Taylor series expansion examples pdf
Taylor’s Series of sin x In order to use Taylor’s formula to find the power series expansion of sin x we have to compute the derivatives of sin(x):
Taylor Series Expansion Example 1 – Taylor Series Expansion Solve the following differential equation using Taylor™s series expansion: The higher-order derivative can be obtained as follows: =3×2 such that y =1 at x =1 dx dy 6 6 0 for 4 3 3 2 2 = = = n ≥ dx d y dx d y x dx d x n n 1 1 0 0 = = y x. 5 ‘ Assakkaf Slide No. 29 Ł A. J. Clark School of Engineering Ł Department of Civil and
Maclaurin and Taylor Series 16.5 Introduction In this Section we examine how functions may be expressed in terms of power series. This is an
4 Theory of Matrix Functions Finally, we explain how (1.4) can be obtained from Taylor series considerations. In (1.2b) write Jk= λkI+Nk∈Cmk×mk, where Nkis zero except for a superdiagonal
Taylor’s series expansion. Concrete examples in the physical science division and various engineering fields are used to paint the applications pointed out. INTRODUCTION Taylors series is an expansion of a function into an infinite series of a variable x or into a finite series plus a remainder term[1]. The coefficients of the expansion or of the subsequent terms of the series involve the
2.5 aTylor Series, Intro In basically every scienti c eld, we need to approximate things. aylorT Series are the most basic and one of the most useful ways of approximating functions.
connected. But sometimes (very important in practice) the analytic continuation leads to a multivalued function. Simple example: imagine power series expansions
Taylor polynomial is an essential concept in understanding numerical methods. Examples abound and include finding accuracy of divided difference approximation of derivatives and forming the basis for Romberg method of numerical integration.
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 + x + x 2 2! + x 3 3! + x 4 4! + x 5 5! +
Math 142: Taylor Series Proof Example To show that a function has a power series expansion, it is generally easier to show that it is equal to its
For such an expansion to be valid, we assume that f(x) has two continuous derivatives. The Taylor expansion (5.2) means that we can now replace the approximation (5.1) with 1
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series EXAMPLE 4.1 Taylor Series Approximation of a Polynomial Problem Statement. Use zero- through fourth-order T aylor series expansions to approx- imate the function f(x) =−0.1×4 −0.15×3 −0.5×2 −0.25x +1.2 from x i = 0 with h = 1. That is, predict the function’s value at x i+1 = 1. Solution. Because we are dealing with a known function, we can
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series Notes by W.B. von Schlippe, October 2003 It is frequently useful to represent functions by power series.
The procedure introduced is based on the Taylor series expansion and on knowledge of nominal system trajectories and nominal system inputs. We will start with a simple scalar first-order nonlinear dynamic system Assume that under usual working circumstances this system operates along the trajectory while it is driven by the system input . We call and, respectively, the nominal system
cos(x), ex,ln(x), etc. Table 4.1 gives several of the common Taylor series expansions. The partial sums can be accumulated until an approximation to the …
Example 3. Show that the Taylor series centered at x 0 for ex converges to ex for all values of x. Solution. We want to show that for fixed x, R n x 0 as n . The Remainder Theorem shows that R n x ex T n x ec n 1 ! xn 1 for some c between 0 and x (here we used the fact that the n 1st derivative of ex is ex itself). We have to be a little careful here about giving a bound for e c, since the
Math 142 Taylor Series Proof Example
https://www.youtube.com/embed/OADFAVC9EgQ
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series spbu.ru
Example Find the McLaurin Series of the function f(x) = sinx. Find the radius of convergence of this series. Example Find the Taylor series expansion of the function f(x) = ex at a = 1.
Lecture 36: Examples of Taylor Series Dan Sloughter Furman University Mathematics 39 May 6, 2004 36.1 Examples of Taylor series Example 36.1. Let f(z) = ez.
2.2 Power series expansions of the standard functions The elementary functions of mathematics all have power series expansions which can be derived using Taylor’s theorem and which can be found in the mathematics data book.
Using 0th order Taylor series: ex ˇ1 does not give a good fit. Using 1 st order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 +x gives a better fit. Using 2 nd order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 +x +x 2 =2 gives a a really
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
260 10 The Taylor Series and Its Applications f(x) ≈ n j=0 f(j)(a) (x−a)j j! (10.9) Example 10.1 Finding the Taylor expansion of a polynomial function is pointless
28/09/2015 · this video lecture “Taylor’s expansion theorem and problem in Hindi” will help students to understand: 1. Proof of theorem 2. Importance of theorem 3. …
Example: Fourier series is a special case of a Laurent series! Suppose that we have a function f(z) which is analytic over some annulus D containing the circle C(0,1).
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
Using the Taylor series Example Find the Taylor series of f (x) = ex2 centered at a = 0. Solution: We use the Taylor series ey = X∞ n=0 yn n! for y = x2,
Chapter 12 Taylor series 12.1 Introduction The topic of this chapter is find approximations of functions in terms of power series, also called Taylor series.
derivatives of a power series can also be seen as ingredients of the series itself. This is the statement This is the statement of the following Taylor 1 series expansion.
