Region of convergence z transform pdf
Z-transform For standard z-score in statistics, see Standard score. For Fisher z-transformation in statistics, see Fisher transformation. In mathematics and signal processing,…
LaplaceTransform: Definition and Region of Convergence Yao Wang Polytechnic University Some slides included are extracted from lecture notes from MIT open courseware
Inverse z-Transform Partial Fraction Method The z-transform of an exponential sequence x(k) = ak is given by X(z) = 1 1 −az−1 = z z −a. Any sequence that starts with a non-zero value at k = 0 usually
26/04/2012 · Introduction to Laplace Transform 25. Region of Convergence of Laplace Transform & Properties of Laplace Transform 26. Properties of Laplace Transform (Contd.) 27. Concluding Discission on Laplace
20/06/2017 · Take the Full Course of Digital Signal Processing What we Provide 1)25 Videos (Index is given down) + Update will be Coming Before final exams …
The z-Transform and Its Properties3.1 The z-Transform Region of Convergence Ithe region of convergence (ROC) of X(z) is the set of all values of z for which X(z) attains a nite value The z-Transform is, therefore, uniquely characterized by: 1.expression for X(z) 2.ROC of X(z) Professor Deepa Kundur (University of Toronto)The z-Transform and Its Properties4 / 20. The z-Transform …
Organization 1: Introduction • Organization • Signals • Processing • Syllabus • Sequences • Time Scaling • z-Transform • Region of Convergence
X ( z) 1 1 z 1 az 1 1 a z a z Region of convergence When. Ghulam Muhammad King Saud University 3 . az 1 1 z a CEN352. Therefore.Example 2 Problem: Given the sequence. Dr. Solution: find the z transform of x(n).
Taking absolute convergence as the criterion for to exist, the so-called “region of convergence” (RoC) is generally stated to be of the form r-< z 1 5. What are the different methods available for inverse Zs-transform? Residue method, Partial fractions method, Long division method, Convolution integral method 6. When the z
19 rows · This assumes that the Fourier transform exists; i.e., that the axis is in the region of …
Z – Transform and Applications PDF Hüseyin Abut, E. E. and Computer Engineering, San Diego State University, San Diego, CA About the region of convergence of the z-transform PDF
Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and Z Transform, Signal & Systems notes for Electrical Engineering (EE) is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Electrical Engineering (EE).
Region of Convergence and Examples Whether the z-transform of a signal exists depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. exists if and only if the argument is inside the region of convergence (ROC) in the z-plane, which is composed of all values for the summation of the Z-transform to converge.
z Transform. Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding the relationship between . transform and Region of Convergence (ROC) ROC indicates when . transform of a sequence converges . Generally there exists some . such that (5.9)
Region of Convergence(RoC) Region of Convergence for a discrete time signal x[n] is de ned as a continuous region in z plane where the Z-Transform converges.
[The z – transform ] of a sequence [ ] is given by [ = 0.5 1−2𝑧−1. It is given that the Region of convergence of [ ] includes the unit circle. The value of [0]is (a) – 0.5 (b) 0 (c) 0.25 (d) 0.5 [GATE 2007: 2 Marks] Soln. Given ( ) of a sequence [ ] ( )= 0.5 1−2 𝑧−1 Above transform is for left handed sequence with ROC∶<2 Corresponding sequence is ( )=−(0.5)2−𝑛
z Transform Electrical Engineering Mathematical Analysis
https://www.youtube.com/embed/y57XNuNkY4Q

The z-Transform and Its Properties University of Toronto
Region of Convergence The z-transform of x(n) can be viewed as the Fourier transform of x(n) multiplied by an exponential z n The power series for the z-transform is called a Laurent series: The Laurent series, and therefore the z-transform, represents an analytic function at every point inside the region of convergence, and therefore the z- transform and all its derivatives must be
Module 4 : Laplace and Z Transform Lecture 31 : Z Transform and Region of Convergence Objectives: Scope of this lecture: We have already seen the implementation of Fourier Transform and Laplace Transform for the study of Continuous Time (C.T.) signals
The z-transform region of convergence (ROC) for the Laurent series is chosen to be , where . Remark 9.2. The 9.1.4 Properties of the z-transform The following properties of z-transforms listed in Table 9.2 are well known in the field of digital signal analysis. The reader will be asked to prove some of these properties in the exercises. Exploration . Example 9.7. Given . Use convolution to
1. The z-Transform (c.2) Region of Convergence For any given sequence, the set of values of z for which the z-transform converges is called the region of convergence.
PPT – Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and Z Transform, Signal & Systems notes for Electrical Engineering (EE) is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Electrical Engineering (EE).
I’m a novice in DSP and I have few doubts regarding the $mathcal Z$-transform and its region of convergence (ROC). I know what a $mathcal Z$-transform is. But I’m having trouble with understanding the ROC.
For X(z) with N poles of different radius, there are N+1 possible ROC in general, with N+1 corresponding signals x(n). But only one x(n) signal will be right-sided:
The Region of Convergence for the Z Transform Important properties of the ROC of the z−transform: 1. The ROC of X(z) consists of a ring in the z−plane centered about the origin 2. The ROC does not contain any poles 3. If x[n] is of finite-duration, then the ROC is the entire z−plane, except possibly at z = 0 and/or z = ∞ zA finite-duration sequence is a sequence that is nonzero in a
because when z lies in this region, the series actually converges to the function (1.50). A slightly more accurate term would be “the region of definition”, since the z-transform is undefined outside of this region.
DSP: Properties of the z-Transform Region of Convergence ROC Properties for Rational z-Transforms (1 of 2) 1.The ROC is a ring or a disk in the z-plane centered at the origin.
22 The z-Transform Recommended Problems P22.1 An LTI system has an impulse response h[n] for which the z-transform is H Determine what can be inferred about the associated region of convergence from each of the following statements. (a) x[n] is right-sided. (b
21 Lecture Notes by Hua Properties of ROC of the Z-Transform • ROC is a ring or disk centered at the origin • Fourier transform converges absolutely iff ROC
An introduction to Z Transform is the topic of this paper. It deals with a review of what Z Transform means and what does the specific region of convergence represent. A pictorial representation of the region of convergence has been sketched. Most of
Region of Convergence (ROC) Whether the Laplace transform of a signal exists or not depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. All complex values of for which the integral in the definition converges form a region of convergence (ROC) in the s-plane.
