Molecular structure pdf bond angle
molecular structure because the bond angles are easy to see. A space-filling model, which shows atoms as spheres and bonds as the penetration of two spheres into one another,
Secl2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Secl2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
Seof2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Seof2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry. Knowing the arrangement of atoms, distribution of electrons, and the shape of the molecule is vastly important in chemistry.
electron and molecular geometry, bond angles, and the VBT hybridization. You should find the Figure 2 You should find the Figure 2 and the on the following page to be helpful.
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.
a few kelvin, there are considerable oscillations (< ps) in the hydrogen bond length and angles [591]. The potential energy surface [1668] and wagging vibration [1743] of the water dimer have been described and molecular orbitals of the water dimer are shown on another page.
Molecular Geometry Lewis structures are good for figuring out how atoms are bonded to each other within a molecule and where any lone pairs of electrons are. They’re quite flexible in terms of how the atoms can be arranged on the page: bond length and angles between bonds don’t necessarily have to match reality. On the other hand, the information you write down in a Lewis structure is
Since experimental evidence indicates that this molecule is bent (bond angle 120º) and has equal length sulfur : oxygen bonds (1.432 Å), a single formula is inadequate, and the actual structure resembles an average of the two formulas.
header.jpg Molecular Geometry Worksheet As you work through the steps in the lab procedures, record your experimental values and the results on this worksheet.
The bond angle in NO$_2$ is $approx 134^mathrm{o}$ and the NO bond length 120 pm, in $ce{N2O4}$ the N-N bond is very long 175 pm and the angle $approx 126^mathrm{o}$. Nitrogen dioxide is paramagnetic with the odd electron in the $sigma$ bonding sp$^2$ orbital in the ‘third’ lobe as it were with the O atoms occupying the other two.
There are three basic steps to determining the bond angles in a molecule: > 1. Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Assume that you must determine the bond angles in “BF”_3. “B” is less electronegative than “F”, so “B” becomes the central atom. If we have three “F” atoms, that means that we are going to use all three electrons from
Lewis structure, then the molecular geometry of the molecules. SO 3 SO 2 CH 4 SF4 PCl5 IF5 N H H H O H H H Cl H C Cl Cl Cl C H H O O C O Cl C Cl Cl Cl H H F S F F F F F. 27 Sigma and pi bonds All single bonds are referred to as ‘sigma’ bonds (σ-bonds). The electron density is concentrated along the bond axis. A multiple bond is made up of a combination of sigma and pi bonds (π-bonds
Molecular Structure SpringerLink
https://www.youtube.com/embed/AjWwHkAlPSo
Molecular structure and bond angles Yeah Chemistry
that the bond angle is in the vicinity of 108”. It looked possible to extend the dilu- It looked possible to extend the dilu- J. Mol. Structure, 10 (1971) 31-38
Molecular Geometry and Hybrid Orbitals + H-C-H bond angle 90o Molecular Geometry Why Should I Care About Molecular Geometry? •Chemical properties:
Molecular geometry optimization Calculation for determining the geometry of a molecule that consists in systematically varying the geometric variables (bond lengths, bond angles, dihedral angles) until an energy minimum is reached.
Check if the VSEPR shape of the molecule is correct by going to the database and examining the crystal structure (the refcode for the [PF 6] – structure is WINFAA). Measure the bond angles on the structure comparing them to the ideal VSEPR model angles in the table in the next section. Measure the bond angles on the [PF 6] – structure and and compare them to the ideal bond angles on an
Six Lewis dot structures can be constructed using one O atom, one F atom, and one N atom. Calculate the formal charges on the atoms in each and use the results to choose the resonance structure …
There are so many things to know about such as molecular geometry, Lewis structure, polarity, hybridization, as well as bond angles, but very little information available online. So in this article, I am going to solve all the confusions regarding of the Sulfur DiFluoride – SF2 molecular geometry .
Lewis Structures, Formal Charges, and Molecular Geometry As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry.