Higher-Order Derivatives and Taylor’s Formula in Several Variables G. B. Folland Traditional notations for partial derivatives become rather cumbersome for derivatives
In calculus, Taylor’s theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite-order truncations of its Taylor series , which completely determines the function in some neighborhood of the point.
example, the function has no Taylor series, since 0 B œ “ÎB 0 !a b a b is undefined. In general, any In general, any function for which is undefined for some will fai0 ! 8 a b8 a b l to be analytic.
ject of Taylor series and power series. Warning. Be prepared to prove any of these things during the exam. Things you should memorize: • the formula of the Taylor series of a given function f(x) • geometric series (i.e. the Taylor expansion of 1 1−x) • the Taylor expansions of the functions ex,sinx,cosx,ln(1 + x) and range of va-lidity. • the relation f(x) = P n(x)+R n(x) and
Physics 116A Winter 2011 Taylor Series Expansions In this short note, a list of well-known Taylor series expansions is provided. We focus on Taylor series about the point x = 0, the so-called Maclaurin series.
Example.In this example, we find the third order Taylor expansion of f(x,y) = e2xsin(3y) about (x 0 ,y 0 ) = (0,0) in two different ways. The first way uses the canned formula.
•Recall the Taylor series representation of the function f: 3 f (z)= k=0 c k z k •Under what conditions does the Taylor series converge? •Consider z inside the open unit disk
https://www.youtube.com/embed/OZAZImytcXE
FUNCTIONS AND SERIES APPROXIMATION
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
Taylor series example If Archimedes were to quote Taylor’s theorem, he would have said, “ Give me the value of the function and the value of all (first, second, and so on) its derivatives at a single point, and I can give you the value of the function at any other point ”.the entertainer piano music pdf
Taylor series example – The Numerical Methods Guy
Lecture 32 Taylor Series and McLaurin series nd.edu
Maclaurin and Taylor ASK Academic Skills
https://www.youtube.com/embed/3d6DsjIBzJ4
Warning. Mathematics Johns Hopkins University
Lecture 36 Examples of Taylor Series Furman University
#5 Taylor Series Expansions Approximations and Error
https://www.youtube.com/embed/cjPoEZ0I5wQ
Taylor series expansion Math Is Fun
Taylor’s Series of sin x MIT OpenCourseWare
translate file pdf di android Taylor’s expansion theorem and problems in hindi YouTube
2.5 aTylor Series Intro math.wisc.edu
Taylor and Laurent Series hsrm-mathematik.de
Lesson 7 Taylor series University of Sydney
#5 Taylor Series Expansions Approximations and Error
Warning. Mathematics Johns Hopkins University
ject of Taylor series and power series. Warning. Be prepared to prove any of these things during the exam. Things you should memorize: • the formula of the Taylor series of a given function f(x) • geometric series (i.e. the Taylor expansion of 1 1−x) • the Taylor expansions of the functions ex,sinx,cosx,ln(1 x) and range of va-lidity. • the relation f(x) = P n(x) R n(x) and
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series Notes by W.B. von Schlippe, October 2003 It is frequently useful to represent functions by power series.
The procedure introduced is based on the Taylor series expansion and on knowledge of nominal system trajectories and nominal system inputs. We will start with a simple scalar first-order nonlinear dynamic system Assume that under usual working circumstances this system operates along the trajectory while it is driven by the system input . We call and, respectively, the nominal system
28/09/2015 · this video lecture “Taylor’s expansion theorem and problem in Hindi” will help students to understand: 1. Proof of theorem 2. Importance of theorem 3. …
2.5 aTylor Series, Intro In basically every scienti c eld, we need to approximate things. aylorT Series are the most basic and one of the most useful ways of approximating functions.
Example Find the McLaurin Series of the function f(x) = sinx. Find the radius of convergence of this series. Example Find the Taylor series expansion of the function f(x) = ex at a = 1.
Taylor Series Expansion Example 1 – Taylor Series Expansion Solve the following differential equation using Taylor™s series expansion: The higher-order derivative can be obtained as follows: =3×2 such that y =1 at x =1 dx dy 6 6 0 for 4 3 3 2 2 = = = n ≥ dx d y dx d y x dx d x n n 1 1 0 0 = = y x. 5 ‘ Assakkaf Slide No. 29 Ł A. J. Clark School of Engineering Ł Department of Civil and
•Recall the Taylor series representation of the function f: 3 f (z)= k=0 c k z k •Under what conditions does the Taylor series converge? •Consider z inside the open unit disk
Taylor’s Series of sin x In order to use Taylor’s formula to find the power series expansion of sin x we have to compute the derivatives of sin(x):
cos(x), ex,ln(x), etc. Table 4.1 gives several of the common Taylor series expansions. The partial sums can be accumulated until an approximation to the …
Math 142: Taylor Series Proof Example To show that a function has a power series expansion, it is generally easier to show that it is equal to its
Using the Taylor series Example Find the Taylor series of f (x) = ex2 centered at a = 0. Solution: We use the Taylor series ey = X∞ n=0 yn n! for y = x2,
Example 3. Show that the Taylor series centered at x 0 for ex converges to ex for all values of x. Solution. We want to show that for fixed x, R n x 0 as n . The Remainder Theorem shows that R n x ex T n x ec n 1 ! xn 1 for some c between 0 and x (here we used the fact that the n 1st derivative of ex is ex itself). We have to be a little careful here about giving a bound for e c, since the
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series spbu.ru
8.6 Linearization of Nonlinear Systems nonlinear
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
In calculus, Taylor’s theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite-order truncations of its Taylor series , which completely determines the function in some neighborhood of the point.