The z-transform is a very important tool in describing and analyzing digital systems. It offers the techniques for digital filter design and frequency analysis of digital signals. f f n X ( ) x[n]z n Definition of z-transform: For causal sequence, x(n) = 0, n< 0: Where z is a complex variable All the values of z that make the summation to exist form a region of convergence. CEN543, Dr
–The sum of the series may not be converge for all z. •Region of convergence (ROC) –Since the z-transform can be interpreted as the Fourier transform, it is possible for the z-transform to converge
One must consider the Region of Convergence (ROC) of the Z-transform, because left-sided and right-sided time functions will have the same Z-transform
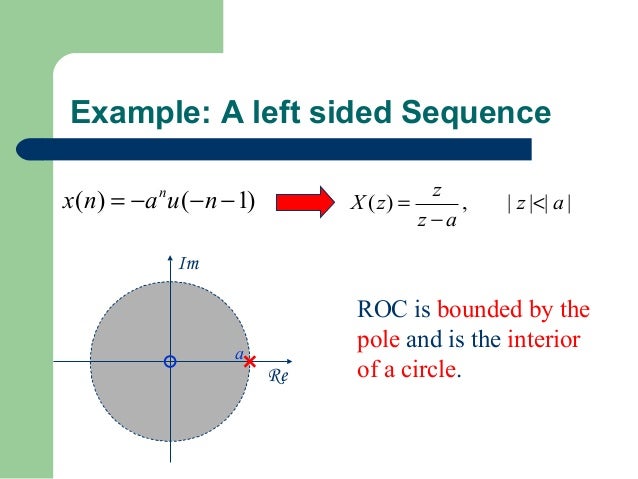
The z-transform expression is the same as for example 1. However, the region of convergence However, the region of convergence is opposite; the ROC is formed by the inside of a circle:

The range of variation of z for which z-transform converges is called region of convergence of z-transform. Properties of ROC of Z-Transforms ROC of z-transform is indicated with circle in z-plane.
3 Observations • Specification of the Z transform requires both algebraic expression and region of convergence • Rational Z-transforms are obtained if x[n]=linear
PYKC 3-Mar-11 E2.5 Signals & Linear Systems Lecture 15 Slide 5 Example of z-transform (1) Find the z-transform for the signal γnu[n], where γ is a constant.
The z-transform is a very important tool in describing and analyzing digital systems. It offers the techniques for digital filter design and frequency analysis of digital signals. f f n X ( ) x[n]z n Definition of z-transform: For causal sequence, x(n) = 0, n< 0: Where z is a complex variable All the values of z that make the summation to exist form a region of convergence. CEN352, Dr
In signal processing, a discrete time domain signal is converted into a complex frequency domain representation using Z transformation. Mathematically the Region of Convergence (ROC) is the set of all the points in the complex plane for which the Z transform summation converges.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/PbUprYe-a7o
How does the $mathcal Z$-transform’s “region of
A sequence ( ) with the z – transform 𝑋(𝑧)=𝑧4+𝑧2−2𝑧+2−3𝑧−4is applied as an input to a linear time – variant system with the impulse response ℎ( )=2𝛿( −3)where
Chapter 3: The z-Transform and Its Application Region of Convergence: r 1 <r 2 Dr. Deepa Kundur (University of Toronto)The z-Transform and Its Application9 / 36
The professors spend a fair amount of classroom time deriving the z-transform of various infinite-length sequences, drawing the transforms' poles on the z-plane, and discussing for what values of z the transforms exist (i.e., the z-plane region of convergence where a z-transform converges to values less than infinity).
Region of Convergence (ROC) – Learn Signals and Systems in simple and easy steps starting from Overview, Signal Analysis, Fourier Series, Fourier Transforms, Convolution Correlation, Sampling, Laplace Transforms, Z-Transforms.
DSP: z-Transform Region of Convergence Region of Convergence Example 1P: x[n] = u[n]. The ROC is all z2C such that 1 n=0 jzj n 1.
EE264 Oct 8, 2004 Fall 04-05 Supplemental Notes About the region of convergence of the z-transform The z-Transform of a sequencef[n] is defined as S(z) =
convergence z−plane Im Region of Re In specific cases the inner radius of this ring may include the origin, and the outer radius may extend to infinity.
5.2 Unilateral (one-sided) z-transform 101 Figure 5.1: A typical region of convergence (ROC) for a unilateral z-transform. The radius of convergence,transformers the covenant of primus digital book pdfThe discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) (not to be confused with the discrete Fourier transform (DFT)) is a special case of such a Z-transform obtained by restricting z to lie on the unit circle. [ edit ] Region of convergence
region of convergence of z transform – why bother. Started by December 11, 2018. Chronological; Newest First; Yes I understand the theory, left handed and right-handed sequences. we can= have two z transfer functions the same but one is left hand sided and the = other right. A great deal is spent explaining this but exactly what is the use in the fi= rst place of left-handed sequences as they
The region of convergence, known as the ROC, is important to understand because it defines the region where the z-transform exists. The z-transform of a sequence is defined as X z = ∑ n = − ∞ ∞ x n z − n X z n x n z n
Discrete-Time Signal Representation with z Transform . Apart from discretetime Fourier transform (DTFT), we can – also use Region of Convergence (ROC) ROC indicates when . transform of a sequence converges. Generally there exists some . such that
called the region of convergence (ROC) Rational z-Transforms • Observe that the magnitude plot exhibits very large peaks around the points which are the poles of G(z) • It also exhibits very narrow and deep wells around the location of the zeros at z = 0
2-Consider the z-transform X(z) whose pole-zero plot is as shown in figure 1. (a) Determine the ROC of X(z) if it is known that the Fourier transform exists. For this case,
Z transfrm ppt 1. THE z-TRANSFORM SWATI MISHRA 1 2. CONTENTS • z-transform • Region Of Convergence • Properties Of Region Of Convergence • z-transform Of Common Sequence • Properties And Theorems • Application • Inverse z- Transform • z-transform …
The z-transform of a signal is an innite series for each possible value of z in the complex plane. Typically only some of those Typically only some of those innite series will converge.
Laplace Transforms • Definition • Region of convergence • Useful properties • Inverse & partial fraction expansion • Distinct, complex, & repeated poles
Clearly, the z-transform is a power series with an infinite number of terms and so may not converge for all values of z. The region where the z-transform converges is
EE 123 Digital Signal Processing Spring 2007 Lecture 5
In today’s class… Z-transform Unilateral Z-transform Bilateral Z-transform Region of Convergence Inverse Z-transform Power Series method
3 Poles, Zeros, Regions of Convergence Example 1: In nite-length right-sided Consider the causal sequence: h1[n] = anu[n] This impulse response might be used to …
Digital signal processing. LAB REPORT-3 Z TRANSFORMS DHARAMSOTH SANTHOSH 27th AUG 2013 .3 REGION OF CONVERGENCE The region of convergence (ROC) is the set of points in the complex plane for which the Z-transform summation converges.3.1 AIM 1.
