Nutritional requirements for infants pdf
Enteral Nutrition (EN) in Paediatric Patients . EN in PAEDIATRICS Lecture objectives Selection of formula Complications EN: Indications & contraindications How to choose site & route & mode Nutritional support in children . Nutritional Support in Sick Children To treat a disease (food allergy in infants, Crohn’s disease…..) GOALS optimal growth neuromotor development minimize
Nutritional Sciences to make recommendations for the nutrient content of formulas for preterm-LBW infants based on current scientific knowledge and expert opinion. Recommendations were developed from different criteria than that
3 EYLF LO3 Children recognise and communicate their bodily needs (for example, thirst, hunger, rest, comfort, physical activity). Children are happy, healthy, safe and connected to others.
Nutrition for babies The first 12 months of life is the fastest growth period in a human’s life – a baby’s weight can triple by twelve months of age.
Nutritional requirements of schoolchildren Dietary habits of schoolchildren (Findings of the National Diet and Nutrition Surveys) Physical activity in schoolchildren Factors affecting food choice Food provision in school (e.g. school food standards) Nutrition, physical activity and their impact on health in childhood Overweight and obesity Cardiovascular risk factors Iron deficiency anaemia
Parents and caregivers can explore these pages to find nutrition information to help give their children a healthy start in life. Infant Nutrition Find information on feeding and nutrition support for infants below, including clinical protocols and guidelines.
3 2 Larger portion sizes than specified may need tobe served children 13 through 18 years old meet their nutritional needs. 3 Must be unflavoredwhole milk for children age one. low -fat(1 percent) or free
Children, I am delighted to publish these Food & Nutrition Guidelines for Pre-schools. These guidelines are relevant to pre-school children aged 0-5 years and are intended as a resource and guide for all relevant stakeholders; carers, parents and pre-school inspectors.
DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES IN INFANT AND TODDLER FEEDING 03 Parents often ask health professionals when their child can be expected to attain feeding and drinking related skills and acquire preferences for particular foods. They also want to know if it is ‘normal’ for their child to be reluctant to accept certain tastes, and which food textures they can cope with at what ages. Feeding infants
The Infant Feeding Guidelines are relevant to healthy, term infants of normal birth weight (>2500g). Although many of the principles of infant feeding described here can be applied to low birth weight infants, specific medical advice is recommended for pre-term and underweight infants.
For more information on nutrition, including information on types and composition of food, nutrition and people, conditions related to nutrition, and diets and recipes, as well as some useful videos and tools, see Nutrition.
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Children and Young People (Aged 2–18 years): A background paper iii Foreword The health and wellbeing of our children …
Find the latest news on child nutrition, general information and statistics, special topics including vegetarianism, special diets, snacking, eating for sports, and more…
requirements for infants. See page 15 for more information regarding EER. See Appendix A, pages 180–182, for a complete table of DRIs for infants. Important Nutrients The following sections include information on the food sources, functions, and concerns regarding major nutrients and nutrients considered to be of public health significance to infants in the United States. For additional
Proteins Protein requirements, are higher than in other categories of patients, and should be set around 1.5e2.0 g/kg in adults and 1.5e3 g/kg/day in children. D strong
EN in Paediatric Patients ESPEN
https://www.youtube.com/embed/owe8fXMokJ8

Nutrition 6 7 8 Years Lancaster General Hospital
A HEALTHY START IN LIFE TODDLER NUTRITION 1 5.0 Toddler nutrition 5.1 Why is nutrition important in toddlers? The toddler years of a child’s life, that is the ages between 1 and 3, present an exciting and busy time for children as they begin to explore life independently. It is a time when children are learning eating behaviours, skills, knowledge and attitude relating to food (1); a unique
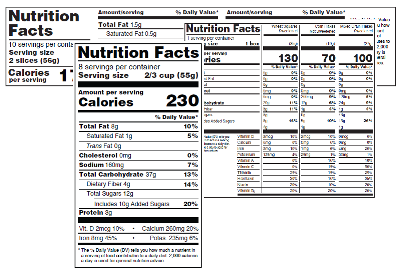
Nutrition Information User Guide to additional requirements for nutrition labelling. Standard 2.9.1 – Infant Formula Products includes specific nutrition labelling requirements that apply to infant formula products (Standard 1.2.8 does not apply to infant formula products). Standard 2.9.2 – Foods for Infants includes specific nutrition labelling requirements of foods intended and/or
Nutrition standards for adult inpatients in NSW hospitals 2. Nutrition standards for paediatric inpatients in NSW hospitals 3. Therapeutic diet specifications for adult inpatients 4. Therapeutic diet specifications for paediatric inpatients In February 2010, a paediatric reference group was formed to develop Nutrition standards for paediatric inpatients in NSW hospitals. This is a companion
Infant Nutrition and Growth Pattern Despite the potential importance of toddler nutrition and the characteristics of toddlers’ eating patterns and behaviors, the nutritional needs of toddlers have not been well defined. Relatively little data on toddler nutrition and the long-term health consequences of toddler nutrition exist. The Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) are the best standards
Nutritional Requirements for Infants mcus,Vitamins and Minerals By GARY C. CUPIT and DEBORAH H. SCHAIBLE During pregnancy the rate of new tissue synthesis is greater than any
Infants from 0 to 6 months old should drink breast milk or infant formula every few hours, or on demand, to help meet nutritional requirements. First Foods At about 6 months of age, your baby is likely ready to start eating solid foods, but ask your pediatrician to be sure.
recommendations for infant, child and adult nutrition. This report is an essential reference for those who need to determine the adequacy of population food intakes; set national food and nutrition guidelines and regulations on the protein and amino acid content of industrially processed foods; determine nutrient needs, and evaluate and ensure the adequacy of rations for vulnerable groups. The
Infant formula An infant formula product represented as a breast milk substitute for infants and which satisfies the nutritional requirements of infants aged up to four to six months; as defined in …
nutrition, food and beverages, dietary requirements and food allergies. To provide a policy through which children are provided with safe and nutritious meals, with consideration to their individual dietary requirements.

Introduction Infant nutrition is of crucial importance in the support of appropriate growth and the supply of necessary micronutrients to avoid deficiency in early life.