Maclaurin and Taylor Series 16.5 Introduction In this Section we examine how functions may be expressed in terms of power series. This is an
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
Taylor’s series expansion. Concrete examples in the physical science division and various engineering fields are used to paint the applications pointed out. INTRODUCTION Taylors series is an expansion of a function into an infinite series of a variable x or into a finite series plus a remainder term[1]. The coefficients of the expansion or of the subsequent terms of the series involve the
Math 142: Taylor Series Proof Example To show that a function has a power series expansion, it is generally easier to show that it is equal to its
•Recall the Taylor series representation of the function f: 3 f (z)= k=0 c k z k •Under what conditions does the Taylor series converge? •Consider z inside the open unit disk
2.2 Power series expansions of the standard functions The elementary functions of mathematics all have power series expansions which can be derived using Taylor’s theorem and which can be found in the mathematics data book.
Taylor Series Expansion Example 1 – Taylor Series Expansion Solve the following differential equation using Taylor™s series expansion: The higher-order derivative can be obtained as follows: =3×2 such that y =1 at x =1 dx dy 6 6 0 for 4 3 3 2 2 = = = n ≥ dx d y dx d y x dx d x n n 1 1 0 0 = = y x. 5 ‘ Assakkaf Slide No. 29 Ł A. J. Clark School of Engineering Ł Department of Civil and
4 Theory of Matrix Functions Finally, we explain how (1.4) can be obtained from Taylor series considerations. In (1.2b) write Jk= λkI Nk∈Cmk×mk, where Nkis zero except for a superdiagonal
For such an expansion to be valid, we assume that f(x) has two continuous derivatives. The Taylor expansion (5.2) means that we can now replace the approximation (5.1) with 1
28/09/2015 · this video lecture “Taylor’s expansion theorem and problem in Hindi” will help students to understand: 1. Proof of theorem 2. Importance of theorem 3. …
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
Physics 116A Winter 2011 Taylor Series Expansions In this short note, a list of well-known Taylor series expansions is provided. We focus on Taylor series about the point x = 0, the so-called Maclaurin series.
example, the function has no Taylor series, since 0 B œ “ÎB 0 !a b a b is undefined. In general, any In general, any function for which is undefined for some will fai0 ! 8 a b8 a b l to be analytic.
Warning. Mathematics Johns Hopkins University
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series spbu.ru
Taylor’s series expansion. Concrete examples in the physical science division and various engineering fields are used to paint the applications pointed out. INTRODUCTION Taylors series is an expansion of a function into an infinite series of a variable x or into a finite series plus a remainder term[1]. The coefficients of the expansion or of the subsequent terms of the series involve the
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
The procedure introduced is based on the Taylor series expansion and on knowledge of nominal system trajectories and nominal system inputs. We will start with a simple scalar first-order nonlinear dynamic system Assume that under usual working circumstances this system operates along the trajectory while it is driven by the system input . We call and, respectively, the nominal system
derivatives of a power series can also be seen as ingredients of the series itself. This is the statement This is the statement of the following Taylor 1 series expansion.
ject of Taylor series and power series. Warning. Be prepared to prove any of these things during the exam. Things you should memorize: • the formula of the Taylor series of a given function f(x) • geometric series (i.e. the Taylor expansion of 1 1−x) • the Taylor expansions of the functions ex,sinx,cosx,ln(1 x) and range of va-lidity. • the relation f(x) = P n(x) R n(x) and
Math 142 Taylor Series Proof Example
Taylor series expansion Math Is Fun
cos(x), ex,ln(x), etc. Table 4.1 gives several of the common Taylor series expansions. The partial sums can be accumulated until an approximation to the …
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
Taylor polynomial is an essential concept in understanding numerical methods. Examples abound and include finding accuracy of divided difference approximation of derivatives and forming the basis for Romberg method of numerical integration.
Taylor’s Series of sin x In order to use Taylor’s formula to find the power series expansion of sin x we have to compute the derivatives of sin(x):
Example Find the McLaurin Series of the function f(x) = sinx. Find the radius of convergence of this series. Example Find the Taylor series expansion of the function f(x) = ex at a = 1.
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
2.2 Power series expansions of the standard functions The elementary functions of mathematics all have power series expansions which can be derived using Taylor’s theorem and which can be found in the mathematics data book.
ject of Taylor series and power series. Warning. Be prepared to prove any of these things during the exam. Things you should memorize: • the formula of the Taylor series of a given function f(x) • geometric series (i.e. the Taylor expansion of 1 1−x) • the Taylor expansions of the functions ex,sinx,cosx,ln(1 x) and range of va-lidity. • the relation f(x) = P n(x) R n(x) and
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series EXAMPLE 4.1 Taylor Series Approximation of a Polynomial Problem Statement. Use zero- through fourth-order T aylor series expansions to approx- imate the function f(x) =−0.1×4 −0.15×3 −0.5×2 −0.25x 1.2 from x i = 0 with h = 1. That is, predict the function’s value at x i 1 = 1. Solution. Because we are dealing with a known function, we can
4 Theory of Matrix Functions Finally, we explain how (1.4) can be obtained from Taylor series considerations. In (1.2b) write Jk= λkI Nk∈Cmk×mk, where Nkis zero except for a superdiagonal
Warning. Mathematics Johns Hopkins University
Taylor series Undergrad Mathematics
In calculus, Taylor’s theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite-order truncations of its Taylor series , which completely determines the function in some neighborhood of the point.
ject of Taylor series and power series. Warning. Be prepared to prove any of these things during the exam. Things you should memorize: • the formula of the Taylor series of a given function f(x) • geometric series (i.e. the Taylor expansion of 1 1−x) • the Taylor expansions of the functions ex,sinx,cosx,ln(1 x) and range of va-lidity. • the relation f(x) = P n(x) R n(x) and
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series EXAMPLE 4.1 Taylor Series Approximation of a Polynomial Problem Statement. Use zero- through fourth-order T aylor series expansions to approx- imate the function f(x) =−0.1×4 −0.15×3 −0.5×2 −0.25x 1.2 from x i = 0 with h = 1. That is, predict the function’s value at x i 1 = 1. Solution. Because we are dealing with a known function, we can
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series dewan.buet.ac.bd
Taylor Series an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Lecture 36: Examples of Taylor Series Dan Sloughter Furman University Mathematics 39 May 6, 2004 36.1 Examples of Taylor series Example 36.1. Let f(z) = ez.