AP Chemistry Chapter 8 Answers – Zumdahl 8.113 The first step always is to draw a valid Lewis structure when predicting molecular structure. When resonance is possible, only one of the possible resonance structures is necessary to predict
For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4 . We can draw the Lewis structure …
C-C bond length in benzene is 140 pm and C-H bond length is 109 pm. The delocalized structure of benzene also accounts for the X-ray data (all C-C bond lengths equal) and the absence of the type of isomerism shown in Fig. 43.1.
The molecular structure of 1 is depicted in Fig. 1, and the bond distances and angles are listed in Table 2. The local geometry of the cobalt ion is an octahedral arrangement with two NCS groups in trans position (N(3)–Co–N(3)′=177.1(2)°) and four pyridine units in a basal plane.
The Valence-Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model •The valence-shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) molecular structure of methane. The tetrahedral arrangement of electron pairs produces a tetrahedral arrangement of hydrogen atoms. Predicting Molecular Geometry • The following rules and figures will help discern electron pair arrangements. 1. Draw the Lewis structure 2. Determine how
Molecular geometry or molecular structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is important to be able to predict and understand the molecular structure of a molecule because many of the properties of a substance are determined by its geometry.
What would be the molecular structure and bond angle of selenium dioxide? If it satisfies the octet rule..which I think it does…Selenium is in the middle and a double bond to …

Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space (). A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common
PCL3 Molecular Electron Geometry, Lewis Structure, Bond Angles and Hybridization by Janice Powell · Published February 7, 2018 · Updated March 8, 2018 PCL3 – Phosphorus Trichloride is a chemical formula of phosphorus and chlorine.
Name _____ Period ___ Bonding, Nomenclature & Molecular Structure . MOLECULAR GEOMETRY . For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis …
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle.
bond, which is shorter than a single bond. The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently bond molecule.
The Lewis structure is drawn with the atoms all in the same plane. As shown in Figure 9.1, however, the actual three-dimensional arrangement has the Cl atoms at the corners of a . tetrahedron, a geometric object with four corners and four faces, each an equilateral triangle. The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles, the angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms
Liquid and solid water. Ice, like all solids, has a well-defined structure; each water molecule is surrounded by four neighboring H 2 Os. two of these are hydrogen-bonded to the oxygen atom on the central H 2 O molecule, and each of the two hydrogen atoms …
polarity, we need to predict molecular shapes Lewis dot structure provides 2D sketch of the distribution of the valence electrons among bonds between atoms and lone pairs; it provides no information about the shape of the molecule . A hierarchy of models VSEPR Consider the problem in terms of electrostatic repulsion between groups of electrons (charge clouds, domains) Valence bond theory
In carbene: Electronic configuration and molecular structure. The bond angle for the singlet state, however, is predicted to be larger than that for the triplet state.
Bond angle(s) 90° μ (Polarity) 0: Structure of cisplatin, an example of a molecule with the square planar coordination geometry. The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners of a square …
https://www.youtube.com/embed/Ui1JWIpFajo
[PDF] Seof2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle
Molecular Structure Topics 3-D structure shape (location of atoms in space) Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbitals Multiple Bonds
of bonds. For example, in the structure below, N has 3 charge clouds (2 atoms + 1 lone pair), C has 3 charge clouds (3 atoms), and O has 4 charge clouds (2 atoms + 2 lone pairs). # of charge # atoms + # lp on central atom Hybrid- zation Sketch Molecular Geometry & approx.. bond angle Example 2 2 atoms sp linear bond angle = 180° H–C≡N: 2 1 atom + 1 lp sp linear bond angle = N/A :N≡N: 3
10/01/2018 · In this video I explain the following Bond Parameters 1. Bond Length 2. Bond Angle.
