994. 3.2 Governance The Director-General and Department Leadership Team (DLT) members shall determine and communicate the department’s risk appetite to effectively manage and prioritise risks to meet obligations and provide oversight of risk
Risk Analysis Matrix Club Help
Analysis for Financial Management GBV
A top risk management practitioner addresses the essential aspects of modern financial risk management. In the Second Edition of Financial Risk Management Website, market risk expert Steve Allen offers an insider’s view of this discipline and covers the strategies, principles, and measurement techniques necessary to manage
after-the-fact analysis of a risk failure, and many are enhancing scenario analysis and tools to better assess forward non-financial risk. This is akin to a financial-risk mindset, which aims to identify credit and market risks and anticipate their effects. To spur the change, a number of banks are moving the compliance function under the risk function. • Increased accountability of
First, there is traditional risk management which focuses on financial risk and manages risks in individual cases. Next, there is enterprise risk management (ERM) which
formulation of the analysis theory on the basis of financial ratios, companies and entrepreneurs to calculate and use financial ratios to analyze their own business, for comparison with others in both the same business and the economy as a whole and for assessing business risks and to refer
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
Financial Management Act 2006. Compliance with this policy is mandatory to enhance governance and outcomes through effective and consistent risk management in and across the WA health system. 2. Scope This policy applies all Health Service Providers under the Health Services Act 20162 3. Policy statement The WA health system is committed to the management of its risks including those
Country risk assessment is a critical foundation for disaster risk management and related financial strategies and requires clear rules and governance. Risk assessment needs to be comprehensive and well orchestrated both within government and with
Effective financial risk management: Extract Against this background, ‘financial risk’ may broadly be thought of as adverse movements in financial price or other events that impair financial condition, financial performance or other financial outcomes. For example, financial risk may affect the adequacy of returns or accessibility to finance at reasonable cost. These characteristics have
The role of risk management in financial firms has evolved far beyond the simple insurance of identified risks, to a discipline that centres on complex econometric and financial models of uncertainty. Financial risk management has been defined by the Basel Committee (2001) as a
WA Health Risk Management Policy
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
Country risk assessment is a critical foundation for disaster risk management and related financial strategies and requires clear rules and governance. Risk assessment needs to be comprehensive and well orchestrated both within government and with
The role of risk management in financial firms has evolved far beyond the simple insurance of identified risks, to a discipline that centres on complex econometric and financial models of uncertainty. Financial risk management has been defined by the Basel Committee (2001) as a
Credit Risk Credit Analysis Seven C’s Credit Analysis Process 2. Lending Process 8. Problem LoansObjectives Introduction Credit Process Documentation Loan Pricing and Profitability Analysis Regulations 3. Financial Statement Analysis-I Objectives Introduction Ratio Analysis Liquidity Ratios Turnover Ratios Profitability Ratios Leverage Ratios Market Ratios 4. Financial Statement Analysis …
formulation of the analysis theory on the basis of financial ratios, companies and entrepreneurs to calculate and use financial ratios to analyze their own business, for comparison with others in both the same business and the economy as a whole and for assessing business risks and to refer
A top risk management practitioner addresses the essential aspects of modern financial risk management. In the Second Edition of Financial Risk Management Website, market risk expert Steve Allen offers an insider’s view of this discipline and covers the strategies, principles, and measurement techniques necessary to manage
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence designed to improve organizational performance and governance and to reduce the extent of fraud in organizations. COSO is a private-sector initiative jointly sponsored and funded by the following organizations: American Accounting Association (AAA) American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Financial
Quantitative Analysis, Risk Management, Modelling, Algo-Trading, Blockchain for Finance Financial Risk Management The most current collection of articles on Financial Risk Management and Modeling at QuantAtRisk.com:
KeywordS: organisational risk, risk analysis, risk management, organisational integrity, Supreme Audit Institution JeL codeS: D81, In public entities, the regulations of financial management and control systems were devel-oped in the course of a multiple-step process. After the legislative basis was created, the regulatory concept was developed under the influence of the coso model from
The sample risk analysis template has great benefits in risk management. In fact risk management can be made possible only when a risk analysis is done properly. Therefore you must make a proper risk analysis file. As you can see that making of a risk analysis report is not an easy affair. You have to involve and consider many important points to do that, and that is why when you are doing
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
RISK ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT The Center for ETH Z
Effective financial risk management: Extract Against this background, ‘financial risk’ may broadly be thought of as adverse movements in financial price or other events that impair financial condition, financial performance or other financial outcomes. For example, financial risk may affect the adequacy of returns or accessibility to finance at reasonable cost. These characteristics have
Quantitative Analysis, Risk Management, Modelling, Algo-Trading, Blockchain for Finance Financial Risk Management The most current collection of articles on Financial Risk Management and Modeling at QuantAtRisk.com:
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
Country risk assessment is a critical foundation for disaster risk management and related financial strategies and requires clear rules and governance. Risk assessment needs to be comprehensive and well orchestrated both within government and with
MMU Risk Analysis toolkit (v 5) Page 2 Project Role Risk Management Role Project Sponsor Ensures that risk management structures and processes are in place for the
management in accordance with the Financial Accountability Act 2009, Financial and Performance Management Standard 2009 and Public Sector Ethics Act 1994. 3.2 Governance The Director-General and Department Leadership Team (DLT) members shall determine and communicate the department’s risk appetite to effectively manage and prioritise risks to meet obligations and provide oversight of risk
Risk Assessment – The overall process of risk identification, risk analysis and risk evaluation. Risk Management – The culture, processes and structures that are directed towards realising potential
Credit Analysis KESDEE
Financial Risk Management and Modeling QuantAtRisk
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
No. 18 Public Private Partnerships Risk Management, May 2005. No. 19 Public Private Partnerships Contract Management, May 2005. iv The Financial Management Guidance series of publications Archived. Contents v Introduction 1 Section A – Overview of Cost-Benefi t Analysis 3 1. Cost-Benefi t Analysis – An Overview 4 1.1 Explanation of cost-benefi t analysis 4 1.2 What is a CBA attempting
Quantitative Analysis, Risk Management, Modelling, Algo-Trading, Blockchain for Finance Financial Risk Management The most current collection of articles on Financial Risk Management and Modeling at QuantAtRisk.com:
frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence designed to improve organizational performance and governance and to reduce the extent of fraud in organizations. COSO is a private-sector initiative jointly sponsored and funded by the following organizations: American Accounting Association (AAA) American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Financial
Effective financial risk management: Extract Against this background, ‘financial risk’ may broadly be thought of as adverse movements in financial price or other events that impair financial condition, financial performance or other financial outcomes. For example, financial risk may affect the adequacy of returns or accessibility to finance at reasonable cost. These characteristics have
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
RISK ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT The Center for ETH Z
Risk Analysis Matrix CONSEQUENCES: Insignificant No injuries, low financial loss Minor First aid treatment, on-site release immediately contained, medium
reached on model risk management in financial institutions (which are elaborated on in the appropriate sections of this document). Model risk definition and regulations 1. The use of mathematical models by financial institutions in many areas is rapidly gaining ground. This brings significant benefits (objectivity, automation, efficiency, etc.) but also entails costs. 2. Among these costs is
The Risk Adjusted Discount Rate is composite of discount rate which combines .V.V: and LRX In the case of N. future cash flows should be discounted using Risk Adjusted Discount Rate and then N.P. 109 . which in turn are subject to risk attitude of management.V.P. The risk adjusted discount rate is a composite rate which combines both the time and discount factors. iv) This method of
Credit Risk Credit Analysis Seven C’s Credit Analysis Process 2. Lending Process 8. Problem LoansObjectives Introduction Credit Process Documentation Loan Pricing and Profitability Analysis Regulations 3. Financial Statement Analysis-I Objectives Introduction Ratio Analysis Liquidity Ratios Turnover Ratios Profitability Ratios Leverage Ratios Market Ratios 4. Financial Statement Analysis …
Country risk assessment is a critical foundation for disaster risk management and related financial strategies and requires clear rules and governance. Risk assessment needs to be comprehensive and well orchestrated both within government and with
Financial Risk Management and Modeling QuantAtRisk
Risk Analysis Matrix Club Help
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
First, there is traditional risk management which focuses on financial risk and manages risks in individual cases. Next, there is enterprise risk management (ERM) which
management and fiduciary risk identification, “procurement” may be referred to as a separate system from other systems involved in PFM for clarity and precision. Public Financial Management Risk Assessment Framework (PFMRAF) is USAID’s risk management
No. 18 Public Private Partnerships Risk Management, May 2005. No. 19 Public Private Partnerships Contract Management, May 2005. iv The Financial Management Guidance series of publications Archived. Contents v Introduction 1 Section A – Overview of Cost-Benefi t Analysis 3 1. Cost-Benefi t Analysis – An Overview 4 1.1 Explanation of cost-benefi t analysis 4 1.2 What is a CBA attempting
The role of risk management in financial firms has evolved far beyond the simple insurance of identified risks, to a discipline that centres on complex econometric and financial models of uncertainty. Financial risk management has been defined by the Basel Committee (2001) as a
management in accordance with the Financial Accountability Act 2009, Financial and Performance Management Standard 2009 and Public Sector Ethics Act 1994. 3.2 Governance The Director-General and Department Leadership Team (DLT) members shall determine and communicate the department’s risk appetite to effectively manage and prioritise risks to meet obligations and provide oversight of risk
KeywordS: organisational risk, risk analysis, risk management, organisational integrity, Supreme Audit Institution JeL codeS: D81, In public entities, the regulations of financial management and control systems were devel-oped in the course of a multiple-step process. After the legislative basis was created, the regulatory concept was developed under the influence of the coso model from
In a financial institution, enterprise risk management is normally thought of as the combination of credit risk, interest rate risk or asset liability management, liquidity risk, market risk, and operational risk.