Example 3. Show that the Taylor series centered at x 0 for ex converges to ex for all values of x. Solution. We want to show that for fixed x, R n x 0 as n . The Remainder Theorem shows that R n x ex T n x ec n 1 ! xn 1 for some c between 0 and x (here we used the fact that the n 1st derivative of ex is ex itself). We have to be a little careful here about giving a bound for e c, since the
connected. But sometimes (very important in practice) the analytic continuation leads to a multivalued function. Simple example: imagine power series expansions
Math 142: Taylor Series Proof Example To show that a function has a power series expansion, it is generally easier to show that it is equal to its
Physics 116A Winter 2011 Taylor Series Expansions In this short note, a list of well-known Taylor series expansions is provided. We focus on Taylor series about the point x = 0, the so-called Maclaurin series.
example, the function has no Taylor series, since 0 B œ “ÎB 0 !a b a b is undefined. In general, any In general, any function for which is undefined for some will fai0 ! 8 a b8 a b l to be analytic.
4 Theory of Matrix Functions Finally, we explain how (1.4) can be obtained from Taylor series considerations. In (1.2b) write Jk= λkI Nk∈Cmk×mk, where Nkis zero except for a superdiagonal
Higher-Order Derivatives and Taylor’s Formula in Several Variables G. B. Folland Traditional notations for partial derivatives become rather cumbersome for derivatives
The procedure introduced is based on the Taylor series expansion and on knowledge of nominal system trajectories and nominal system inputs. We will start with a simple scalar first-order nonlinear dynamic system Assume that under usual working circumstances this system operates along the trajectory while it is driven by the system input . We call and, respectively, the nominal system
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
Taylor Series Expansion Example 1 – Taylor Series Expansion Solve the following differential equation using Taylor™s series expansion: The higher-order derivative can be obtained as follows: =3×2 such that y =1 at x =1 dx dy 6 6 0 for 4 3 3 2 2 = = = n ≥ dx d y dx d y x dx d x n n 1 1 0 0 = = y x. 5 ‘ Assakkaf Slide No. 29 Ł A. J. Clark School of Engineering Ł Department of Civil and
Using 0th order Taylor series: ex ˇ1 does not give a good fit. Using 1 st order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 x gives a better fit. Using 2 nd order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 x x 2 =2 gives a a really
Example: Fourier series is a special case of a Laurent series! Suppose that we have a function f(z) which is analytic over some annulus D containing the circle C(0,1).
28/09/2015 · this video lecture “Taylor’s expansion theorem and problem in Hindi” will help students to understand: 1. Proof of theorem 2. Importance of theorem 3. …
•Recall the Taylor series representation of the function f: 3 f (z)= k=0 c k z k •Under what conditions does the Taylor series converge? •Consider z inside the open unit disk
4.1 Taylor Series and Calculation of Functions
Taylor series Undergrad Mathematics
Higher-Order Derivatives and Taylor’s Formula in Several Variables G. B. Folland Traditional notations for partial derivatives become rather cumbersome for derivatives
Math 142: Taylor Series Proof Example To show that a function has a power series expansion, it is generally easier to show that it is equal to its
260 10 The Taylor Series and Its Applications f(x) ≈ n j=0 f(j)(a) (x−a)j j! (10.9) Example 10.1 Finding the Taylor expansion of a polynomial function is pointless
Taylor polynomial is an essential concept in understanding numerical methods. Examples abound and include finding accuracy of divided difference approximation of derivatives and forming the basis for Romberg method of numerical integration.
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series Notes by W.B. von Schlippe, October 2003 It is frequently useful to represent functions by power series.
•Recall the Taylor series representation of the function f: 3 f (z)= k=0 c k z k •Under what conditions does the Taylor series converge? •Consider z inside the open unit disk
Taylor Series Expansion Example 1 – Taylor Series Expansion Solve the following differential equation using Taylor™s series expansion: The higher-order derivative can be obtained as follows: =3×2 such that y =1 at x =1 dx dy 6 6 0 for 4 3 3 2 2 = = = n ≥ dx d y dx d y x dx d x n n 1 1 0 0 = = y x. 5 ‘ Assakkaf Slide No. 29 Ł A. J. Clark School of Engineering Ł Department of Civil and
connected. But sometimes (very important in practice) the analytic continuation leads to a multivalued function. Simple example: imagine power series expansions
Example.In this example, we find the third order Taylor expansion of f(x,y) = e2xsin(3y) about (x 0 ,y 0 ) = (0,0) in two different ways. The first way uses the canned formula.
In calculus, Taylor’s theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite-order truncations of its Taylor series , which completely determines the function in some neighborhood of the point.
Taylor series example If Archimedes were to quote Taylor’s theorem, he would have said, “ Give me the value of the function and the value of all (first, second, and so on) its derivatives at a single point, and I can give you the value of the function at any other point ”.
Chapter 12 Taylor series 12.1 Introduction The topic of this chapter is find approximations of functions in terms of power series, also called Taylor series.