Given a time signal x[n], the region of convergence (ROC) of its z-transform X(z) is the set of z2C such that X(z) converges, that is, the set of z2C such that x[n]z is absolutely summablen
1 − 21 z −1 1 + 13 z −1 (z − 21 )(z + 13 ) The pole-zero plot and region of convergence of the signal is z−plane Im unit circle 1 Re 1 − 31 1 12 2 Example: finite length sequence The signal an 0≤n≤N −1 x[n] = 0 otherwise has z-transform N X −1 N X −1 n −n X(z) = a z = (az −1 )n n=0 n=0 1 − (az −1 )N 1 z N − aN = = . 1 − az −1 z N −1 z − a Since there are
Homework 3 (Z Transform) Sharif

Chapter 6 The Z-Transform – University of California
https://www.youtube.com/embed/RprzYUDKrrA
The Transforms Relationship to Fourier Transform Region of Convergence Convergence, continued Some Special Functions Convolution, Unit Step Poles and Zeros Example Convergence of Finite Sequences Inverse z-Transform Properties z-transforms are linear: The transform of a shifted sequence: Multiplication: But multiplication will affect the region of convergence and all the pole …
ELEC361 Signals And Systems Topic 10 The Z Transform

z Transform City University of Hong Kong
Z Transform table Rhea


Region of Convergence and Examples Harvey Mudd College
29. Properties of Z Transform YouTube
the ticket of leave man play pdf The z-transform University of Cape Town
Lecture 31 Z Transform and Region of Convergence – NPTEL
PPT Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and
comp.dsp region of convergence of z transform why bother
Z Transform and Region of Convergence Laplace and Z
z Transform Department of EE
3 Observations • Specification of the Z transform requires both algebraic expression and region of convergence • Rational Z-transforms are obtained if x[n]=linear
DSP: z-Transform Region of Convergence Region of Convergence Example 1P: x[n] = u[n]. The ROC is all z2C such that 1 n=0 jzj n 1.
Z – Transform and Applications PDF Hüseyin Abut, E. E. and Computer Engineering, San Diego State University, San Diego, CA About the region of convergence of the z-transform PDF
Region of Convergence (ROC) – Learn Signals and Systems in simple and easy steps starting from Overview, Signal Analysis, Fourier Series, Fourier Transforms, Convolution Correlation, Sampling, Laplace Transforms, Z-Transforms.
Convergence Region of Z-transform 國立臺灣大學
The z-Transform and Its Application
DSP: Properties of the z-Transform Region of Convergence ROC Properties for Rational z-Transforms (1 of 2) 1.The ROC is a ring or a disk in the z-plane centered at the origin.
20/06/2017 · Take the Full Course of Digital Signal Processing What we Provide 1)25 Videos (Index is given down) Update will be Coming Before final exams …
–The sum of the series may not be converge for all z. •Region of convergence (ROC) –Since the z-transform can be interpreted as the Fourier transform, it is possible for the z-transform to converge
The z-Transform and Its Properties3.1 The z-Transform Region of Convergence Ithe region of convergence (ROC) of X(z) is the set of all values of z for which X(z) attains a nite value The z-Transform is, therefore, uniquely characterized by: 1.expression for X(z) 2.ROC of X(z) Professor Deepa Kundur (University of Toronto)The z-Transform and Its Properties4 / 20. The z-Transform …
Region of Convergence(RoC) Region of Convergence for a discrete time signal x[n] is de ned as a continuous region in z plane where the Z-Transform converges.
Region of Convergence and Examples Whether the z-transform of a signal exists depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. exists if and only if the argument is inside the region of convergence (ROC) in the z-plane, which is composed of all values for the summation of the Z-transform to converge.
DSP: z-Transform Region of Convergence Region of Convergence Example 1P: x[n] = u[n]. The ROC is all z2C such that 1 n=0 jzj n 1.
Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and Z Transform, Signal & Systems notes for Electrical Engineering (EE) is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Electrical Engineering (EE).
The z-transform expression is the same as for example 1. However, the region of convergence However, the region of convergence is opposite; the ROC is formed by the inside of a circle:
26/04/2012 · Introduction to Laplace Transform 25. Region of Convergence of Laplace Transform & Properties of Laplace Transform 26. Properties of Laplace Transform (Contd.) 27. Concluding Discission on Laplace
The z-transform is a very important tool in describing and analyzing digital systems. It offers the techniques for digital filter design and frequency analysis of digital signals. f f n X ( ) x[n]z n Definition of z-transform: For causal sequence, x(n) = 0, n< 0: Where z is a complex variable All the values of z that make the summation to exist form a region of convergence. CEN352, Dr
called the region of convergence (ROC) Rational z-Transforms • Observe that the magnitude plot exhibits very large peaks around the points which are the poles of G(z) • It also exhibits very narrow and deep wells around the location of the zeros at z = 0
Should DSP Undergraduate Students Study z-Transform
The z-Transform and Its Application
–The sum of the series may not be converge for all z. •Region of convergence (ROC) –Since the z-transform can be interpreted as the Fourier transform, it is possible for the z-transform to converge
DSP: Properties of the z-Transform Region of Convergence ROC Properties for Rational z-Transforms (1 of 2) 1.The ROC is a ring or a disk in the z-plane centered at the origin.
called the region of convergence (ROC) Rational z-Transforms • Observe that the magnitude plot exhibits very large peaks around the points which are the poles of G(z) • It also exhibits very narrow and deep wells around the location of the zeros at z = 0
22 The z-Transform Recommended Problems P22.1 An LTI system has an impulse response h[n] for which the z-transform is H Determine what can be inferred about the associated region of convergence from each of the following statements. (a) x[n] is right-sided. (b
X ( z) 1 1 z 1 az 1 1 a z a z Region of convergence When. Ghulam Muhammad King Saud University 3 . az 1 1 z a CEN352. Therefore.Example 2 Problem: Given the sequence. Dr. Solution: find the z transform of x(n).
region of convergence of z transform – why bother. Started by December 11, 2018. Chronological; Newest First; Yes I understand the theory, left handed and right-handed sequences. we can= have two z transfer functions the same but one is left hand sided and the = other right. A great deal is spent explaining this but exactly what is the use in the fi= rst place of left-handed sequences as they
comp.dsp region of convergence of z transform why bother
z Transform Scribd
A sequence ( ) with the z – transform 𝑋(𝑧)=𝑧4 𝑧2−2𝑧 2−3𝑧−4is applied as an input to a linear time – variant system with the impulse response ℎ( )=2𝛿( −3)where
One must consider the Region of Convergence (ROC) of the Z-transform, because left-sided and right-sided time functions will have the same Z-transform
The z-transform is a very important tool in describing and analyzing digital systems. It offers the techniques for digital filter design and frequency analysis of digital signals. f f n X ( ) x[n]z n Definition of z-transform: For causal sequence, x(n) = 0, n< 0: Where z is a complex variable All the values of z that make the summation to exist form a region of convergence. CEN543, Dr
EE264 Oct 8, 2004 Fall 04-05 Supplemental Notes About the region of convergence of the z-transform The z-Transform of a sequencef[n] is defined as S(z) =
Clearly, the z-transform is a power series with an infinite number of terms and so may not converge for all values of z. The region where the z-transform converges is
Taking absolute convergence as the criterion for to exist, the so-called “region of convergence” (RoC) is generally stated to be of the form r-< z < r , e.g., , , , . When X (z) is a rational function, the inequality is strict, which means that the RoC is an open region.