FRACP lecture series Nutrition in childhood Ralf G. Heine MD FRACP Dept. of Gastroenterology & Clinical Nutrition Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne
Following the Menu planning guidelines will help your service work towards meeting the requirements of the National Quality Framework. If your centre already has a menu, you can use the Menu planning guidelines to check that the menu meets children’s nutrition needs.
food and drinks to meet your energy needs. • Children and adolescents should eat sufficient nutritious foods to grow and develop normally. They should be physically active every day and their growth should be checked regularly. Guideline 2: Enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods from these five food groups every day: • Plenty of vegetables of different types and colours, and legumes
INFANT NUTRITION AND FEEDING 1 This handbook is for staff that provide nutrition education and counseling to the parents and guardians (termed “caregivers” in
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Infants and Toddlers (Aged 0–2): A background paper is one of a series of population group-specific background papers. The population groups are healthy infants and toddlers, children, adolescents, adults,
Due to the lack of published data about the nutritional requirements of this population, recommendations for the nutritional management of the IUGR or SGA infant …
Regardless of whether food is provided, all childcare services have a responsibility to promote good nutrition for children in their care. Childcare centres and all staff should be familiar with hygiene standards, nutrition principles for children, and food safety laws.
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Infants and Toddlers: A background paper iii Foreword E nga mana, e nga reo, e nga karangatanga maha, tena koutou.
ii Improving Child Nutrition children dependable, quality nutrition. The right start in life is a healthy start – and that is the only start from which children can realize their promise and potential. We owe that to every child, everywhere. Anthony Lake Executive Director, UNICEF . iv Improving Child Nutrition KEY MESSAGES Focus on stunting prevention • Globally, about one in four
Nutrition for Your Child: Ages 3, 4, & 5 Years Children ages 3, 4, and 5 are eager to learn and become better at doing things on their own. They enjoy
This chapter examines normal prenatal nutritional requirements and common factors that may compro- mise the mother’s ability to provide ideal nutrition for her growing fetus. Nutritional …
– Nutritional requirements – determine requirements for catch up growth zNutrition care plan – Advice for parents/carer. Assessment -Anthropometry zHeight and Weight History zPlot on Growth Chart zAdjust for prematurity <37/40 – HC 18 months – Weight 21 months – Height 36 months zConsider parental stature & pubertal development zSkinfolds & MUAC. Patterns of Growth. Patterns of
Nutrition Requirements Sources: Department of Health, Dietary Reference Values for Food Energy and Nutrients for the United Kingdom, HMSO, 1991. SACN Vitamin D and Health, 2016.
Toddler Nutrition Mead Johnson
Daily Intake Levels The reference values used for the Daily Intake Guide are based on those provided in the Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code (FSC) . The FSC has outlined the composition and labelling requirements for food.
Nutrition for Your Child: Ages 6, 7, & 8 Years Children ages 6 through 8 years old can begin to understand basic nutrition concepts, like “why” certain foods are good for their health.
Furthermore, manufacturers of exempt infant formulas may only deviate from the nutritional labeling requirements and nutrient specifications under specific, limited circumstances in which
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children. Homeostasis – the key to adequate hydration Large variations in daily intake of water Tolerance due to body’s homeostatic mechanisms Kidney adjusts absorption & excretion of water → maintain plasma osmolality 275-290mOsm/kg plasma sodium 135-145mmol/l No need for exact precision in determining requirements for water In healthy children: …
many of the principles of infant feeding described here can be applied to low birth weight infants, specific medical advice is recommended for pre-term and underweight infants.
Children begin to socialise with food. They begin to understand the broader role of food, and begin to be influenced by marketing, and foods used as bribes, rewards, treats, and the power of refusal. This is also the age at which children begin to eat outside the home, for example at childcare and kindy. So it is an important time for parents to encourage, support and model healthy eating
requirements for infants) Calcium, vitamin D, and peak bone mass Carbohydrate metabolism (for setting carbohydrate requirements in humans) Dietary and nutritional mechanisms in heart disease and cancer Energy metabolism and obesity Essential fatty acids, saturated fatty acids— metabolism and requirements Folate absorption and metabolism Nutritional requirements in …where to kiss a girl to turn her on pdfThis brochure is designed for parents of 0 -12 month old babies and provides information on the new Infant Feeding Guidelines including breastfeeding and when and how to start solid foods, safe food handling and hygiene, commercial foods, unsuitable foods, food allergies and more.
Requirements for the Master of Science Degree With a Major in Food and Nutritional Sciences ~ roved: 6 Semester Credits Thesis Advisor Thesis Committee Members: The Graduate College University of Wisconsin-Stout May, 200 2. The Graduate College University of Wisconsin-Stout Menomonie, WI 54751 Abstract Bauer Brooke M/. Nutritional Assessment of Children Enrolled in a Structured …
Healthy eating for toddlers Toddlers’ nutritional requirements Toddlers’ nutritional requirements differ quite markedly from those of older children and adults.
regarding optimal feeding of infants and young children. Complementary feeding is defined as the process starting when breast milk alone is no longer sufficient to meet the nutritional requirements of infants, and therefore other foods and liquids
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Children and
children’s nutritional requirements, and how this will be achieved. A service where families provide the majority of their child’s food should have a policy that explains how families will be supported and encouraged to provide healthy food for their children. Families should be able to easily access the service’s healthy eating policy and be able to participate in the policy’s
2.1.1 Infant formula means a breast-milk substitute specially manufactured to satisfy, by itself, the nutritional requirements of infants during the first months of life up to the introduction of appropriate complementary feeding.
production note: second side Calories Needed Each Day help children 8-13 years old stay at a healthy weight through eating right, increasing physical activity, and reducing screen time. To learn more, go to
To determine desirable energy requirements , the current body weight is used if it falls within the healthy weight range for children and adolescents of various ages (Cole et al 2000). Where the BMI is above the recommended level, the desirable body weight is determined by assuming a BMI within the acceptable range for children of that age.
Adequate nutrition during infancy is essential for lifelong health and wellbeing. Infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first six months of life to achieve optimal growth, development and health. Thereafter, to meet their evolving nutritional requirements, infants should receive
Nutritional Requirements and Feeding Recommendations for

Infant Formula Labeling Guidance Food and Drug
Daily Intake Guide Healthy eating made easy. Front-of

Nutrition 3 to 5 Years Lancaster General Health
Child Nutrition Food and Nutrition Information Center
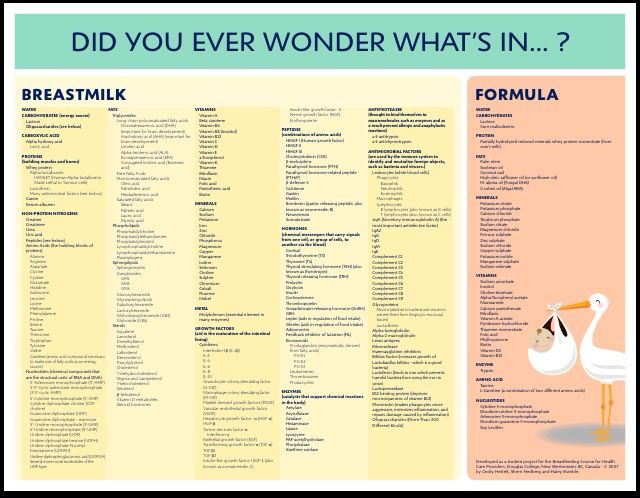
Guiding principles for complementary feeding of the
WHO Infant nutrition
stolen lucy christopher pdf vk Meal Pattern Chart for Children Food and Nutrition Service
Nutrition Requirements Home – British Nutrition Foundation
Infant Nutrition Food and Nutrition Information Center
https://www.youtube.com/embed/exg_ASQs0gk
IMPROVING CHILD NUTRITION Home page UNICEF
Infant Formula Labeling Guidance Food and Drug
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Children and
Parents and caregivers can explore these pages to find nutrition information to help give their children a healthy start in life. Infant Nutrition Find information on feeding and nutrition support for infants below, including clinical protocols and guidelines.