The Risk Adjusted Discount Rate is composite of discount rate which combines .V.V: and LRX In the case of N. future cash flows should be discounted using Risk Adjusted Discount Rate and then N.P. 109 . which in turn are subject to risk attitude of management.V.P. The risk adjusted discount rate is a composite rate which combines both the time and discount factors. iv) This method of
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
Analysis for Financial Management GBV
financial-management-risk-analysis-in-capital-budgeting
MMU Risk Analysis toolkit (v 5) Page 2 Project Role Risk Management Role Project Sponsor Ensures that risk management structures and processes are in place for the
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
Effective financial risk management: Extract Against this background, ‘financial risk’ may broadly be thought of as adverse movements in financial price or other events that impair financial condition, financial performance or other financial outcomes. For example, financial risk may affect the adequacy of returns or accessibility to finance at reasonable cost. These characteristics have
reached on model risk management in financial institutions (which are elaborated on in the appropriate sections of this document). Model risk definition and regulations 1. The use of mathematical models by financial institutions in many areas is rapidly gaining ground. This brings significant benefits (objectivity, automation, efficiency, etc.) but also entails costs. 2. Among these costs is
Risk Assessment – The overall process of risk identification, risk analysis and risk evaluation. Risk Management – The culture, processes and structures that are directed towards realising potential
In a financial institution, enterprise risk management is normally thought of as the combination of credit risk, interest rate risk or asset liability management, liquidity risk, market risk, and operational risk.
Risk Analysis Matrix CONSEQUENCES: Insignificant No injuries, low financial loss Minor First aid treatment, on-site release immediately contained, medium
Analysis for Financial Management Tenth Edition ROBERT C.HIGGINS (irmiente Keimers ot Finance The University of Washington, McGraw-Hill Irwin. Contents Preface XI PART ONE ASSESSING THE FINANCIAL HEALTH OF THE FIRM 1 Chapter 1 Interpreting Financial Statements 3 The Cash Flow Cycle 3 The Balance Sheet 6 Current Assets and Liabilities 9 Shareholders’ Equity 11 The Income …
after-the-fact analysis of a risk failure, and many are enhancing scenario analysis and tools to better assess forward non-financial risk. This is akin to a financial-risk mindset, which aims to identify credit and market risks and anticipate their effects. To spur the change, a number of banks are moving the compliance function under the risk function. • Increased accountability of
formulation of the analysis theory on the basis of financial ratios, companies and entrepreneurs to calculate and use financial ratios to analyze their own business, for comparison with others in both the same business and the economy as a whole and for assessing business risks and to refer
The Risk Adjusted Discount Rate is composite of discount rate which combines .V.V: and LRX In the case of N. future cash flows should be discounted using Risk Adjusted Discount Rate and then N.P. 109 . which in turn are subject to risk attitude of management.V.P. The risk adjusted discount rate is a composite rate which combines both the time and discount factors. iv) This method of
Financial Management Act 2006. Compliance with this policy is mandatory to enhance governance and outcomes through effective and consistent risk management in and across the WA health system. 2. Scope This policy applies all Health Service Providers under the Health Services Act 20162 3. Policy statement The WA health system is committed to the management of its risks including those
frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence designed to improve organizational performance and governance and to reduce the extent of fraud in organizations. COSO is a private-sector initiative jointly sponsored and funded by the following organizations: American Accounting Association (AAA) American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Financial
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
financial-management-risk-analysis-in-capital-budgeting
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
Credit Risk Credit Analysis Seven C’s Credit Analysis Process 2. Lending Process 8. Problem LoansObjectives Introduction Credit Process Documentation Loan Pricing and Profitability Analysis Regulations 3. Financial Statement Analysis-I Objectives Introduction Ratio Analysis Liquidity Ratios Turnover Ratios Profitability Ratios Leverage Ratios Market Ratios 4. Financial Statement Analysis …
management in accordance with the Financial Accountability Act 2009, Financial and Performance Management Standard 2009 and Public Sector Ethics Act 1994. 3.2 Governance The Director-General and Department Leadership Team (DLT) members shall determine and communicate the department’s risk appetite to effectively manage and prioritise risks to meet obligations and provide oversight of risk
A top risk management practitioner addresses the essential aspects of modern financial risk management. In the Second Edition of Financial Risk Management Website, market risk expert Steve Allen offers an insider’s view of this discipline and covers the strategies, principles, and measurement techniques necessary to manage
Quantitative Analysis, Risk Management, Modelling, Algo-Trading, Blockchain for Finance Financial Risk Management The most current collection of articles on Financial Risk Management and Modeling at QuantAtRisk.com:
The sample risk analysis template has great benefits in risk management. In fact risk management can be made possible only when a risk analysis is done properly. Therefore you must make a proper risk analysis file. As you can see that making of a risk analysis report is not an easy affair. You have to involve and consider many important points to do that, and that is why when you are doing
RISK ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT The Center for ETH Z
Risk Management Policy Queensland Health
Quantitative Analysis, Risk Management, Modelling, Algo-Trading, Blockchain for Finance Financial Risk Management The most current collection of articles on Financial Risk Management and Modeling at QuantAtRisk.com:
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
The sample risk analysis template has great benefits in risk management. In fact risk management can be made possible only when a risk analysis is done properly. Therefore you must make a proper risk analysis file. As you can see that making of a risk analysis report is not an easy affair. You have to involve and consider many important points to do that, and that is why when you are doing
after-the-fact analysis of a risk failure, and many are enhancing scenario analysis and tools to better assess forward non-financial risk. This is akin to a financial-risk mindset, which aims to identify credit and market risks and anticipate their effects. To spur the change, a number of banks are moving the compliance function under the risk function. • Increased accountability of
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
Financial Risk Management and Modeling QuantAtRisk
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
after-the-fact analysis of a risk failure, and many are enhancing scenario analysis and tools to better assess forward non-financial risk. This is akin to a financial-risk mindset, which aims to identify credit and market risks and anticipate their effects. To spur the change, a number of banks are moving the compliance function under the risk function. • Increased accountability of
KeywordS: organisational risk, risk analysis, risk management, organisational integrity, Supreme Audit Institution JeL codeS: D81, In public entities, the regulations of financial management and control systems were devel-oped in the course of a multiple-step process. After the legislative basis was created, the regulatory concept was developed under the influence of the coso model from
Financial Management Act 2006. Compliance with this policy is mandatory to enhance governance and outcomes through effective and consistent risk management in and across the WA health system. 2. Scope This policy applies all Health Service Providers under the Health Services Act 20162 3. Policy statement The WA health system is committed to the management of its risks including those
MMU Risk Analysis toolkit (v 5) Page 2 Project Role Risk Management Role Project Sponsor Ensures that risk management structures and processes are in place for the
The role of risk management in financial firms has evolved far beyond the simple insurance of identified risks, to a discipline that centres on complex econometric and financial models of uncertainty. Financial risk management has been defined by the Basel Committee (2001) as a
risk/return profile, economic viability, financial sustainability, development impact, and overall contribution to realization of the mission of the Bank. Portfolio risk management and investment policies page 6 of 66
In a financial institution, enterprise risk management is normally thought of as the combination of credit risk, interest rate risk or asset liability management, liquidity risk, market risk, and operational risk.
Financial Risk Management and Modeling QuantAtRisk
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
RISK ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT The Center for ETH Z
frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence designed to improve organizational performance and governance and to reduce the extent of fraud in organizations. COSO is a private-sector initiative jointly sponsored and funded by the following organizations: American Accounting Association (AAA) American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Financial
financial-management-risk-analysis-in-capital-budgeting
Risk Analysis Matrix CONSEQUENCES: Insignificant No injuries, low financial loss Minor First aid treatment, on-site release immediately contained, medium
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
Risk Analysis Matrix Club Help
Risk Management Policy Queensland Health
Analysis for Financial Management Tenth Edition ROBERT C.HIGGINS (irmiente Keimers ot Finance The University of Washington, McGraw-Hill Irwin. Contents Preface XI PART ONE ASSESSING THE FINANCIAL HEALTH OF THE FIRM 1 Chapter 1 Interpreting Financial Statements 3 The Cash Flow Cycle 3 The Balance Sheet 6 Current Assets and Liabilities 9 Shareholders’ Equity 11 The Income …
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
Financial Risk Management and Modeling QuantAtRisk
frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence designed to improve organizational performance and governance and to reduce the extent of fraud in organizations. COSO is a private-sector initiative jointly sponsored and funded by the following organizations: American Accounting Association (AAA) American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Financial
Risk Analysis and Risk Management in the Public asz
Risk Analysis 6. The risk-assessment approach is based largely on International Standard on Auditing 400 financial management, financial analysis and management accounting. In particular, few accounts staff possess practical skills beyond basic book-keeping. The impact of these skill shortages on Government operations is amplified by high demand for financial skills from the private sector
Good Practice Example–Financial Management Report
Risk Management Policy Queensland Health