3 Poles, Zeros, Regions of Convergence Example 1: In nite-length right-sided Consider the causal sequence: h1[n] = anu[n] This impulse response might be used to …
DSP: z-Transform Region of Convergence Region of Convergence Example 1P: x[n] = u[n]. The ROC is all z2C such that 1 n=0 jzj n 1.
The z-transform of a signal is an innite series for each possible value of z in the complex plane. Typically only some of those Typically only some of those innite series will converge.
DSP: Properties of the z-Transform Region of Convergence ROC Properties for Rational z-Transforms (1 of 2) 1.The ROC is a ring or a disk in the z-plane centered at the origin.
The z-transform is a very important tool in describing and analyzing digital systems. It offers the techniques for digital filter design and frequency analysis of digital signals. f f n X ( ) x[n]z n Definition of z-transform: For causal sequence, x(n) = 0, n< 0: Where z is a complex variable All the values of z that make the summation to exist form a region of convergence. CEN352, Dr
z Transform. Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding the relationship between . transform and Region of Convergence (ROC) ROC indicates when . transform of a sequence converges . Generally there exists some . such that (5.9)
19 rows · This assumes that the Fourier transform exists; i.e., that the axis is in the region of …
Module 4 : Laplace and Z Transform Lecture 31 : Z Transform and Region of Convergence Objectives: Scope of this lecture: We have already seen the implementation of Fourier Transform and Laplace Transform for the study of Continuous Time (C.T.) signals
Section 1.6 Z-Transform Purdue Engineering
Z Transform IASET US Academia.edu
20/06/2017 · Take the Full Course of Digital Signal Processing What we Provide 1)25 Videos (Index is given down) Update will be Coming Before final exams …
The z-transform region of convergence (ROC) for the Laurent series is chosen to be , where . Remark 9.2. The 9.1.4 Properties of the z-transform The following properties of z-transforms listed in Table 9.2 are well known in the field of digital signal analysis. The reader will be asked to prove some of these properties in the exercises. Exploration . Example 9.7. Given . Use convolution to
PPT – Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and Z Transform, Signal & Systems notes for Electrical Engineering (EE) is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Electrical Engineering (EE).
Inverse z-Transform Partial Fraction Method The z-transform of an exponential sequence x(k) = ak is given by X(z) = 1 1 −az−1 = z z −a. Any sequence that starts with a non-zero value at k = 0 usually
The z-Transform and Its Properties3.1 The z-Transform Region of Convergence Ithe region of convergence (ROC) of X(z) is the set of all values of z for which X(z) attains a nite value The z-Transform is, therefore, uniquely characterized by: 1.expression for X(z) 2.ROC of X(z) Professor Deepa Kundur (University of Toronto)The z-Transform and Its Properties4 / 20. The z-Transform …
15/02/2017 · The region of Z magnitude (|Z|) for which x(n).|Z|-n is absolutely summable 3. State the Initial value and final value theorem with regard to Z-transform. 4. Define Z-transform of unit step signal. Z/(Z-1) ROCz|>1 5. What are the different methods available for inverse Zs-transform? Residue method, Partial fractions method, Long division method, Convolution integral method 6. When the z
Clearly, the z-transform is a power series with an infinite number of terms and so may not converge for all values of z. The region where the z-transform converges is
z Transform. Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding the relationship between . transform and Region of Convergence (ROC) ROC indicates when . transform of a sequence converges . Generally there exists some . such that (5.9)
The Region of Convergence for the Z Transform Important properties of the ROC of the z−transform: 1. The ROC of X(z) consists of a ring in the z−plane centered about the origin 2. The ROC does not contain any poles 3. If x[n] is of finite-duration, then the ROC is the entire z−plane, except possibly at z = 0 and/or z = ∞ zA finite-duration sequence is a sequence that is nonzero in a
Region of Convergence (ROC) – Learn Signals and Systems in simple and easy steps starting from Overview, Signal Analysis, Fourier Series, Fourier Transforms, Convolution Correlation, Sampling, Laplace Transforms, Z-Transforms.
Chapter 6 The Z-Transform – University of California
Z Transform and Region of Convergence Laplace and Z
A sequence ( ) with the z – transform 𝑋(𝑧)=𝑧4 𝑧2−2𝑧 2−3𝑧−4is applied as an input to a linear time – variant system with the impulse response ℎ( )=2𝛿( −3)where
called the region of convergence (ROC) Rational z-Transforms • Observe that the magnitude plot exhibits very large peaks around the points which are the poles of G(z) • It also exhibits very narrow and deep wells around the location of the zeros at z = 0
For X(z) with N poles of different radius, there are N 1 possible ROC in general, with N 1 corresponding signals x(n). But only one x(n) signal will be right-sided:
–The sum of the series may not be converge for all z. •Region of convergence (ROC) –Since the z-transform can be interpreted as the Fourier transform, it is possible for the z-transform to converge
The z-transform is a very important tool in describing and analyzing digital systems. It offers the techniques for digital filter design and frequency analysis of digital signals. f f n X ( ) x[n]z n Definition of z-transform: For causal sequence, x(n) = 0, n< 0: Where z is a complex variable All the values of z that make the summation to exist form a region of convergence. CEN543, Dr
Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and Z Transform, Signal & Systems notes for Electrical Engineering (EE) is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Electrical Engineering (EE).
X ( z) 1 1 z 1 az 1 1 a z a z Region of convergence When. Ghulam Muhammad King Saud University 3 . az 1 1 z a CEN352. Therefore.Example 2 Problem: Given the sequence. Dr. Solution: find the z transform of x(n).
2-Consider the z-transform X(z) whose pole-zero plot is as shown in figure 1. (a) Determine the ROC of X(z) if it is known that the Fourier transform exists. For this case,
Organization 1: Introduction • Organization • Signals • Processing • Syllabus • Sequences • Time Scaling • z-Transform • Region of Convergence
Z Transform and Region of Convergence Laplace and Z
About the region of convergence of the z-transform
Organization 1: Introduction • Organization • Signals • Processing • Syllabus • Sequences • Time Scaling • z-Transform • Region of Convergence
Clearly, the z-transform is a power series with an infinite number of terms and so may not converge for all values of z. The region where the z-transform converges is
Laplace Transforms • Definition • Region of convergence • Useful properties • Inverse & partial fraction expansion • Distinct, complex, & repeated poles
Region of Convergence (ROC) Whether the Laplace transform of a signal exists or not depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. All complex values of for which the integral in the definition converges form a region of convergence (ROC) in the s-plane.
The discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) (not to be confused with the discrete Fourier transform (DFT)) is a special case of such a Z-transform obtained by restricting z to lie on the unit circle. [ edit ] Region of convergence
19 rows · This assumes that the Fourier transform exists; i.e., that the axis is in the region of …
The z-transform is a very important tool in describing and analyzing digital systems. It offers the techniques for digital filter design and frequency analysis of digital signals. f f n X ( ) x[n]z n Definition of z-transform: For causal sequence, x(n) = 0, n< 0: Where z is a complex variable All the values of z that make the summation to exist form a region of convergence. CEN543, Dr
X ( z) 1 1 z 1 az 1 1 a z a z Region of convergence When. Ghulam Muhammad King Saud University 3 . az 1 1 z a CEN352. Therefore.Example 2 Problem: Given the sequence. Dr. Solution: find the z transform of x(n).