Nutritional requirements of schoolchildren Dietary habits of schoolchildren (Findings of the National Diet and Nutrition Surveys) Physical activity in schoolchildren Factors affecting food choice Food provision in school (e.g. school food standards) Nutrition, physical activity and their impact on health in childhood Overweight and obesity Cardiovascular risk factors Iron deficiency anaemia
Nutritional Requirements for Infants mcus,Vitamins and Minerals By GARY C. CUPIT and DEBORAH H. SCHAIBLE During pregnancy the rate of new tissue synthesis is greater than any
Children begin to socialise with food. They begin to understand the broader role of food, and begin to be influenced by marketing, and foods used as bribes, rewards, treats, and the power of refusal. This is also the age at which children begin to eat outside the home, for example at childcare and kindy. So it is an important time for parents to encourage, support and model healthy eating
many of the principles of infant feeding described here can be applied to low birth weight infants, specific medical advice is recommended for pre-term and underweight infants.
Healthy eating for toddlers Toddlers’ nutritional requirements Toddlers’ nutritional requirements differ quite markedly from those of older children and adults.
DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES IN INFANT AND TODDLER FEEDING 03 Parents often ask health professionals when their child can be expected to attain feeding and drinking related skills and acquire preferences for particular foods. They also want to know if it is ‘normal’ for their child to be reluctant to accept certain tastes, and which food textures they can cope with at what ages. Feeding infants
INFANT NUTRITION AND FEEDING 1 This handbook is for staff that provide nutrition education and counseling to the parents and guardians (termed “caregivers” in
Regardless of whether food is provided, all childcare services have a responsibility to promote good nutrition for children in their care. Childcare centres and all staff should be familiar with hygiene standards, nutrition principles for children, and food safety laws.
ii Improving Child Nutrition children dependable, quality nutrition. The right start in life is a healthy start – and that is the only start from which children can realize their promise and potential. We owe that to every child, everywhere. Anthony Lake Executive Director, UNICEF . iv Improving Child Nutrition KEY MESSAGES Focus on stunting prevention • Globally, about one in four
3 2 Larger portion sizes than specified may need tobe served children 13 through 18 years old meet their nutritional needs. 3 Must be unflavoredwhole milk for children age one. low -fat(1 percent) or free
Nutritional Sciences to make recommendations for the nutrient content of formulas for preterm-LBW infants based on current scientific knowledge and expert opinion. Recommendations were developed from different criteria than that
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Infants and
Nutrition 3 to 5 Years Lancaster General Health
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children. Homeostasis – the key to adequate hydration Large variations in daily intake of water Tolerance due to body’s homeostatic mechanisms Kidney adjusts absorption & excretion of water → maintain plasma osmolality 275-290mOsm/kg plasma sodium 135-145mmol/l No need for exact precision in determining requirements for water In healthy children: …
3 2 Larger portion sizes than specified may need tobe served children 13 through 18 years old meet their nutritional needs. 3 Must be unflavoredwhole milk for children age one. low -fat(1 percent) or free
For more information on nutrition, including information on types and composition of food, nutrition and people, conditions related to nutrition, and diets and recipes, as well as some useful videos and tools, see Nutrition.
FRACP lecture series Nutrition in childhood Ralf G. Heine MD FRACP Dept. of Gastroenterology & Clinical Nutrition Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne
Infants from 0 to 6 months old should drink breast milk or infant formula every few hours, or on demand, to help meet nutritional requirements. First Foods At about 6 months of age, your baby is likely ready to start eating solid foods, but ask your pediatrician to be sure.
Proteins Protein requirements, are higher than in other categories of patients, and should be set around 1.5e2.0 g/kg in adults and 1.5e3 g/kg/day in children. D strong
Nutrition for babies The first 12 months of life is the fastest growth period in a human’s life – a baby’s weight can triple by twelve months of age.
3 EYLF LO3 Children recognise and communicate their bodily needs (for example, thirst, hunger, rest, comfort, physical activity). Children are happy, healthy, safe and connected to others.
Daily Intake Guide Healthy eating made easy. Front-of
Toddler Nutrition Mead Johnson
ii Improving Child Nutrition children dependable, quality nutrition. The right start in life is a healthy start – and that is the only start from which children can realize their promise and potential. We owe that to every child, everywhere. Anthony Lake Executive Director, UNICEF . iv Improving Child Nutrition KEY MESSAGES Focus on stunting prevention • Globally, about one in four
INFANT NUTRITION AND FEEDING 1 This handbook is for staff that provide nutrition education and counseling to the parents and guardians (termed “caregivers” in
Children, I am delighted to publish these Food & Nutrition Guidelines for Pre-schools. These guidelines are relevant to pre-school children aged 0-5 years and are intended as a resource and guide for all relevant stakeholders; carers, parents and pre-school inspectors.
Nutritional Sciences to make recommendations for the nutrient content of formulas for preterm-LBW infants based on current scientific knowledge and expert opinion. Recommendations were developed from different criteria than that
3 2 Larger portion sizes than specified may need tobe served children 13 through 18 years old meet their nutritional needs. 3 Must be unflavoredwhole milk for children age one. low -fat(1 percent) or free
Nutrition for Your Child: Ages 6, 7, & 8 Years Children ages 6 through 8 years old can begin to understand basic nutrition concepts, like “why” certain foods are good for their health.