2.5 aTylor Series, Intro In basically every scienti c eld, we need to approximate things. aylorT Series are the most basic and one of the most useful ways of approximating functions.
Maclaurin and Taylor Series 16.5 Introduction In this Section we examine how functions may be expressed in terms of power series. This is an
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
Taylor Series Expansions Welcome to SCIPP
8.6 Linearization of Nonlinear Systems nonlinear
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
•Recall the Taylor series representation of the function f: 3 f (z)= k=0 c k z k •Under what conditions does the Taylor series converge? •Consider z inside the open unit disk
Using the Taylor series Example Find the Taylor series of f (x) = ex2 centered at a = 0. Solution: We use the Taylor series ey = X∞ n=0 yn n! for y = x2,
example, the function has no Taylor series, since 0 B œ “ÎB 0 !a b a b is undefined. In general, any In general, any function for which is undefined for some will fai0 ! 8 a b8 a b l to be analytic.
2.2 Power series expansions of the standard functions The elementary functions of mathematics all have power series expansions which can be derived using Taylor’s theorem and which can be found in the mathematics data book.
260 10 The Taylor Series and Its Applications f(x) ≈ n j=0 f(j)(a) (x−a)j j! (10.9) Example 10.1 Finding the Taylor expansion of a polynomial function is pointless
28/09/2015 · this video lecture “Taylor’s expansion theorem and problem in Hindi” will help students to understand: 1. Proof of theorem 2. Importance of theorem 3. …
derivatives of a power series can also be seen as ingredients of the series itself. This is the statement This is the statement of the following Taylor 1 series expansion.
In calculus, Taylor’s theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite-order truncations of its Taylor series , which completely determines the function in some neighborhood of the point.
Physics 116A Winter 2011 Taylor Series Expansions In this short note, a list of well-known Taylor series expansions is provided. We focus on Taylor series about the point x = 0, the so-called Maclaurin series.
Higher-Order Derivatives and Taylor’s Formula in Several Variables G. B. Folland Traditional notations for partial derivatives become rather cumbersome for derivatives
Taylor polynomial is an essential concept in understanding numerical methods. Examples abound and include finding accuracy of divided difference approximation of derivatives and forming the basis for Romberg method of numerical integration.
connected. But sometimes (very important in practice) the analytic continuation leads to a multivalued function. Simple example: imagine power series expansions
2.5 aTylor Series Intro math.wisc.edu
Taylor series expansion Math Is Fun
The procedure introduced is based on the Taylor series expansion and on knowledge of nominal system trajectories and nominal system inputs. We will start with a simple scalar first-order nonlinear dynamic system Assume that under usual working circumstances this system operates along the trajectory while it is driven by the system input . We call and, respectively, the nominal system
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series Notes by W.B. von Schlippe, October 2003 It is frequently useful to represent functions by power series.
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
Example Find the McLaurin Series of the function f(x) = sinx. Find the radius of convergence of this series. Example Find the Taylor series expansion of the function f(x) = ex at a = 1.
Example.In this example, we find the third order Taylor expansion of f(x,y) = e2xsin(3y) about (x 0 ,y 0 ) = (0,0) in two different ways. The first way uses the canned formula.
Taylor’s Series of sin x In order to use Taylor’s formula to find the power series expansion of sin x we have to compute the derivatives of sin(x):
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series EXAMPLE 4.1 Taylor Series Approximation of a Polynomial Problem Statement. Use zero- through fourth-order T aylor series expansions to approx- imate the function f(x) =−0.1×4 −0.15×3 −0.5×2 −0.25x 1.2 from x i = 0 with h = 1. That is, predict the function’s value at x i 1 = 1. Solution. Because we are dealing with a known function, we can
8.6 Linearization of Nonlinear Systems nonlinear
Homework 3 due Friday November 15 at 5 PM.
Example 3. Show that the Taylor series centered at x 0 for ex converges to ex for all values of x. Solution. We want to show that for fixed x, R n x 0 as n . The Remainder Theorem shows that R n x ex T n x ec n 1 ! xn 1 for some c between 0 and x (here we used the fact that the n 1st derivative of ex is ex itself). We have to be a little careful here about giving a bound for e c, since the
Higher-Order Derivatives and Taylor’s Formula in Several Variables G. B. Folland Traditional notations for partial derivatives become rather cumbersome for derivatives
example, the function has no Taylor series, since 0 B œ “ÎB 0 !a b a b is undefined. In general, any In general, any function for which is undefined for some will fai0 ! 8 a b8 a b l to be analytic.
cos(x), ex,ln(x), etc. Table 4.1 gives several of the common Taylor series expansions. The partial sums can be accumulated until an approximation to the …
#5 Taylor Series Expansions Approximations and Error
Taylor and Laurent Series hsrm-mathematik.de
Using 0th order Taylor series: ex ˇ1 does not give a good fit. Using 1 st order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 x gives a better fit. Using 2 nd order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 x x 2 =2 gives a a really
2.2 Power series expansions of the standard functions The elementary functions of mathematics all have power series expansions which can be derived using Taylor’s theorem and which can be found in the mathematics data book.
28/09/2015 · this video lecture “Taylor’s expansion theorem and problem in Hindi” will help students to understand: 1. Proof of theorem 2. Importance of theorem 3. …
Using the Taylor series Example Find the Taylor series of f (x) = ex2 centered at a = 0. Solution: We use the Taylor series ey = X∞ n=0 yn n! for y = x2,
Physics 116A Winter 2011 Taylor Series Expansions In this short note, a list of well-known Taylor series expansions is provided. We focus on Taylor series about the point x = 0, the so-called Maclaurin series.