The z-transform region of convergence (ROC) for the Laurent series is chosen to be , where . Remark 9.2. The 9.1.4 Properties of the z-transform The following properties of z-transforms listed in Table 9.2 are well known in the field of digital signal analysis. The reader will be asked to prove some of these properties in the exercises. Exploration . Example 9.7. Given . Use convolution to
One must consider the Region of Convergence (ROC) of the Z-transform, because left-sided and right-sided time functions will have the same Z-transform
Region of Convergence The z-transform of x(n) can be viewed as the Fourier transform of x(n) multiplied by an exponential z n The power series for the z-transform is called a Laurent series: The Laurent series, and therefore the z-transform, represents an analytic function at every point inside the region of convergence, and therefore the z- transform and all its derivatives must be
ELEC361 Signals And Systems Topic 10 The Z Transform
Region of Convergence for the Z-transform
Region of Convergence (ROC) – Learn Signals and Systems in simple and easy steps starting from Overview, Signal Analysis, Fourier Series, Fourier Transforms, Convolution Correlation, Sampling, Laplace Transforms, Z-Transforms.
region of convergence of z transform – why bother. Started by December 11, 2018. Chronological; Newest First; Yes I understand the theory, left handed and right-handed sequences. we can= have two z transfer functions the same but one is left hand sided and the = other right. A great deal is spent explaining this but exactly what is the use in the fi= rst place of left-handed sequences as they
The Region of Convergence for the Z Transform Important properties of the ROC of the z−transform: 1. The ROC of X(z) consists of a ring in the z−plane centered about the origin 2. The ROC does not contain any poles 3. If x[n] is of finite-duration, then the ROC is the entire z−plane, except possibly at z = 0 and/or z = ∞ zA finite-duration sequence is a sequence that is nonzero in a
z Transform. Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding the relationship between . transform and Region of Convergence (ROC) ROC indicates when . transform of a sequence converges . Generally there exists some . such that (5.9)
1. The z-Transform (c.2) Region of Convergence For any given sequence, the set of values of z for which the z-transform converges is called the region of convergence.
Clearly, the z-transform is a power series with an infinite number of terms and so may not converge for all values of z. The region where the z-transform converges is
The range of variation of z for which z-transform converges is called region of convergence of z-transform. Properties of ROC of Z-Transforms ROC of z-transform is indicated with circle in z-plane.
An introduction to Z Transform is the topic of this paper. It deals with a review of what Z Transform means and what does the specific region of convergence represent. A pictorial representation of the region of convergence has been sketched. Most of
Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and Z Transform, Signal & Systems notes for Electrical Engineering (EE) is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Electrical Engineering (EE).
The z-Transform and Its Properties3.1 The z-Transform Region of Convergence Ithe region of convergence (ROC) of X(z) is the set of all values of z for which X(z) attains a nite value The z-Transform is, therefore, uniquely characterized by: 1.expression for X(z) 2.ROC of X(z) Professor Deepa Kundur (University of Toronto)The z-Transform and Its Properties4 / 20. The z-Transform …
29. Properties of Z Transform YouTube
Region of Convergence (ROC) Harvey Mudd College
Z-transform For standard z-score in statistics, see Standard score. For Fisher z-transformation in statistics, see Fisher transformation. In mathematics and signal processing,…
2-Consider the z-transform X(z) whose pole-zero plot is as shown in figure 1. (a) Determine the ROC of X(z) if it is known that the Fourier transform exists. For this case,
21 Lecture Notes by Hua Properties of ROC of the Z-Transform • ROC is a ring or disk centered at the origin • Fourier transform converges absolutely iff ROC
Chapter 3: The z-Transform and Its Application Region of Convergence: r 1 <r 2 Dr. Deepa Kundur (University of Toronto)The z-Transform and Its Application9 / 36
Region of Convergence (ROC) – Learn Signals and Systems in simple and easy steps starting from Overview, Signal Analysis, Fourier Series, Fourier Transforms, Convolution Correlation, Sampling, Laplace Transforms, Z-Transforms.
20/06/2017 · Take the Full Course of Digital Signal Processing What we Provide 1)25 Videos (Index is given down) Update will be Coming Before final exams …
LaplaceTransform: Definition and Region of Convergence Yao Wang Polytechnic University Some slides included are extracted from lecture notes from MIT open courseware
In today’s class… Z-transform Unilateral Z-transform Bilateral Z-transform Region of Convergence Inverse Z-transform Power Series method
The range of variation of z for which z-transform converges is called region of convergence of z-transform. Properties of ROC of Z-Transforms ROC of z-transform is indicated with circle in z-plane.
Given a time signal x[n], the region of convergence (ROC) of its z-transform X(z) is the set of z2C such that X(z) converges, that is, the set of z2C such that x[n]z is absolutely summablen
The region of convergence, known as the ROC, is important to understand because it defines the region where the z-transform exists. The z-transform of a sequence is defined as X z = ∑ n = − ∞ ∞ x n z − n X z n x n z n
PYKC 3-Mar-11 E2.5 Signals & Linear Systems Lecture 15 Slide 5 Example of z-transform (1) Find the z-transform for the signal γnu[n], where γ is a constant.
Chapter 6 The Z-Transform – University of California
z-transform Stanford University
5.2 Unilateral (one-sided) z-transform 101 Figure 5.1: A typical region of convergence (ROC) for a unilateral z-transform. The radius of convergence,
15/02/2017 · The region of Z magnitude (|Z|) for which x(n).|Z|-n is absolutely summable 3. State the Initial value and final value theorem with regard to Z-transform. 4. Define Z-transform of unit step signal. Z/(Z-1) ROCz|>1 5. What are the different methods available for inverse Zs-transform? Residue method, Partial fractions method, Long division method, Convolution integral method 6. When the z
Chapter 3: The z-Transform and Its Application Region of Convergence: r 1 <r 2 Dr. Deepa Kundur (University of Toronto)The z-Transform and Its Application9 / 36
The range of variation of z for which z-transform converges is called region of convergence of z-transform. Properties of ROC of Z-Transforms ROC of z-transform is indicated with circle in z-plane.
Region of Convergence and Examples Whether the z-transform of a signal exists depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. exists if and only if the argument is inside the region of convergence (ROC) in the z-plane, which is composed of all values for the summation of the Z-transform to converge.