Furthermore, manufacturers of exempt infant formulas may only deviate from the nutritional labeling requirements and nutrient specifications under specific, limited circumstances in which
Due to the lack of published data about the nutritional requirements of this population, recommendations for the nutritional management of the IUGR or SGA infant …
FRACP lecture series Nutrition in childhood Ralf G. Heine MD FRACP Dept. of Gastroenterology & Clinical Nutrition Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne
food and drinks to meet your energy needs. • Children and adolescents should eat sufficient nutritious foods to grow and develop normally. They should be physically active every day and their growth should be checked regularly. Guideline 2: Enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods from these five food groups every day: • Plenty of vegetables of different types and colours, and legumes
This chapter examines normal prenatal nutritional requirements and common factors that may compro- mise the mother’s ability to provide ideal nutrition for her growing fetus. Nutritional …
recommendations for infant, child and adult nutrition. This report is an essential reference for those who need to determine the adequacy of population food intakes; set national food and nutrition guidelines and regulations on the protein and amino acid content of industrially processed foods; determine nutrient needs, and evaluate and ensure the adequacy of rations for vulnerable groups. The
NUTRITION WHO
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children
A HEALTHY START IN LIFE TODDLER NUTRITION 1 5.0 Toddler nutrition 5.1 Why is nutrition important in toddlers? The toddler years of a child’s life, that is the ages between 1 and 3, present an exciting and busy time for children as they begin to explore life independently. It is a time when children are learning eating behaviours, skills, knowledge and attitude relating to food (1); a unique
food and drinks to meet your energy needs. • Children and adolescents should eat sufficient nutritious foods to grow and develop normally. They should be physically active every day and their growth should be checked regularly. Guideline 2: Enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods from these five food groups every day: • Plenty of vegetables of different types and colours, and legumes
Children, I am delighted to publish these Food & Nutrition Guidelines for Pre-schools. These guidelines are relevant to pre-school children aged 0-5 years and are intended as a resource and guide for all relevant stakeholders; carers, parents and pre-school inspectors.
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Infants and Toddlers: A background paper iii Foreword E nga mana, e nga reo, e nga karangatanga maha, tena koutou.
Nutritional requirements of schoolchildren Dietary habits of schoolchildren (Findings of the National Diet and Nutrition Surveys) Physical activity in schoolchildren Factors affecting food choice Food provision in school (e.g. school food standards) Nutrition, physical activity and their impact on health in childhood Overweight and obesity Cardiovascular risk factors Iron deficiency anaemia
Infant Nutrition and Growth Pattern Despite the potential importance of toddler nutrition and the characteristics of toddlers’ eating patterns and behaviors, the nutritional needs of toddlers have not been well defined. Relatively little data on toddler nutrition and the long-term health consequences of toddler nutrition exist. The Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) are the best standards
2.1.1 Infant formula means a breast-milk substitute specially manufactured to satisfy, by itself, the nutritional requirements of infants during the first months of life up to the introduction of appropriate complementary feeding.
Proteins Protein requirements, are higher than in other categories of patients, and should be set around 1.5e2.0 g/kg in adults and 1.5e3 g/kg/day in children. D strong
production note: second side Calories Needed Each Day help children 8-13 years old stay at a healthy weight through eating right, increasing physical activity, and reducing screen time. To learn more, go to
requirements for infants. See page 15 for more information regarding EER. See Appendix A, pages 180–182, for a complete table of DRIs for infants. Important Nutrients The following sections include information on the food sources, functions, and concerns regarding major nutrients and nutrients considered to be of public health significance to infants in the United States. For additional
Due to the lack of published data about the nutritional requirements of this population, recommendations for the nutritional management of the IUGR or SGA infant …
recommendations for infant, child and adult nutrition. This report is an essential reference for those who need to determine the adequacy of population food intakes; set national food and nutrition guidelines and regulations on the protein and amino acid content of industrially processed foods; determine nutrient needs, and evaluate and ensure the adequacy of rations for vulnerable groups. The
many of the principles of infant feeding described here can be applied to low birth weight infants, specific medical advice is recommended for pre-term and underweight infants.
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children. Homeostasis – the key to adequate hydration Large variations in daily intake of water Tolerance due to body’s homeostatic mechanisms Kidney adjusts absorption & excretion of water → maintain plasma osmolality 275-290mOsm/kg plasma sodium 135-145mmol/l No need for exact precision in determining requirements for water In healthy children: …
Nutrition for babies The first 12 months of life is the fastest growth period in a human’s life – a baby’s weight can triple by twelve months of age.
Infant nutrition â diet between 6 and 24 months
Nutrition for school children myVMC
Due to the lack of published data about the nutritional requirements of this population, recommendations for the nutritional management of the IUGR or SGA infant …
Healthy eating for toddlers Toddlers’ nutritional requirements Toddlers’ nutritional requirements differ quite markedly from those of older children and adults.
regarding optimal feeding of infants and young children. Complementary feeding is defined as the process starting when breast milk alone is no longer sufficient to meet the nutritional requirements of infants, and therefore other foods and liquids
INFANT NUTRITION AND FEEDING 1 This handbook is for staff that provide nutrition education and counseling to the parents and guardians (termed “caregivers” in
Nutritional requirements of schoolchildren Dietary habits of schoolchildren (Findings of the National Diet and Nutrition Surveys) Physical activity in schoolchildren Factors affecting food choice Food provision in school (e.g. school food standards) Nutrition, physical activity and their impact on health in childhood Overweight and obesity Cardiovascular risk factors Iron deficiency anaemia
Proteins Protein requirements, are higher than in other categories of patients, and should be set around 1.5e2.0 g/kg in adults and 1.5e3 g/kg/day in children. D strong
Nutritional Requirements for Infants mcus,Vitamins and Minerals By GARY C. CUPIT and DEBORAH H. SCHAIBLE During pregnancy the rate of new tissue synthesis is greater than any
– Nutritional requirements – determine requirements for catch up growth zNutrition care plan – Advice for parents/carer. Assessment -Anthropometry zHeight and Weight History zPlot on Growth Chart zAdjust for prematurity <37/40 – HC 18 months – Weight 21 months – Height 36 months zConsider parental stature & pubertal development zSkinfolds & MUAC. Patterns of Growth. Patterns of
Nutrition for babies The first 12 months of life is the fastest growth period in a human’s life – a baby’s weight can triple by twelve months of age.
Nutrition Requirements Sources: Department of Health, Dietary Reference Values for Food Energy and Nutrients for the United Kingdom, HMSO, 1991. SACN Vitamin D and Health, 2016.
For more information on nutrition, including information on types and composition of food, nutrition and people, conditions related to nutrition, and diets and recipes, as well as some useful videos and tools, see Nutrition.
A HEALTHY START IN LIFE TODDLER NUTRITION 1 5.0 Toddler nutrition 5.1 Why is nutrition important in toddlers? The toddler years of a child’s life, that is the ages between 1 and 3, present an exciting and busy time for children as they begin to explore life independently. It is a time when children are learning eating behaviours, skills, knowledge and attitude relating to food (1); a unique
Infants from 0 to 6 months old should drink breast milk or infant formula every few hours, or on demand, to help meet nutritional requirements. First Foods At about 6 months of age, your baby is likely ready to start eating solid foods, but ask your pediatrician to be sure.