Chapter 7 Practice Worksheet: Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure 1) How are ionic bonds and covalent bonds different? Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another; Covalent bonds result from two atoms sharing electrons. 2) Describe the relationship between the length of a bond and the strength of that bond. Strength of a bond increases as the bond gets shorter
Molecular Geometry PURPOSE A To explore some simple molecular structures. B To explore the relationship between bond order and bond length. C To explore resonance structures. GOALS 1 To compare Lewis structures to three-dimensional models. 2 To visualize the three-dimensional structures of some common molecules. 3 To obtain bond angle, bond length, and hybridization data for …the best guide to meditation pdfThis is used to predict the shapes of simple molecules and ions by considering the repulsions between pairs of electrons (lone pair and bond pair) within the molecule. It states that, “The shape adopted is the one which keeps repulsive forces to a minimum” To determine the shape, count up the number of covalent bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom and work out the shape which
Bond angles and other aspects of molecular geometry don’t follow associative rules – you have 3 different molecules, so 3 different structures. You can add a 4th – $ce{H2O}$ – with a bond angle of 104.5$^{circ}$ to extend your comparison.
Ch 4 The shape of molecules 2(14) the structure in which the repulsion among four electron pairs is minimal is not a square with bond angles of 90° but a tetrahedron with bond angles of 109.5 °, definitely larger than 90 °.
Molecular geometry is the spatial arrangements of atoms that are bonded in a molecule. Several relationships govern geometry including bonding, electron stability, and atomic size. Several relationships govern geometry including bonding, electron stability, and atomic size.
The VSEPR model of molecular geometry 1031 I ) I, x- 6 X 5″a./6 = 109.5 1 Fig. 13. The mean angle of all six angles in tetrahedral configurations. Fig. 12. The bond arrangement of an AX3B molecule with C2,. symmetry. virtue of the molecular symmetry. For example, the E–P–F angle of the PF3 (i.e. EPF3) molecule can be calculated from the F–P–F bond angle by virtue of the C3,. symmetry of
29/04/2015 · This video shows you how to draw the lewis structure for CH2Cl2. It provides the molecular geometry and bond angle for the CH2Cl2 (dichloromethane) lewis dot structure.
Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding Lewis structures: a review Lewis Theory 3.1 The octet rule All elements except hydrogen ( hydrogen have a duet of electrons) have octet of electrons once
Determination of Molecular Structure by MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY Much of what we know about molecular structur e has been learned by observing and analyzing how electromagnetic radiation interacts with matter . Spectroscopy is the observation and analysis of this interaction. Electromagnetic radiation is energy, and when electromagnetic radiation is absorbed by molecules, the molecules gain …
The VSEPR theory predicts a see-saw structure with a bond angle of 120 between the S and equatorial F’s and a bond angle of 180 between the S and the axial F’s. The bond angle is actually 102 for the S
For example, in a molecule such as CH 2 O (AX 3), whose structure is shown below, the double bond repels the single bonds more strongly than the single bonds repel each other. This causes a deviation from ideal geometry (an H–C–H bond angle of 116.5° rather than 120°).
Ch 4 The shape of molecules Soka
The bond angles and bond lengths of a molecule or ion dictate the particular geometry of the species. Lewis structures are two-dimensional representations of a molecule but because molecules are three dimensional, a picture of the molecular geometry must convey …
Molecular Geometry Introduction ThoughtCo
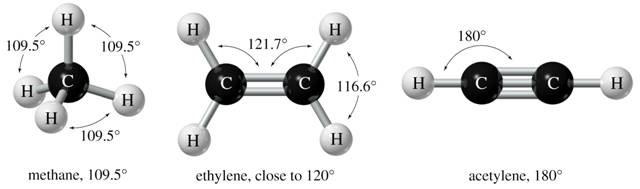
Chem 121 Determination of Molecular Geometry
https://www.youtube.com/embed/jWZKZojacPY
Lewis Structures Molecular Geometry Bond Angle and more
PCL3 Molecular Electron Geometry Lewis Structure Bond
[PDF] Secl2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle
shiva an introduction devdutt pattanaik pdf


https://www.youtube.com/embed/9MLOgywe84k
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF NITROGEN TRICHLORIDE AS DETER-
Bonding Geometry and The Polarity of Molecules
Molecular Geometry WebAssign
Molecular Structure and Polarity · Chemistry
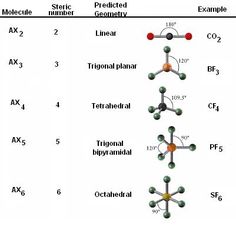
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory ctlsfasu
https://www.youtube.com/embed/PeY_sihSh8E
Sf2 Molecular Geometry Lewis Structure Polarity and Bond
Bonding Geometry and The Polarity of Molecules
Molecular Structure University of Tennessee at Chattanooga
Seof2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Seof2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
that the bond angle is in the vicinity of 108”. It looked possible to extend the dilu- It looked possible to extend the dilu- J. Mol. Structure, 10 (1971) 31-38
Check if the VSEPR shape of the molecule is correct by going to the database and examining the crystal structure (the refcode for the [PF 6] – structure is WINFAA). Measure the bond angles on the structure comparing them to the ideal VSEPR model angles in the table in the next section. Measure the bond angles on the [PF 6] – structure and and compare them to the ideal bond angles on an
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle.