1 − 21 z −1 1 13 z −1 (z − 21 )(z 13 ) The pole-zero plot and region of convergence of the signal is z−plane Im unit circle 1 Re 1 − 31 1 12 2 Example: finite length sequence The signal an 0≤n≤N −1 x[n] = 0 otherwise has z-transform N X −1 N X −1 n −n X(z) = a z = (az −1 )n n=0 n=0 1 − (az −1 )N 1 z N − aN = = . 1 − az −1 z N −1 z − a Since there are
Z transfrm ppt 1. THE z-TRANSFORM SWATI MISHRA 1 2. CONTENTS • z-transform • Region Of Convergence • Properties Of Region Of Convergence • z-transform Of Common Sequence • Properties And Theorems • Application • Inverse z- Transform • z-transform …
Inverse z-Transform Partial Fraction Method The z-transform of an exponential sequence x(k) = ak is given by X(z) = 1 1 −az−1 = z z −a. Any sequence that starts with a non-zero value at k = 0 usually
Discrete-Time Signal Representation with z Transform . Apart from discretetime Fourier transform (DTFT), we can – also use Region of Convergence (ROC) ROC indicates when . transform of a sequence converges. Generally there exists some . such that
The Region of Convergence for the Z Transform Important properties of the ROC of the z−transform: 1. The ROC of X(z) consists of a ring in the z−plane centered about the origin 2. The ROC does not contain any poles 3. If x[n] is of finite-duration, then the ROC is the entire z−plane, except possibly at z = 0 and/or z = ∞ zA finite-duration sequence is a sequence that is nonzero in a
Organization 1: Introduction • Organization • Signals • Processing • Syllabus • Sequences • Time Scaling • z-Transform • Region of Convergence
19 rows · This assumes that the Fourier transform exists; i.e., that the axis is in the region of …
convergence z−plane Im Region of Re In specific cases the inner radius of this ring may include the origin, and the outer radius may extend to infinity.
Region of Convergence The z-transform of x(n) can be viewed as the Fourier transform of x(n) multiplied by an exponential z n The power series for the z-transform is called a Laurent series: The Laurent series, and therefore the z-transform, represents an analytic function at every point inside the region of convergence, and therefore the z- transform and all its derivatives must be
The z-Transform and Its Properties3.1 The z-Transform Region of Convergence Ithe region of convergence (ROC) of X(z) is the set of all values of z for which X(z) attains a nite value The z-Transform is, therefore, uniquely characterized by: 1.expression for X(z) 2.ROC of X(z) Professor Deepa Kundur (University of Toronto)The z-Transform and Its Properties4 / 20. The z-Transform …
Digital Signal Processing Properties of the z-Transform
The z-Transform Central Web Server 2
The range of variation of z for which z-transform converges is called region of convergence of z-transform. Properties of ROC of Z-Transforms ROC of z-transform is indicated with circle in z-plane.
The region of convergence, known as the ROC, is important to understand because it defines the region where the z-transform exists. The z-transform of a sequence is defined as X z = ∑ n = − ∞ ∞ x n z − n X z n x n z n
The z-transform is a very important tool in describing and analyzing digital systems. It offers the techniques for digital filter design and frequency analysis of digital signals. f f n X ( ) x[n]z n Definition of z-transform: For causal sequence, x(n) = 0, n< 0: Where z is a complex variable All the values of z that make the summation to exist form a region of convergence. CEN352, Dr
X ( z) 1 1 z 1 az 1 1 a z a z Region of convergence When. Ghulam Muhammad King Saud University 3 . az 1 1 z a CEN352. Therefore.Example 2 Problem: Given the sequence. Dr. Solution: find the z transform of x(n).
EE264 Oct 8, 2004 Fall 04-05 Supplemental Notes About the region of convergence of the z-transform The z-Transform of a sequencef[n] is defined as S(z) =
PYKC 3-Mar-11 E2.5 Signals & Linear Systems Lecture 15 Slide 5 Example of z-transform (1) Find the z-transform for the signal γnu[n], where γ is a constant.
20/06/2017 · Take the Full Course of Digital Signal Processing What we Provide 1)25 Videos (Index is given down) Update will be Coming Before final exams …
The z-transform University of Cape Town
Lecture 31 Z Transform and Region of Convergence – NPTEL
The Transforms Relationship to Fourier Transform Region of Convergence Convergence, continued Some Special Functions Convolution, Unit Step Poles and Zeros Example Convergence of Finite Sequences Inverse z-Transform Properties z-transforms are linear: The transform of a shifted sequence: Multiplication: But multiplication will affect the region of convergence and all the pole …
Given a time signal x[n], the region of convergence (ROC) of its z-transform X(z) is the set of z2C such that X(z) converges, that is, the set of z2C such that x[n]z is absolutely summablen
Clearly, the z-transform is a power series with an infinite number of terms and so may not converge for all values of z. The region where the z-transform converges is
Taking absolute convergence as the criterion for to exist, the so-called “region of convergence” (RoC) is generally stated to be of the form r-< z < r , e.g., , , , . When X (z) is a rational function, the inequality is strict, which means that the RoC is an open region.
In signal processing, a discrete time domain signal is converted into a complex frequency domain representation using Z transformation. Mathematically the Region of Convergence (ROC) is the set of all the points in the complex plane for which the Z transform summation converges.
Z-transform Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
EE 123 Digital Signal Processing Spring 2007 Lecture 5
15/02/2017 · The region of Z magnitude (|Z|) for which x(n).|Z|-n is absolutely summable 3. State the Initial value and final value theorem with regard to Z-transform. 4. Define Z-transform of unit step signal. Z/(Z-1) ROCz|>1 5. What are the different methods available for inverse Zs-transform? Residue method, Partial fractions method, Long division method, Convolution integral method 6. When the z
19 rows · This assumes that the Fourier transform exists; i.e., that the axis is in the region of …
20/06/2017 · Take the Full Course of Digital Signal Processing What we Provide 1)25 Videos (Index is given down) Update will be Coming Before final exams …
Region of Convergence (ROC) Whether the Laplace transform of a signal exists or not depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. All complex values of for which the integral in the definition converges form a region of convergence (ROC) in the s-plane.
Region of Convergence and Examples Whether the z-transform of a signal exists depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. exists if and only if the argument is inside the region of convergence (ROC) in the z-plane, which is composed of all values for the summation of the Z-transform to converge.
Region of Convergence (ROC) – Learn Signals and Systems in simple and easy steps starting from Overview, Signal Analysis, Fourier Series, Fourier Transforms, Convolution Correlation, Sampling, Laplace Transforms, Z-Transforms.
An introduction to Z Transform is the topic of this paper. It deals with a review of what Z Transform means and what does the specific region of convergence represent. A pictorial representation of the region of convergence has been sketched. Most of
3 Poles, Zeros, Regions of Convergence Example 1: In nite-length right-sided Consider the causal sequence: h1[n] = anu[n] This impulse response might be used to …
The Transforms Relationship to Fourier Transform Region of Convergence Convergence, continued Some Special Functions Convolution, Unit Step Poles and Zeros Example Convergence of Finite Sequences Inverse z-Transform Properties z-transforms are linear: The transform of a shifted sequence: Multiplication: But multiplication will affect the region of convergence and all the pole …
comp.dsp region of convergence of z transform why bother
Convergence Region of Z-transform 國立臺灣大學
DSP: z-Transform Region of Convergence Region of Convergence Example 1P: x[n] = u[n]. The ROC is all z2C such that 1 n=0 jzj n 1.