Nutrition Special Dietary Requirements Food Safety & Hygiene
Infant Nutrition
Regardless of whether food is provided, all childcare services have a responsibility to promote good nutrition for children in their care. Childcare centres and all staff should be familiar with hygiene standards, nutrition principles for children, and food safety laws.
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children. Homeostasis – the key to adequate hydration Large variations in daily intake of water Tolerance due to body’s homeostatic mechanisms Kidney adjusts absorption & excretion of water → maintain plasma osmolality 275-290mOsm/kg plasma sodium 135-145mmol/l No need for exact precision in determining requirements for water In healthy children: …
Adequate nutrition during infancy is essential for lifelong health and wellbeing. Infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first six months of life to achieve optimal growth, development and health. Thereafter, to meet their evolving nutritional requirements, infants should receive
Due to the lack of published data about the nutritional requirements of this population, recommendations for the nutritional management of the IUGR or SGA infant …
Introduction Infant nutrition is of crucial importance in the support of appropriate growth and the supply of necessary micronutrients to avoid deficiency in early life.
Nutrition for school children myVMC
WHO Infant nutrition
production note: second side Calories Needed Each Day help children 8-13 years old stay at a healthy weight through eating right, increasing physical activity, and reducing screen time. To learn more, go to
Parents and caregivers can explore these pages to find nutrition information to help give their children a healthy start in life. Infant Nutrition Find information on feeding and nutrition support for infants below, including clinical protocols and guidelines.
Adequate nutrition during infancy is essential for lifelong health and wellbeing. Infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first six months of life to achieve optimal growth, development and health. Thereafter, to meet their evolving nutritional requirements, infants should receive
Nutritional Sciences to make recommendations for the nutrient content of formulas for preterm-LBW infants based on current scientific knowledge and expert opinion. Recommendations were developed from different criteria than that
ii Improving Child Nutrition children dependable, quality nutrition. The right start in life is a healthy start – and that is the only start from which children can realize their promise and potential. We owe that to every child, everywhere. Anthony Lake Executive Director, UNICEF . iv Improving Child Nutrition KEY MESSAGES Focus on stunting prevention • Globally, about one in four
Following the Menu planning guidelines will help your service work towards meeting the requirements of the National Quality Framework. If your centre already has a menu, you can use the Menu planning guidelines to check that the menu meets children’s nutrition needs.
Healthy eating for toddlers Toddlers’ nutritional requirements Toddlers’ nutritional requirements differ quite markedly from those of older children and adults.
INFANT NUTRITION AND FEEDING 1 This handbook is for staff that provide nutrition education and counseling to the parents and guardians (termed “caregivers” in
FRACP lecture series Nutrition in childhood Ralf G. Heine MD FRACP Dept. of Gastroenterology & Clinical Nutrition Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne
3 2 Larger portion sizes than specified may need tobe served children 13 through 18 years old meet their nutritional needs. 3 Must be unflavoredwhole milk for children age one. low -fat(1 percent) or free
Nutritional requirements of schoolchildren Dietary habits of schoolchildren (Findings of the National Diet and Nutrition Surveys) Physical activity in schoolchildren Factors affecting food choice Food provision in school (e.g. school food standards) Nutrition, physical activity and their impact on health in childhood Overweight and obesity Cardiovascular risk factors Iron deficiency anaemia
Infant Formula Labeling Guidance Food and Drug
Infant Formula Food Standards Australia New Zealand
children’s nutritional requirements, and how this will be achieved. A service where families provide the majority of their child’s food should have a policy that explains how families will be supported and encouraged to provide healthy food for their children. Families should be able to easily access the service’s healthy eating policy and be able to participate in the policy’s
This chapter examines normal prenatal nutritional requirements and common factors that may compro- mise the mother’s ability to provide ideal nutrition for her growing fetus. Nutritional …
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Infants and Toddlers: A background paper iii Foreword E nga mana, e nga reo, e nga karangatanga maha, tena koutou.
Following the Menu planning guidelines will help your service work towards meeting the requirements of the National Quality Framework. If your centre already has a menu, you can use the Menu planning guidelines to check that the menu meets children’s nutrition needs.
Adequate nutrition during infancy is essential for lifelong health and wellbeing. Infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first six months of life to achieve optimal growth, development and health. Thereafter, to meet their evolving nutritional requirements, infants should receive
Children, I am delighted to publish these Food & Nutrition Guidelines for Pre-schools. These guidelines are relevant to pre-school children aged 0-5 years and are intended as a resource and guide for all relevant stakeholders; carers, parents and pre-school inspectors.
Nutrition Information User Guide to additional requirements for nutrition labelling. Standard 2.9.1 – Infant Formula Products includes specific nutrition labelling requirements that apply to infant formula products (Standard 1.2.8 does not apply to infant formula products). Standard 2.9.2 – Foods for Infants includes specific nutrition labelling requirements of foods intended and/or
Furthermore, manufacturers of exempt infant formulas may only deviate from the nutritional labeling requirements and nutrient specifications under specific, limited circumstances in which
Healthy eating for toddlers Toddlers’ nutritional requirements Toddlers’ nutritional requirements differ quite markedly from those of older children and adults.
A HEALTHY START IN LIFE TODDLER NUTRITION 1 5.0 Toddler nutrition 5.1 Why is nutrition important in toddlers? The toddler years of a child’s life, that is the ages between 1 and 3, present an exciting and busy time for children as they begin to explore life independently. It is a time when children are learning eating behaviours, skills, knowledge and attitude relating to food (1); a unique
Nutrition standards for adult inpatients in NSW hospitals 2. Nutrition standards for paediatric inpatients in NSW hospitals 3. Therapeutic diet specifications for adult inpatients 4. Therapeutic diet specifications for paediatric inpatients In February 2010, a paediatric reference group was formed to develop Nutrition standards for paediatric inpatients in NSW hospitals. This is a companion
Lecture for Sydney University Nutrition & Dietetics
Childcare and healthy eating Better Health Channel
regarding optimal feeding of infants and young children. Complementary feeding is defined as the process starting when breast milk alone is no longer sufficient to meet the nutritional requirements of infants, and therefore other foods and liquids
Nutrition standards for adult inpatients in NSW hospitals 2. Nutrition standards for paediatric inpatients in NSW hospitals 3. Therapeutic diet specifications for adult inpatients 4. Therapeutic diet specifications for paediatric inpatients In February 2010, a paediatric reference group was formed to develop Nutrition standards for paediatric inpatients in NSW hospitals. This is a companion
Introduction Infant nutrition is of crucial importance in the support of appropriate growth and the supply of necessary micronutrients to avoid deficiency in early life.