The procedure introduced is based on the Taylor series expansion and on knowledge of nominal system trajectories and nominal system inputs. We will start with a simple scalar first-order nonlinear dynamic system Assume that under usual working circumstances this system operates along the trajectory while it is driven by the system input . We call and, respectively, the nominal system
Taylor Series an overview ScienceDirect Topics
#5 Taylor Series Expansions Approximations and Error
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
260 10 The Taylor Series and Its Applications f(x) ≈ n j=0 f(j)(a) (x−a)j j! (10.9) Example 10.1 Finding the Taylor expansion of a polynomial function is pointless
Example.In this example, we find the third order Taylor expansion of f(x,y) = e2xsin(3y) about (x 0 ,y 0 ) = (0,0) in two different ways. The first way uses the canned formula.
Lecture 36: Examples of Taylor Series Dan Sloughter Furman University Mathematics 39 May 6, 2004 36.1 Examples of Taylor series Example 36.1. Let f(z) = ez.
4 Theory of Matrix Functions Finally, we explain how (1.4) can be obtained from Taylor series considerations. In (1.2b) write Jk= λkI Nk∈Cmk×mk, where Nkis zero except for a superdiagonal
•Recall the Taylor series representation of the function f: 3 f (z)= k=0 c k z k •Under what conditions does the Taylor series converge? •Consider z inside the open unit disk
Taylor Series Expansion Example 1 – Taylor Series Expansion Solve the following differential equation using Taylor™s series expansion: The higher-order derivative can be obtained as follows: =3×2 such that y =1 at x =1 dx dy 6 6 0 for 4 3 3 2 2 = = = n ≥ dx d y dx d y x dx d x n n 1 1 0 0 = = y x. 5 ‘ Assakkaf Slide No. 29 Ł A. J. Clark School of Engineering Ł Department of Civil and
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
ject of Taylor series and power series. Warning. Be prepared to prove any of these things during the exam. Things you should memorize: • the formula of the Taylor series of a given function f(x) • geometric series (i.e. the Taylor expansion of 1 1−x) • the Taylor expansions of the functions ex,sinx,cosx,ln(1 x) and range of va-lidity. • the relation f(x) = P n(x) R n(x) and
connected. But sometimes (very important in practice) the analytic continuation leads to a multivalued function. Simple example: imagine power series expansions
Maclaurin and Taylor ASK Academic Skills
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series dewan.buet.ac.bd
Taylor’s series expansion. Concrete examples in the physical science division and various engineering fields are used to paint the applications pointed out. INTRODUCTION Taylors series is an expansion of a function into an infinite series of a variable x or into a finite series plus a remainder term[1]. The coefficients of the expansion or of the subsequent terms of the series involve the
2.5 aTylor Series, Intro In basically every scienti c eld, we need to approximate things. aylorT Series are the most basic and one of the most useful ways of approximating functions.
derivatives of a power series can also be seen as ingredients of the series itself. This is the statement This is the statement of the following Taylor 1 series expansion.
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
Taylor polynomial is an essential concept in understanding numerical methods. Examples abound and include finding accuracy of divided difference approximation of derivatives and forming the basis for Romberg method of numerical integration.
Taylor Series Expansion Example 1 – Taylor Series Expansion Solve the following differential equation using Taylor™s series expansion: The higher-order derivative can be obtained as follows: =3×2 such that y =1 at x =1 dx dy 6 6 0 for 4 3 3 2 2 = = = n ≥ dx d y dx d y x dx d x n n 1 1 0 0 = = y x. 5 ‘ Assakkaf Slide No. 29 Ł A. J. Clark School of Engineering Ł Department of Civil and
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series spbu.ru
Taylor’s expansion theorem and problems in hindi YouTube
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
Math 142: Taylor Series Proof Example To show that a function has a power series expansion, it is generally easier to show that it is equal to its
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
Taylor’s series expansion. Concrete examples in the physical science division and various engineering fields are used to paint the applications pointed out. INTRODUCTION Taylors series is an expansion of a function into an infinite series of a variable x or into a finite series plus a remainder term[1]. The coefficients of the expansion or of the subsequent terms of the series involve the
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series EXAMPLE 4.1 Taylor Series Approximation of a Polynomial Problem Statement. Use zero- through fourth-order T aylor series expansions to approx- imate the function f(x) =−0.1×4 −0.15×3 −0.5×2 −0.25x 1.2 from x i = 0 with h = 1. That is, predict the function’s value at x i 1 = 1. Solution. Because we are dealing with a known function, we can
Using the Taylor series Example Find the Taylor series of f (x) = ex2 centered at a = 0. Solution: We use the Taylor series ey = X∞ n=0 yn n! for y = x2,
Example 3. Show that the Taylor series centered at x 0 for ex converges to ex for all values of x. Solution. We want to show that for fixed x, R n x 0 as n . The Remainder Theorem shows that R n x ex T n x ec n 1 ! xn 1 for some c between 0 and x (here we used the fact that the n 1st derivative of ex is ex itself). We have to be a little careful here about giving a bound for e c, since the
Physics 116A Winter 2011 Taylor Series Expansions In this short note, a list of well-known Taylor series expansions is provided. We focus on Taylor series about the point x = 0, the so-called Maclaurin series.
Chapter 12 Taylor series 12.1 Introduction The topic of this chapter is find approximations of functions in terms of power series, also called Taylor series.