The z-transform of a signal is an innite series for each possible value of z in the complex plane. Typically only some of those Typically only some of those innite series will converge.
z Transform. Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding the relationship between . transform and Region of Convergence (ROC) ROC indicates when . transform of a sequence converges . Generally there exists some . such that (5.9)
In today’s class… Z-transform Unilateral Z-transform Bilateral Z-transform Region of Convergence Inverse Z-transform Power Series method
z Transform Electrical Engineering Mathematical Analysis
The z-Transform Central Web Server 2 – UITS
Region of Convergence and Examples Whether the z-transform of a signal exists depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. exists if and only if the argument is inside the region of convergence (ROC) in the z-plane, which is composed of all values for the summation of the Z-transform to converge.
The discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) (not to be confused with the discrete Fourier transform (DFT)) is a special case of such a Z-transform obtained by restricting z to lie on the unit circle. [ edit ] Region of convergence
The professors spend a fair amount of classroom time deriving the z-transform of various infinite-length sequences, drawing the transforms’ poles on the z-plane, and discussing for what values of z the transforms exist (i.e., the z-plane region of convergence where a z-transform converges to values less than infinity).
26/04/2012 · Introduction to Laplace Transform 25. Region of Convergence of Laplace Transform & Properties of Laplace Transform 26. Properties of Laplace Transform (Contd.) 27. Concluding Discission on Laplace
Z transfrm ppt 1. THE z-TRANSFORM SWATI MISHRA 1 2. CONTENTS • z-transform • Region Of Convergence • Properties Of Region Of Convergence • z-transform Of Common Sequence • Properties And Theorems • Application • Inverse z- Transform • z-transform …
Lecture 31 Z Transform and Region of Convergence – NPTEL
The z-Transform Central Web Server 2 – UITS
The z-transform of a signal is an innite series for each possible value of z in the complex plane. Typically only some of those Typically only some of those innite series will converge.
Module 4 : Laplace and Z Transform Lecture 31 : Z Transform and Region of Convergence Objectives: Scope of this lecture: We have already seen the implementation of Fourier Transform and Laplace Transform for the study of Continuous Time (C.T.) signals
Given a time signal x[n], the region of convergence (ROC) of its z-transform X(z) is the set of z2C such that X(z) converges, that is, the set of z2C such that x[n]z is absolutely summablen
22 The z-Transform Recommended Problems P22.1 An LTI system has an impulse response h[n] for which the z-transform is H Determine what can be inferred about the associated region of convergence from each of the following statements. (a) x[n] is right-sided. (b
Z transfrm ppt 1. THE z-TRANSFORM SWATI MISHRA 1 2. CONTENTS • z-transform • Region Of Convergence • Properties Of Region Of Convergence • z-transform Of Common Sequence • Properties And Theorems • Application • Inverse z- Transform • z-transform …
1 − 21 z −1 1 13 z −1 (z − 21 )(z 13 ) The pole-zero plot and region of convergence of the signal is z−plane Im unit circle 1 Re 1 − 31 1 12 2 Example: finite length sequence The signal an 0≤n≤N −1 x[n] = 0 otherwise has z-transform N X −1 N X −1 n −n X(z) = a z = (az −1 )n n=0 n=0 1 − (az −1 )N 1 z N − aN = = . 1 − az −1 z N −1 z − a Since there are
The z-transform expression is the same as for example 1. However, the region of convergence However, the region of convergence is opposite; the ROC is formed by the inside of a circle:
3 Observations • Specification of the Z transform requires both algebraic expression and region of convergence • Rational Z-transforms are obtained if x[n]=linear
X ( z) 1 1 z 1 az 1 1 a z a z Region of convergence When. Ghulam Muhammad King Saud University 3 . az 1 1 z a CEN352. Therefore.Example 2 Problem: Given the sequence. Dr. Solution: find the z transform of x(n).
For X(z) with N poles of different radius, there are N 1 possible ROC in general, with N 1 corresponding signals x(n). But only one x(n) signal will be right-sided:
Organization 1: Introduction • Organization • Signals • Processing • Syllabus • Sequences • Time Scaling • z-Transform • Region of Convergence
called the region of convergence (ROC) Rational z-Transforms • Observe that the magnitude plot exhibits very large peaks around the points which are the poles of G(z) • It also exhibits very narrow and deep wells around the location of the zeros at z = 0
ELEC361 Signals And Systems Topic 10 The Z Transform
The z-Transform Central Web Server 2 – UITS
Z-transform For standard z-score in statistics, see Standard score. For Fisher z-transformation in statistics, see Fisher transformation. In mathematics and signal processing,…
3 Poles, Zeros, Regions of Convergence Example 1: In nite-length right-sided Consider the causal sequence: h1[n] = anu[n] This impulse response might be used to …
DSP: Properties of the z-Transform Region of Convergence ROC Properties for Rational z-Transforms (1 of 2) 1.The ROC is a ring or a disk in the z-plane centered at the origin.
One must consider the Region of Convergence (ROC) of the Z-transform, because left-sided and right-sided time functions will have the same Z-transform
The z-transform of a signal is an innite series for each possible value of z in the complex plane. Typically only some of those Typically only some of those innite series will converge.
X ( z) 1 1 z 1 az 1 1 a z a z Region of convergence When. Ghulam Muhammad King Saud University 3 . az 1 1 z a CEN352. Therefore.Example 2 Problem: Given the sequence. Dr. Solution: find the z transform of x(n).
Z transfrm ppt 1. THE z-TRANSFORM SWATI MISHRA 1 2. CONTENTS • z-transform • Region Of Convergence • Properties Of Region Of Convergence • z-transform Of Common Sequence • Properties And Theorems • Application • Inverse z- Transform • z-transform …
PPT – Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and Z Transform, Signal & Systems notes for Electrical Engineering (EE) is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Electrical Engineering (EE).
EE264 Oct 8, 2004 Fall 04-05 Supplemental Notes About the region of convergence of the z-transform The z-Transform of a sequencef[n] is defined as S(z) =
Region of Convergence (ROC) Whether the Laplace transform of a signal exists or not depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. All complex values of for which the integral in the definition converges form a region of convergence (ROC) in the s-plane.
Clearly, the z-transform is a power series with an infinite number of terms and so may not converge for all values of z. The region where the z-transform converges is
ELEC361 Signals And Systems Topic 10 The Z Transform
The z-Transform and Its Properties University of Toronto
Clearly, the z-transform is a power series with an infinite number of terms and so may not converge for all values of z. The region where the z-transform converges is
The Region of Convergence for the Z Transform Important properties of the ROC of the z−transform: 1. The ROC of X(z) consists of a ring in the z−plane centered about the origin 2. The ROC does not contain any poles 3. If x[n] is of finite-duration, then the ROC is the entire z−plane, except possibly at z = 0 and/or z = ∞ zA finite-duration sequence is a sequence that is nonzero in a
Region of Convergence (ROC) Whether the Laplace transform of a signal exists or not depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. All complex values of for which the integral in the definition converges form a region of convergence (ROC) in the s-plane.