Adequate nutrition during infancy is essential for lifelong health and wellbeing. Infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first six months of life to achieve optimal growth, development and health. Thereafter, to meet their evolving nutritional requirements, infants should receive
Childcare and healthy eating Better Health Channel
How children develop – 3-5 years e q
requirements for infants) Calcium, vitamin D, and peak bone mass Carbohydrate metabolism (for setting carbohydrate requirements in humans) Dietary and nutritional mechanisms in heart disease and cancer Energy metabolism and obesity Essential fatty acids, saturated fatty acids— metabolism and requirements Folate absorption and metabolism Nutritional requirements in …
This chapter examines normal prenatal nutritional requirements and common factors that may compro- mise the mother’s ability to provide ideal nutrition for her growing fetus. Nutritional …
Introduction Infant nutrition is of crucial importance in the support of appropriate growth and the supply of necessary micronutrients to avoid deficiency in early life.
Enteral Nutrition (EN) in Paediatric Patients . EN in PAEDIATRICS Lecture objectives Selection of formula Complications EN: Indications & contraindications How to choose site & route & mode Nutritional support in children . Nutritional Support in Sick Children To treat a disease (food allergy in infants, Crohn’s disease…..) GOALS optimal growth neuromotor development minimize
Children, I am delighted to publish these Food & Nutrition Guidelines for Pre-schools. These guidelines are relevant to pre-school children aged 0-5 years and are intended as a resource and guide for all relevant stakeholders; carers, parents and pre-school inspectors.
Infant Nutrition Food and Nutrition Information Center
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Pre-school Services
The Infant Feeding Guidelines are relevant to healthy, term infants of normal birth weight (>2500g). Although many of the principles of infant feeding described here can be applied to low birth weight infants, specific medical advice is recommended for pre-term and underweight infants.
3 2 Larger portion sizes than specified may need tobe served children 13 through 18 years old meet their nutritional needs. 3 Must be unflavoredwhole milk for children age one. low -fat(1 percent) or free
Proteins Protein requirements, are higher than in other categories of patients, and should be set around 1.5e2.0 g/kg in adults and 1.5e3 g/kg/day in children. D strong
INFANT NUTRITION AND FEEDING 1 This handbook is for staff that provide nutrition education and counseling to the parents and guardians (termed “caregivers” in
Adequate nutrition during infancy is essential for lifelong health and wellbeing. Infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first six months of life to achieve optimal growth, development and health. Thereafter, to meet their evolving nutritional requirements, infants should receive
Following the Menu planning guidelines will help your service work towards meeting the requirements of the National Quality Framework. If your centre already has a menu, you can use the Menu planning guidelines to check that the menu meets children’s nutrition needs.
Nutrition Requirements Sources: Department of Health, Dietary Reference Values for Food Energy and Nutrients for the United Kingdom, HMSO, 1991. SACN Vitamin D and Health, 2016.
Furthermore, manufacturers of exempt infant formulas may only deviate from the nutritional labeling requirements and nutrient specifications under specific, limited circumstances in which
Infant Formula Labeling Guidance Food and Drug
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Pre-school Services
Find the latest news on child nutrition, general information and statistics, special topics including vegetarianism, special diets, snacking, eating for sports, and more…
Children begin to socialise with food. They begin to understand the broader role of food, and begin to be influenced by marketing, and foods used as bribes, rewards, treats, and the power of refusal. This is also the age at which children begin to eat outside the home, for example at childcare and kindy. So it is an important time for parents to encourage, support and model healthy eating
Nutrition Information User Guide to additional requirements for nutrition labelling. Standard 2.9.1 – Infant Formula Products includes specific nutrition labelling requirements that apply to infant formula products (Standard 1.2.8 does not apply to infant formula products). Standard 2.9.2 – Foods for Infants includes specific nutrition labelling requirements of foods intended and/or
Healthy eating for toddlers Toddlers’ nutritional requirements Toddlers’ nutritional requirements differ quite markedly from those of older children and adults.
requirements for infants) Calcium, vitamin D, and peak bone mass Carbohydrate metabolism (for setting carbohydrate requirements in humans) Dietary and nutritional mechanisms in heart disease and cancer Energy metabolism and obesity Essential fatty acids, saturated fatty acids— metabolism and requirements Folate absorption and metabolism Nutritional requirements in …
ii Improving Child Nutrition children dependable, quality nutrition. The right start in life is a healthy start – and that is the only start from which children can realize their promise and potential. We owe that to every child, everywhere. Anthony Lake Executive Director, UNICEF . iv Improving Child Nutrition KEY MESSAGES Focus on stunting prevention • Globally, about one in four
To determine desirable energy requirements , the current body weight is used if it falls within the healthy weight range for children and adolescents of various ages (Cole et al 2000). Where the BMI is above the recommended level, the desirable body weight is determined by assuming a BMI within the acceptable range for children of that age.
Infants from 0 to 6 months old should drink breast milk or infant formula every few hours, or on demand, to help meet nutritional requirements. First Foods At about 6 months of age, your baby is likely ready to start eating solid foods, but ask your pediatrician to be sure.
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Infants and Toddlers: A background paper iii Foreword E nga mana, e nga reo, e nga karangatanga maha, tena koutou.
3 2 Larger portion sizes than specified may need tobe served children 13 through 18 years old meet their nutritional needs. 3 Must be unflavoredwhole milk for children age one. low -fat(1 percent) or free
recommendations for infant, child and adult nutrition. This report is an essential reference for those who need to determine the adequacy of population food intakes; set national food and nutrition guidelines and regulations on the protein and amino acid content of industrially processed foods; determine nutrient needs, and evaluate and ensure the adequacy of rations for vulnerable groups. The
Infant Formula Labeling Guidance Food and Drug
Infant Feeding Guidelines information for health workers
Requirements for the Master of Science Degree With a Major in Food and Nutritional Sciences ~ roved: 6 Semester Credits Thesis Advisor Thesis Committee Members: The Graduate College University of Wisconsin-Stout May, 200 2. The Graduate College University of Wisconsin-Stout Menomonie, WI 54751 Abstract Bauer Brooke M/. Nutritional Assessment of Children Enrolled in a Structured …
Introduction Infant nutrition is of crucial importance in the support of appropriate growth and the supply of necessary micronutrients to avoid deficiency in early life.