The molecular structure of 1 is depicted in Fig. 1, and the bond distances and angles are listed in Table 2. The local geometry of the cobalt ion is an octahedral arrangement with two NCS groups in trans position (N(3)–Co–N(3)′=177.1(2)°) and four pyridine units in a basal plane.
For example, in a molecule such as CH 2 O (AX 3), whose structure is shown below, the double bond repels the single bonds more strongly than the single bonds repel each other. This causes a deviation from ideal geometry (an H–C–H bond angle of 116.5° rather than 120°).
The Lewis structure is drawn with the atoms all in the same plane. As shown in Figure 9.1, however, the actual three-dimensional arrangement has the Cl atoms at the corners of a . tetrahedron, a geometric object with four corners and four faces, each an equilateral triangle. The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles, the angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms
For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4 . We can draw the Lewis structure …
Secl2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Secl2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
Bond angle(s) 90° μ (Polarity) 0: Structure of cisplatin, an example of a molecule with the square planar coordination geometry. The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners of a square …
a few kelvin, there are considerable oscillations (< ps) in the hydrogen bond length and angles [591]. The potential energy surface [1668] and wagging vibration [1743] of the water dimer have been described and molecular orbitals of the water dimer are shown on another page.
Molecular Geometry PURPOSE A To explore some simple molecular structures. B To explore the relationship between bond order and bond length. C To explore resonance structures. GOALS 1 To compare Lewis structures to three-dimensional models. 2 To visualize the three-dimensional structures of some common molecules. 3 To obtain bond angle, bond length, and hybridization data for …
of bonds. For example, in the structure below, N has 3 charge clouds (2 atoms 1 lone pair), C has 3 charge clouds (3 atoms), and O has 4 charge clouds (2 atoms 2 lone pairs). # of charge # atoms # lp on central atom Hybrid- zation Sketch Molecular Geometry & approx.. bond angle Example 2 2 atoms sp linear bond angle = 180° H–C≡N: 2 1 atom 1 lp sp linear bond angle = N/A :N≡N: 3
Structure of Benzene Chemistry Assignment
Molecular Structure Exercises
that the bond angle is in the vicinity of 108”. It looked possible to extend the dilu- It looked possible to extend the dilu- J. Mol. Structure, 10 (1971) 31-38
Molecular Structure Topics 3-D structure shape (location of atoms in space) Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbitals Multiple Bonds
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space (). A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common
The bond angle in NO$_2$ is $approx 134^mathrm{o}$ and the NO bond length 120 pm, in $ce{N2O4}$ the N-N bond is very long 175 pm and the angle $approx 126^mathrm{o}$. Nitrogen dioxide is paramagnetic with the odd electron in the $sigma$ bonding sp$^2$ orbital in the ‘third’ lobe as it were with the O atoms occupying the other two.
Bond angles and other aspects of molecular geometry don’t follow associative rules – you have 3 different molecules, so 3 different structures. You can add a 4th – $ce{H2O}$ – with a bond angle of 104.5$^{circ}$ to extend your comparison.