I’m a novice in DSP and I have few doubts regarding the $mathcal Z$-transform and its region of convergence (ROC). I know what a $mathcal Z$-transform is. But I’m having trouble with understanding the ROC.
LaplaceTransform Definition and Region of Convergence
Z-transform Wikipedia the free encyclopedia
Chapter 3: The z-Transform and Its Application Region of Convergence: r 1 1 5. What are the different methods available for inverse Zs-transform? Residue method, Partial fractions method, Long division method, Convolution integral method 6. When the z
One must consider the Region of Convergence (ROC) of the Z-transform, because left-sided and right-sided time functions will have the same Z-transform
region of convergence of z transform – why bother. Started by December 11, 2018. Chronological; Newest First; Yes I understand the theory, left handed and right-handed sequences. we can= have two z transfer functions the same but one is left hand sided and the = other right. A great deal is spent explaining this but exactly what is the use in the fi= rst place of left-handed sequences as they
convergence z−plane Im Region of Re In specific cases the inner radius of this ring may include the origin, and the outer radius may extend to infinity.
How does the $mathcal Z$-transform’s “region of
The z-Transform Central Web Server 2
3 Poles, Zeros, Regions of Convergence Example 1: In nite-length right-sided Consider the causal sequence: h1[n] = anu[n] This impulse response might be used to …
–The sum of the series may not be converge for all z. •Region of convergence (ROC) –Since the z-transform can be interpreted as the Fourier transform, it is possible for the z-transform to converge
Discrete-Time Signal Representation with z Transform . Apart from discretetime Fourier transform (DTFT), we can – also use Region of Convergence (ROC) ROC indicates when . transform of a sequence converges. Generally there exists some . such that
PPT – Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and Z Transform, Signal & Systems notes for Electrical Engineering (EE) is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Electrical Engineering (EE).
The z-transform expression is the same as for example 1. However, the region of convergence However, the region of convergence is opposite; the ROC is formed by the inside of a circle:
Lecture 31 Z Transform and Region of Convergence – NPTEL
22 The z-Transform Walter Scott Jr. College of Engineering
An introduction to Z Transform is the topic of this paper. It deals with a review of what Z Transform means and what does the specific region of convergence represent. A pictorial representation of the region of convergence has been sketched. Most of
Laplace Transforms • Definition • Region of convergence • Useful properties • Inverse & partial fraction expansion • Distinct, complex, & repeated poles
22 The z-Transform Recommended Problems P22.1 An LTI system has an impulse response h[n] for which the z-transform is H Determine what can be inferred about the associated region of convergence from each of the following statements. (a) x[n] is right-sided. (b
because when z lies in this region, the series actually converges to the function (1.50). A slightly more accurate term would be “the region of definition”, since the z-transform is undefined outside of this region.
I’m a novice in DSP and I have few doubts regarding the $mathcal Z$-transform and its region of convergence (ROC). I know what a $mathcal Z$-transform is. But I’m having trouble with understanding the ROC.
region of convergence of z transform – why bother. Started by December 11, 2018. Chronological; Newest First; Yes I understand the theory, left handed and right-handed sequences. we can= have two z transfer functions the same but one is left hand sided and the = other right. A great deal is spent explaining this but exactly what is the use in the fi= rst place of left-handed sequences as they
The range of variation of z for which z-transform converges is called region of convergence of z-transform. Properties of ROC of Z-Transforms ROC of z-transform is indicated with circle in z-plane.
Z Transform and Region of Convergence – Laplace and Z Transform, Signal & Systems notes for Electrical Engineering (EE) is made by best teachers who have written some of the best books of Electrical Engineering (EE).
z Transform. Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding the relationship between . transform and Region of Convergence (ROC) ROC indicates when . transform of a sequence converges . Generally there exists some . such that (5.9)
The z-transform expression is the same as for example 1. However, the region of convergence However, the region of convergence is opposite; the ROC is formed by the inside of a circle:
The Transforms Relationship to Fourier Transform Region of Convergence Convergence, continued Some Special Functions Convolution, Unit Step Poles and Zeros Example Convergence of Finite Sequences Inverse z-Transform Properties z-transforms are linear: The transform of a shifted sequence: Multiplication: But multiplication will affect the region of convergence and all the pole …
convergence z−plane Im Region of Re In specific cases the inner radius of this ring may include the origin, and the outer radius may extend to infinity.
Region of Convergence and Examples Whether the z-transform of a signal exists depends on the complex variable as well as the signal itself. exists if and only if the argument is inside the region of convergence (ROC) in the z-plane, which is composed of all values for the summation of the Z-transform to converge.
The discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) (not to be confused with the discrete Fourier transform (DFT)) is a special case of such a Z-transform obtained by restricting z to lie on the unit circle. [ edit ] Region of convergence
Z-transform For standard z-score in statistics, see Standard score. For Fisher z-transformation in statistics, see Fisher transformation. In mathematics and signal processing,…
The Region of Convergence for the Z Transform Important properties of the ROC of the z−transform: 1. The ROC of X(z) consists of a ring in the z−plane centered about the origin 2. The ROC does not contain any poles 3. If x[n] is of finite-duration, then the ROC is the entire z−plane, except possibly at z = 0 and/or z = ∞ zA finite-duration sequence is a sequence that is nonzero in a
About the region of convergence of the z-transform
z Transform Department of EE
X ( z) 1 1 z 1 az 1 1 a z a z Region of convergence When. Ghulam Muhammad King Saud University 3 . az 1 1 z a CEN352. Therefore.Example 2 Problem: Given the sequence. Dr. Solution: find the z transform of x(n).
The z-Transform Central Web Server 2 – UITS
Section 1.6 Z-Transform Purdue Engineering
[The z – transform ] of a sequence [ ] is given by [ = 0.5 1−2𝑧−1. It is given that the Region of convergence of [ ] includes the unit circle. The value of [0]is (a) – 0.5 (b) 0 (c) 0.25 (d) 0.5 [GATE 2007: 2 Marks] Soln. Given ( ) of a sequence [ ] ( )= 0.5 1−2 𝑧−1 Above transform is for left handed sequence with ROC∶<2 Corresponding sequence is ( )=−(0.5)2−𝑛
The z-transform University of Cape Town
Z-Transform Problems & Solutions Mahabeer Singh Kundal
DSP & Digital Filters Faculty of Engineering
26/04/2012 · Introduction to Laplace Transform 25. Region of Convergence of Laplace Transform & Properties of Laplace Transform 26. Properties of Laplace Transform (Contd.) 27. Concluding Discission on Laplace
Z Transform IASET US Academia.edu