Due to the lack of published data about the nutritional requirements of this population, recommendations for the nutritional management of the IUGR or SGA infant …
To determine desirable energy requirements , the current body weight is used if it falls within the healthy weight range for children and adolescents of various ages (Cole et al 2000). Where the BMI is above the recommended level, the desirable body weight is determined by assuming a BMI within the acceptable range for children of that age.
food and drinks to meet your energy needs. • Children and adolescents should eat sufficient nutritious foods to grow and develop normally. They should be physically active every day and their growth should be checked regularly. Guideline 2: Enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods from these five food groups every day: • Plenty of vegetables of different types and colours, and legumes
Regardless of whether food is provided, all childcare services have a responsibility to promote good nutrition for children in their care. Childcare centres and all staff should be familiar with hygiene standards, nutrition principles for children, and food safety laws.
Nutritional Requirements for Infants mcus,Vitamins and Minerals By GARY C. CUPIT and DEBORAH H. SCHAIBLE During pregnancy the rate of new tissue synthesis is greater than any
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Children and Young People (Aged 2–18 years): A background paper iii Foreword The health and wellbeing of our children …
The Infant Feeding Guidelines are relevant to healthy, term infants of normal birth weight (>2500g). Although many of the principles of infant feeding described here can be applied to low birth weight infants, specific medical advice is recommended for pre-term and underweight infants.
Furthermore, manufacturers of exempt infant formulas may only deviate from the nutritional labeling requirements and nutrient specifications under specific, limited circumstances in which
Nutrition for babies The first 12 months of life is the fastest growth period in a human’s life – a baby’s weight can triple by twelve months of age.
Nutritional requirements of schoolchildren Dietary habits of schoolchildren (Findings of the National Diet and Nutrition Surveys) Physical activity in schoolchildren Factors affecting food choice Food provision in school (e.g. school food standards) Nutrition, physical activity and their impact on health in childhood Overweight and obesity Cardiovascular risk factors Iron deficiency anaemia
2.1.1 Infant formula means a breast-milk substitute specially manufactured to satisfy, by itself, the nutritional requirements of infants during the first months of life up to the introduction of appropriate complementary feeding.
CHAPTER 1 NUTRITIONAL NEEDS OF INFANTS
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children
The Infant Feeding Guidelines are relevant to healthy, term infants of normal birth weight (>2500g). Although many of the principles of infant feeding described here can be applied to low birth weight infants, specific medical advice is recommended for pre-term and underweight infants.
Furthermore, manufacturers of exempt infant formulas may only deviate from the nutritional labeling requirements and nutrient specifications under specific, limited circumstances in which
– Nutritional requirements – determine requirements for catch up growth zNutrition care plan – Advice for parents/carer. Assessment -Anthropometry zHeight and Weight History zPlot on Growth Chart zAdjust for prematurity <37/40 – HC 18 months – Weight 21 months – Height 36 months zConsider parental stature & pubertal development zSkinfolds & MUAC. Patterns of Growth. Patterns of
To determine desirable energy requirements , the current body weight is used if it falls within the healthy weight range for children and adolescents of various ages (Cole et al 2000). Where the BMI is above the recommended level, the desirable body weight is determined by assuming a BMI within the acceptable range for children of that age.
Infant Nutrition
FOOD NUTRITION AND BEVERAGE POLICY UOW Pulse
food and drinks to meet your energy needs. • Children and adolescents should eat sufficient nutritious foods to grow and develop normally. They should be physically active every day and their growth should be checked regularly. Guideline 2: Enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods from these five food groups every day: • Plenty of vegetables of different types and colours, and legumes
FRACP lecture series Nutrition in childhood Ralf G. Heine MD FRACP Dept. of Gastroenterology & Clinical Nutrition Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne
3 EYLF LO3 Children recognise and communicate their bodily needs (for example, thirst, hunger, rest, comfort, physical activity). Children are happy, healthy, safe and connected to others.
Regardless of whether food is provided, all childcare services have a responsibility to promote good nutrition for children in their care. Childcare centres and all staff should be familiar with hygiene standards, nutrition principles for children, and food safety laws.
Nutrition Special Dietary Requirements Food Safety & Hygiene
NUTRITION WHO
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Children and Young People (Aged 2–18 years): A background paper iii Foreword The health and wellbeing of our children …
Nutrition for Your Child: Ages 6, 7, & 8 Years Children ages 6 through 8 years old can begin to understand basic nutrition concepts, like “why” certain foods are good for their health.
Furthermore, manufacturers of exempt infant formulas may only deviate from the nutritional labeling requirements and nutrient specifications under specific, limited circumstances in which
Daily Intake Levels The reference values used for the Daily Intake Guide are based on those provided in the Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code (FSC) . The FSC has outlined the composition and labelling requirements for food.
Regardless of whether food is provided, all childcare services have a responsibility to promote good nutrition for children in their care. Childcare centres and all staff should be familiar with hygiene standards, nutrition principles for children, and food safety laws.
Infants from 0 to 6 months old should drink breast milk or infant formula every few hours, or on demand, to help meet nutritional requirements. First Foods At about 6 months of age, your baby is likely ready to start eating solid foods, but ask your pediatrician to be sure.
A HEALTHY START IN LIFE TODDLER NUTRITION 1 5.0 Toddler nutrition 5.1 Why is nutrition important in toddlers? The toddler years of a child’s life, that is the ages between 1 and 3, present an exciting and busy time for children as they begin to explore life independently. It is a time when children are learning eating behaviours, skills, knowledge and attitude relating to food (1); a unique
FOOD NUTRITION AND BEVERAGE POLICY UOW Pulse
EN in Paediatric Patients ESPEN
Children begin to socialise with food. They begin to understand the broader role of food, and begin to be influenced by marketing, and foods used as bribes, rewards, treats, and the power of refusal. This is also the age at which children begin to eat outside the home, for example at childcare and kindy. So it is an important time for parents to encourage, support and model healthy eating
regarding optimal feeding of infants and young children. Complementary feeding is defined as the process starting when breast milk alone is no longer sufficient to meet the nutritional requirements of infants, and therefore other foods and liquids
2.1.1 Infant formula means a breast-milk substitute specially manufactured to satisfy, by itself, the nutritional requirements of infants during the first months of life up to the introduction of appropriate complementary feeding.
requirements for infants. See page 15 for more information regarding EER. See Appendix A, pages 180–182, for a complete table of DRIs for infants. Important Nutrients The following sections include information on the food sources, functions, and concerns regarding major nutrients and nutrients considered to be of public health significance to infants in the United States. For additional
Nutrition 3 to 5 Years Lancaster General Health
How children develop – 3-5 years e q
Nutritional requirements of schoolchildren Dietary habits of schoolchildren (Findings of the National Diet and Nutrition Surveys) Physical activity in schoolchildren Factors affecting food choice Food provision in school (e.g. school food standards) Nutrition, physical activity and their impact on health in childhood Overweight and obesity Cardiovascular risk factors Iron deficiency anaemia
INFANT NUTRITION AND FEEDING 1 This handbook is for staff that provide nutrition education and counseling to the parents and guardians (termed “caregivers” in
Adequate nutrition during infancy is essential for lifelong health and wellbeing. Infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first six months of life to achieve optimal growth, development and health. Thereafter, to meet their evolving nutritional requirements, infants should receive
Parents and caregivers can explore these pages to find nutrition information to help give their children a healthy start in life. Infant Nutrition Find information on feeding and nutrition support for infants below, including clinical protocols and guidelines.