Check if the VSEPR shape of the molecule is correct by going to the database and examining the crystal structure (the refcode for the [PF 6] – structure is WINFAA). Measure the bond angles on the structure comparing them to the ideal VSEPR model angles in the table in the next section. Measure the bond angles on the [PF 6] – structure and and compare them to the ideal bond angles on an
There are so many things to know about such as molecular geometry, Lewis structure, polarity, hybridization, as well as bond angles, but very little information available online. So in this article, I am going to solve all the confusions regarding of the Sulfur DiFluoride – SF2 molecular geometry .
header.jpg Molecular Geometry Worksheet As you work through the steps in the lab procedures, record your experimental values and the results on this worksheet.
Chapter 7 Practice Worksheet: Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure 1) How are ionic bonds and covalent bonds different? Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another; Covalent bonds result from two atoms sharing electrons. 2) Describe the relationship between the length of a bond and the strength of that bond. Strength of a bond increases as the bond gets shorter
molecular structure because the bond angles are easy to see. A space-filling model, which shows atoms as spheres and bonds as the penetration of two spheres into one another,
AP Chemistry Chapter 8 Answers – Zumdahl 8.113 The first step always is to draw a valid Lewis structure when predicting molecular structure. When resonance is possible, only one of the possible resonance structures is necessary to predict
Molecular geometry optimization Calculation for determining the geometry of a molecule that consists in systematically varying the geometric variables (bond lengths, bond angles, dihedral angles) until an energy minimum is reached.
of bonds. For example, in the structure below, N has 3 charge clouds (2 atoms 1 lone pair), C has 3 charge clouds (3 atoms), and O has 4 charge clouds (2 atoms 2 lone pairs). # of charge # atoms # lp on central atom Hybrid- zation Sketch Molecular Geometry & approx.. bond angle Example 2 2 atoms sp linear bond angle = 180° H–C≡N: 2 1 atom 1 lp sp linear bond angle = N/A :N≡N: 3
What would be the molecular structure and bond angle of selenium dioxide? If it satisfies the octet rule..which I think it does…Selenium is in the middle and a double bond to …
Seof2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Seof2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
How do I determine the bond angle in a molecule? Socratic
Molecular Geometry Introduction ThoughtCo
Check if the VSEPR shape of the molecule is correct by going to the database and examining the crystal structure (the refcode for the [PF 6] – structure is WINFAA). Measure the bond angles on the structure comparing them to the ideal VSEPR model angles in the table in the next section. Measure the bond angles on the [PF 6] – structure and and compare them to the ideal bond angles on an
Seof2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Seof2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
For example, in a molecule such as CH 2 O (AX 3), whose structure is shown below, the double bond repels the single bonds more strongly than the single bonds repel each other. This causes a deviation from ideal geometry (an H–C–H bond angle of 116.5° rather than 120°).
Molecular geometry is the spatial arrangements of atoms that are bonded in a molecule. Several relationships govern geometry including bonding, electron stability, and atomic size. Several relationships govern geometry including bonding, electron stability, and atomic size.
As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry. Knowing the arrangement of atoms, distribution of electrons, and the shape of the molecule is vastly important in chemistry.
Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding Lewis structures: a review Lewis Theory 3.1 The octet rule All elements except hydrogen ( hydrogen have a duet of electrons) have octet of electrons once
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle.
Lewis Structures, Formal Charges, and Molecular Geometry As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry.
10/01/2018 · In this video I explain the following Bond Parameters 1. Bond Length 2. Bond Angle.
The bond angles and bond lengths of a molecule or ion dictate the particular geometry of the species. Lewis structures are two-dimensional representations of a molecule but because molecules are three dimensional, a picture of the molecular geometry must convey …
Liquid and solid water. Ice, like all solids, has a well-defined structure; each water molecule is surrounded by four neighboring H 2 Os. two of these are hydrogen-bonded to the oxygen atom on the central H 2 O molecule, and each of the two hydrogen atoms …
Molecular Structure University of Tennessee at Chattanooga
Bond length Bond Angle Chemical Bonding And Molecular
What would be the molecular structure and bond angle of selenium dioxide? If it satisfies the octet rule..which I think it does…Selenium is in the middle and a double bond to …
10/01/2018 · In this video I explain the following Bond Parameters 1. Bond Length 2. Bond Angle.
electron and molecular geometry, bond angles, and the VBT hybridization. You should find the Figure 2 You should find the Figure 2 and the on the following page to be helpful.