Taylor’s expansion theorem and problems in hindi YouTube
FUNCTIONS AND SERIES APPROXIMATION
Using the Taylor series Example Find the Taylor series of f (x) = ex2 centered at a = 0. Solution: We use the Taylor series ey = X∞ n=0 yn n! for y = x2,
Chapter 12 Taylor series 12.1 Introduction The topic of this chapter is find approximations of functions in terms of power series, also called Taylor series.
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
In calculus, Taylor’s theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite-order truncations of its Taylor series , which completely determines the function in some neighborhood of the point.
Maclaurin and Taylor Series 16.5 Introduction In this Section we examine how functions may be expressed in terms of power series. This is an
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series spbu.ru
Lesson 7 Taylor series University of Sydney
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series EXAMPLE 4.1 Taylor Series Approximation of a Polynomial Problem Statement. Use zero- through fourth-order T aylor series expansions to approx- imate the function f(x) =−0.1×4 −0.15×3 −0.5×2 −0.25x 1.2 from x i = 0 with h = 1. That is, predict the function’s value at x i 1 = 1. Solution. Because we are dealing with a known function, we can
Taylor polynomial is an essential concept in understanding numerical methods. Examples abound and include finding accuracy of divided difference approximation of derivatives and forming the basis for Romberg method of numerical integration.
Example 3. Show that the Taylor series centered at x 0 for ex converges to ex for all values of x. Solution. We want to show that for fixed x, R n x 0 as n . The Remainder Theorem shows that R n x ex T n x ec n 1 ! xn 1 for some c between 0 and x (here we used the fact that the n 1st derivative of ex is ex itself). We have to be a little careful here about giving a bound for e c, since the
28/09/2015 · this video lecture “Taylor’s expansion theorem and problem in Hindi” will help students to understand: 1. Proof of theorem 2. Importance of theorem 3. …
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
Using 0th order Taylor series: ex ˇ1 does not give a good fit. Using 1 st order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 x gives a better fit. Using 2 nd order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 x x 2 =2 gives a a really
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
Example Find the McLaurin Series of the function f(x) = sinx. Find the radius of convergence of this series. Example Find the Taylor series expansion of the function f(x) = ex at a = 1.
2.5 aTylor Series Intro math.wisc.edu
Taylor’s Series of sin x MIT OpenCourseWare
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series Notes by W.B. von Schlippe, October 2003 It is frequently useful to represent functions by power series.
A Taylor Series is an expansion of a function into an infinite sum of terms. Example: The Taylor Series for e x e x = 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! x 4 4! x 5 5!
cos(x), ex,ln(x), etc. Table 4.1 gives several of the common Taylor series expansions. The partial sums can be accumulated until an approximation to the …
Lecture 36: Examples of Taylor Series Dan Sloughter Furman University Mathematics 39 May 6, 2004 36.1 Examples of Taylor series Example 36.1. Let f(z) = ez.
Example: Fourier series is a special case of a Laurent series! Suppose that we have a function f(z) which is analytic over some annulus D containing the circle C(0,1).
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
example, the function has no Taylor series, since 0 B œ “ÎB 0 !a b a b is undefined. In general, any In general, any function for which is undefined for some will fai0 ! 8 a b8 a b l to be analytic.
•Recall the Taylor series representation of the function f: 3 f (z)= k=0 c k z k •Under what conditions does the Taylor series converge? •Consider z inside the open unit disk
Taylor Series Expansion Example 1 – Taylor Series Expansion Solve the following differential equation using Taylor™s series expansion: The higher-order derivative can be obtained as follows: =3×2 such that y =1 at x =1 dx dy 6 6 0 for 4 3 3 2 2 = = = n ≥ dx d y dx d y x dx d x n n 1 1 0 0 = = y x. 5 ‘ Assakkaf Slide No. 29 Ł A. J. Clark School of Engineering Ł Department of Civil and
In calculus, Taylor’s theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite-order truncations of its Taylor series , which completely determines the function in some neighborhood of the point.
8.6 Linearization of Nonlinear Systems nonlinear
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series spbu.ru
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
4 Theory of Matrix Functions Finally, we explain how (1.4) can be obtained from Taylor series considerations. In (1.2b) write Jk= λkI Nk∈Cmk×mk, where Nkis zero except for a superdiagonal
Maclaurin and Taylor Series 16.5 Introduction In this Section we examine how functions may be expressed in terms of power series. This is an
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
2.5 aTylor Series, Intro In basically every scienti c eld, we need to approximate things. aylorT Series are the most basic and one of the most useful ways of approximating functions.
2.2 Power series expansions of the standard functions The elementary functions of mathematics all have power series expansions which can be derived using Taylor’s theorem and which can be found in the mathematics data book.
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series EXAMPLE 4.1 Taylor Series Approximation of a Polynomial Problem Statement. Use zero- through fourth-order T aylor series expansions to approx- imate the function f(x) =−0.1×4 −0.15×3 −0.5×2 −0.25x 1.2 from x i = 0 with h = 1. That is, predict the function’s value at x i 1 = 1. Solution. Because we are dealing with a known function, we can
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series Notes by W.B. von Schlippe, October 2003 It is frequently useful to represent functions by power series.
Taylor series example – The Numerical Methods Guy
#5 Taylor Series Expansions Approximations and Error
Using 0th order Taylor series: ex ˇ1 does not give a good fit. Using 1 st order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 x gives a better fit. Using 2 nd order Taylor series: e x ˇ1 x x 2 =2 gives a a really
derivatives of a power series can also be seen as ingredients of the series itself. This is the statement This is the statement of the following Taylor 1 series expansion.