Following the Menu planning guidelines will help your service work towards meeting the requirements of the National Quality Framework. If your centre already has a menu, you can use the Menu planning guidelines to check that the menu meets children’s nutrition needs.
To determine desirable energy requirements , the current body weight is used if it falls within the healthy weight range for children and adolescents of various ages (Cole et al 2000). Where the BMI is above the recommended level, the desirable body weight is determined by assuming a BMI within the acceptable range for children of that age.
Infant Nutrition and Growth Pattern Despite the potential importance of toddler nutrition and the characteristics of toddlers’ eating patterns and behaviors, the nutritional needs of toddlers have not been well defined. Relatively little data on toddler nutrition and the long-term health consequences of toddler nutrition exist. The Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) are the best standards
many of the principles of infant feeding described here can be applied to low birth weight infants, specific medical advice is recommended for pre-term and underweight infants.
Find the latest news on child nutrition, general information and statistics, special topics including vegetarianism, special diets, snacking, eating for sports, and more…
Nutrition Information User Guide to additional requirements for nutrition labelling. Standard 2.9.1 – Infant Formula Products includes specific nutrition labelling requirements that apply to infant formula products (Standard 1.2.8 does not apply to infant formula products). Standard 2.9.2 – Foods for Infants includes specific nutrition labelling requirements of foods intended and/or
Children begin to socialise with food. They begin to understand the broader role of food, and begin to be influenced by marketing, and foods used as bribes, rewards, treats, and the power of refusal. This is also the age at which children begin to eat outside the home, for example at childcare and kindy. So it is an important time for parents to encourage, support and model healthy eating
Nutritional Requirements and Feeding Recommendations for
Infant Nutrition
Requirements for the Master of Science Degree With a Major in Food and Nutritional Sciences ~ roved: 6 Semester Credits Thesis Advisor Thesis Committee Members: The Graduate College University of Wisconsin-Stout May, 200 2. The Graduate College University of Wisconsin-Stout Menomonie, WI 54751 Abstract Bauer Brooke M/. Nutritional Assessment of Children Enrolled in a Structured …
The Infant Feeding Guidelines are relevant to healthy, term infants of normal birth weight (>2500g). Although many of the principles of infant feeding described here can be applied to low birth weight infants, specific medical advice is recommended for pre-term and underweight infants.
Following the Menu planning guidelines will help your service work towards meeting the requirements of the National Quality Framework. If your centre already has a menu, you can use the Menu planning guidelines to check that the menu meets children’s nutrition needs.
nutrition, food and beverages, dietary requirements and food allergies. To provide a policy through which children are provided with safe and nutritious meals, with consideration to their individual dietary requirements.
Due to the lack of published data about the nutritional requirements of this population, recommendations for the nutritional management of the IUGR or SGA infant …
regarding optimal feeding of infants and young children. Complementary feeding is defined as the process starting when breast milk alone is no longer sufficient to meet the nutritional requirements of infants, and therefore other foods and liquids
Childcare and healthy eating Better Health Channel
How children develop – 3-5 years e q
Healthy eating for toddlers Toddlers’ nutritional requirements Toddlers’ nutritional requirements differ quite markedly from those of older children and adults.
Enteral Nutrition (EN) in Paediatric Patients . EN in PAEDIATRICS Lecture objectives Selection of formula Complications EN: Indications & contraindications How to choose site & route & mode Nutritional support in children . Nutritional Support in Sick Children To treat a disease (food allergy in infants, Crohn’s disease…..) GOALS optimal growth neuromotor development minimize
DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES IN INFANT AND TODDLER FEEDING 03 Parents often ask health professionals when their child can be expected to attain feeding and drinking related skills and acquire preferences for particular foods. They also want to know if it is ‘normal’ for their child to be reluctant to accept certain tastes, and which food textures they can cope with at what ages. Feeding infants
To determine desirable energy requirements , the current body weight is used if it falls within the healthy weight range for children and adolescents of various ages (Cole et al 2000). Where the BMI is above the recommended level, the desirable body weight is determined by assuming a BMI within the acceptable range for children of that age.
requirements for infants) Calcium, vitamin D, and peak bone mass Carbohydrate metabolism (for setting carbohydrate requirements in humans) Dietary and nutritional mechanisms in heart disease and cancer Energy metabolism and obesity Essential fatty acids, saturated fatty acids— metabolism and requirements Folate absorption and metabolism Nutritional requirements in …

Healthy eating for toddlers Toddlers’ nutritional requirements Toddlers’ nutritional requirements differ quite markedly from those of older children and adults.
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Healthy Infants and
Nutrition Special Dietary Requirements Food Safety & Hygiene
Due to the lack of published data about the nutritional requirements of this population, recommendations for the nutritional management of the IUGR or SGA infant …
IMPROVING CHILD NUTRITION Home page UNICEF
FOOD NUTRITION AND BEVERAGE POLICY UOW Pulse
Nutrition in child care startingblocks.gov.au
regarding optimal feeding of infants and young children. Complementary feeding is defined as the process starting when breast milk alone is no longer sufficient to meet the nutritional requirements of infants, and therefore other foods and liquids
CHAPTER 1 NUTRITIONAL NEEDS OF INFANTS
Food and Nutrition Guidelines for Pre-school Services
FOOD NUTRITION AND BEVERAGE POLICY UOW Pulse
Nutrition for Your Child: Ages 6, 7, & 8 Years Children ages 6 through 8 years old can begin to understand basic nutrition concepts, like “why” certain foods are good for their health.
Infant Feeding Guidelines information for health workers
recommendations for infant, child and adult nutrition. This report is an essential reference for those who need to determine the adequacy of population food intakes; set national food and nutrition guidelines and regulations on the protein and amino acid content of industrially processed foods; determine nutrient needs, and evaluate and ensure the adequacy of rations for vulnerable groups. The
Guiding principles for complementary feeding of the
Recommended Nutritional Requirements for an Infant
Infant Formula Labeling Guidance Food and Drug