Chapter 7 Practice Worksheet: Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure 1) How are ionic bonds and covalent bonds different? Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another; Covalent bonds result from two atoms sharing electrons. 2) Describe the relationship between the length of a bond and the strength of that bond. Strength of a bond increases as the bond gets shorter
This is used to predict the shapes of simple molecules and ions by considering the repulsions between pairs of electrons (lone pair and bond pair) within the molecule. It states that, “The shape adopted is the one which keeps repulsive forces to a minimum” To determine the shape, count up the number of covalent bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom and work out the shape which
that the bond angle is in the vicinity of 108”. It looked possible to extend the dilu- It looked possible to extend the dilu- J. Mol. Structure, 10 (1971) 31-38
Lewis Structures, Formal Charges, and Molecular Geometry As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry.
Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding Lewis structures: a review Lewis Theory 3.1 The octet rule All elements except hydrogen ( hydrogen have a duet of electrons) have octet of electrons once
Since experimental evidence indicates that this molecule is bent (bond angle 120º) and has equal length sulfur : oxygen bonds (1.432 Å), a single formula is inadequate, and the actual structure resembles an average of the two formulas.
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.
There are three basic steps to determining the bond angles in a molecule: > 1. Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Assume that you must determine the bond angles in “BF”_3. “B” is less electronegative than “F”, so “B” becomes the central atom. If we have three “F” atoms, that means that we are going to use all three electrons from
Molecular Structure and Polarity · Chemistry
3 Molecular structure and bonding Solution Manual & Test
For example, in a molecule such as CH 2 O (AX 3), whose structure is shown below, the double bond repels the single bonds more strongly than the single bonds repel each other. This causes a deviation from ideal geometry (an H–C–H bond angle of 116.5° rather than 120°).
The Lewis structure is drawn with the atoms all in the same plane. As shown in Figure 9.1, however, the actual three-dimensional arrangement has the Cl atoms at the corners of a . tetrahedron, a geometric object with four corners and four faces, each an equilateral triangle. The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles, the angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms
This is used to predict the shapes of simple molecules and ions by considering the repulsions between pairs of electrons (lone pair and bond pair) within the molecule. It states that, “The shape adopted is the one which keeps repulsive forces to a minimum” To determine the shape, count up the number of covalent bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom and work out the shape which
Check if the VSEPR shape of the molecule is correct by going to the database and examining the crystal structure (the refcode for the [PF 6] – structure is WINFAA). Measure the bond angles on the structure comparing them to the ideal VSEPR model angles in the table in the next section. Measure the bond angles on the [PF 6] – structure and and compare them to the ideal bond angles on an
In carbene: Electronic configuration and molecular structure. The bond angle for the singlet state, however, is predicted to be larger than that for the triplet state.
electron and molecular geometry, bond angles, and the VBT hybridization. You should find the Figure 2 You should find the Figure 2 and the on the following page to be helpful.
For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4 . We can draw the Lewis structure …
Since experimental evidence indicates that this molecule is bent (bond angle 120º) and has equal length sulfur : oxygen bonds (1.432 Å), a single formula is inadequate, and the actual structure resembles an average of the two formulas.
Molecular geometry or molecular structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is important to be able to predict and understand the molecular structure of a molecule because many of the properties of a substance are determined by its geometry.
The bond angle in NO$_2$ is $approx 134^mathrm{o}$ and the NO bond length 120 pm, in $ce{N2O4}$ the N-N bond is very long 175 pm and the angle $approx 126^mathrm{o}$. Nitrogen dioxide is paramagnetic with the odd electron in the $sigma$ bonding sp$^2$ orbital in the ‘third’ lobe as it were with the O atoms occupying the other two.