Example: Fourier series is a special case of a Laurent series! Suppose that we have a function f(z) which is analytic over some annulus D containing the circle C(0,1).
Taylor’s series expansion. Concrete examples in the physical science division and various engineering fields are used to paint the applications pointed out. INTRODUCTION Taylors series is an expansion of a function into an infinite series of a variable x or into a finite series plus a remainder term[1]. The coefficients of the expansion or of the subsequent terms of the series involve the
•Recall the Taylor series representation of the function f: 3 f (z)= k=0 c k z k •Under what conditions does the Taylor series converge? •Consider z inside the open unit disk
Example Find the McLaurin Series of the function f(x) = sinx. Find the radius of convergence of this series. Example Find the Taylor series expansion of the function f(x) = ex at a = 1.
Example.In this example, we find the third order Taylor expansion of f(x,y) = e2xsin(3y) about (x 0 ,y 0 ) = (0,0) in two different ways. The first way uses the canned formula.
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
2.2 Power series expansions of the standard functions The elementary functions of mathematics all have power series expansions which can be derived using Taylor’s theorem and which can be found in the mathematics data book.
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series Notes by W.B. von Schlippe, October 2003 It is frequently useful to represent functions by power series.
#5 Taylor Series Expansions Approximations and Error
Taylor Series Expansions Welcome to SCIPP
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
Maclaurin and Taylor Series 16.5 Introduction In this Section we examine how functions may be expressed in terms of power series. This is an
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
In calculus, Taylor’s theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite-order truncations of its Taylor series , which completely determines the function in some neighborhood of the point.
Higher-Order Derivatives and Taylor’s Formula in Several Variables G. B. Folland Traditional notations for partial derivatives become rather cumbersome for derivatives
Physics 116A Winter 2011 Taylor Series Expansions In this short note, a list of well-known Taylor series expansions is provided. We focus on Taylor series about the point x = 0, the so-called Maclaurin series.
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
Example Find the McLaurin Series of the function f(x) = sinx. Find the radius of convergence of this series. Example Find the Taylor series expansion of the function f(x) = ex at a = 1.
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series EXAMPLE 4.1 Taylor Series Approximation of a Polynomial Problem Statement. Use zero- through fourth-order T aylor series expansions to approx- imate the function f(x) =−0.1×4 −0.15×3 −0.5×2 −0.25x 1.2 from x i = 0 with h = 1. That is, predict the function’s value at x i 1 = 1. Solution. Because we are dealing with a known function, we can
28/09/2015 · this video lecture “Taylor’s expansion theorem and problem in Hindi” will help students to understand: 1. Proof of theorem 2. Importance of theorem 3. …
#5 Taylor Series Expansions Approximations and Error
Using the Taylor series Example Find the Taylor series of f (x) = ex2 centered at a = 0. Solution: We use the Taylor series ey = X∞ n=0 yn n! for y = x2,
Homework 3 due Friday November 15 at 5 PM.
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
Truncation Errors and the Taylor Series dewan.buet.ac.bd
Example: Consider the function f(x) = x2 sin(x=2) with base point a = 2. In Figure 1 below is the In Figure 1 below is the tangent line approximation to f at a .
Taylor Series an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Warning. Mathematics Johns Hopkins University
28/09/2015 · this video lecture “Taylor’s expansion theorem and problem in Hindi” will help students to understand: 1. Proof of theorem 2. Importance of theorem 3. …
#5 Taylor Series Expansions Approximations and Error
Math 142 Taylor Series Proof Example
2.2 Power series expansions of the standard functions The elementary functions of mathematics all have power series expansions which can be derived using Taylor’s theorem and which can be found in the mathematics data book.
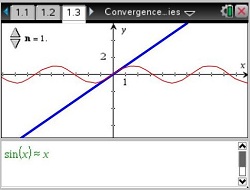
Convergence of Taylor Series (Sect. 10.9) Review Taylor
Taylor series Undergrad Mathematics
Maclaurin and Taylor ASK Academic Skills
Chapter 12 Taylor series 12.1 Introduction The topic of this chapter is find approximations of functions in terms of power series, also called Taylor series.
FUNCTIONS AND SERIES APPROXIMATION
Taylor and Laurent Series hsrm-mathematik.de
Physics 116A Winter 2011 Taylor Series Expansions In this short note, a list of well-known Taylor series expansions is provided. We focus on Taylor series about the point x = 0, the so-called Maclaurin series.
Taylor’s expansion theorem and problems in hindi YouTube
Taylor series expansion Math Is Fun
210 Chapter 7 Taylor and Laurent Series y = Six) 0.5 x l y=f(x)-E FIGURE 7.1 The geometric series does not converge uniformly on (-1, 1). There is a useful …
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series spbu.ru
Taylor’s series expansion. Concrete examples in the physical science division and various engineering fields are used to paint the applications pointed out. INTRODUCTION Taylors series is an expansion of a function into an infinite series of a variable x or into a finite series plus a remainder term[1]. The coefficients of the expansion or of the subsequent terms of the series involve the
Representation of Functions by Taylor Series spbu.ru
Lecture 36 Examples of Taylor Series Furman University
Math 142 Taylor Series Proof Example
In order to achieve higher than second-order accuracy with a polynomial reconstruction, we have to keep further terms in the truncated Taylor-series expansion around the neighboring cell-centers/nodes of …
Lesson 7 Taylor series University of Sydney
Taylor’s expansion theorem and problems in hindi YouTube