Ch 4 The shape of molecules 2(14) the structure in which the repulsion among four electron pairs is minimal is not a square with bond angles of 90° but a tetrahedron with bond angles of 109.5 °, definitely larger than 90 °.
a few kelvin, there are considerable oscillations (< ps) in the hydrogen bond length and angles [591]. The potential energy surface [1668] and wagging vibration [1743] of the water dimer have been described and molecular orbitals of the water dimer are shown on another page.
header.jpg Molecular Geometry Worksheet As you work through the steps in the lab procedures, record your experimental values and the results on this worksheet.
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory ctlsfasu
Molecular Geometry Introduction ThoughtCo
The bond angle in NO$_2$ is $approx 134^mathrm{o}$ and the NO bond length 120 pm, in $ce{N2O4}$ the N-N bond is very long 175 pm and the angle $approx 126^mathrm{o}$. Nitrogen dioxide is paramagnetic with the odd electron in the $sigma$ bonding sp$^2$ orbital in the ‘third’ lobe as it were with the O atoms occupying the other two.
Liquid and solid water. Ice, like all solids, has a well-defined structure; each water molecule is surrounded by four neighboring H 2 Os. two of these are hydrogen-bonded to the oxygen atom on the central H 2 O molecule, and each of the two hydrogen atoms …
Lewis structure, then the molecular geometry of the molecules. SO 3 SO 2 CH 4 SF4 PCl5 IF5 N H H H O H H H Cl H C Cl Cl Cl C H H O O C O Cl C Cl Cl Cl H H F S F F F F F. 27 Sigma and pi bonds All single bonds are referred to as ‘sigma’ bonds (σ-bonds). The electron density is concentrated along the bond axis. A multiple bond is made up of a combination of sigma and pi bonds (π-bonds
electron and molecular geometry, bond angles, and the VBT hybridization. You should find the Figure 2 You should find the Figure 2 and the on the following page to be helpful.
For example, in a molecule such as CH 2 O (AX 3), whose structure is shown below, the double bond repels the single bonds more strongly than the single bonds repel each other. This causes a deviation from ideal geometry (an H–C–H bond angle of 116.5° rather than 120°).
AP Chemistry Chapter 8 Answers – Zumdahl 8.113 The first step always is to draw a valid Lewis structure when predicting molecular structure. When resonance is possible, only one of the possible resonance structures is necessary to predict
Chapter 7 Practice Worksheet: Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure 1) How are ionic bonds and covalent bonds different? Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another; Covalent bonds result from two atoms sharing electrons. 2) Describe the relationship between the length of a bond and the strength of that bond. Strength of a bond increases as the bond gets shorter
Molecular Geometry and Hybrid Orbitals H-C-H bond angle 90o Molecular Geometry Why Should I Care About Molecular Geometry? •Chemical properties:
C-C bond length in benzene is 140 pm and C-H bond length is 109 pm. The delocalized structure of benzene also accounts for the X-ray data (all C-C bond lengths equal) and the absence of the type of isomerism shown in Fig. 43.1.
The bond angles and bond lengths of a molecule or ion dictate the particular geometry of the species. Lewis structures are two-dimensional representations of a molecule but because molecules are three dimensional, a picture of the molecular geometry must convey …
Molecular geometry or molecular structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is important to be able to predict and understand the molecular structure of a molecule because many of the properties of a substance are determined by its geometry.
header.jpg Molecular Geometry Worksheet As you work through the steps in the lab procedures, record your experimental values and the results on this worksheet.
Square planar molecular geometry Wikipedia
Chem 121 Determination of Molecular Geometry
The VSEPR theory predicts a see-saw structure with a bond angle of 120 between the S and equatorial F’s and a bond angle of 180 between the S and the axial F’s. The bond angle is actually 102 for the S
For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4 . We can draw the Lewis structure …
Molecular Geometry and Hybrid Orbitals H-C-H bond angle 90o Molecular Geometry Why Should I Care About Molecular Geometry? •Chemical properties:
Molecular Geometry PURPOSE A To explore some simple molecular structures. B To explore the relationship between bond order and bond length. C To explore resonance structures. GOALS 1 To compare Lewis structures to three-dimensional models. 2 To visualize the three-dimensional structures of some common molecules. 3 To obtain bond angle, bond length, and hybridization data for …
Seof2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Seof2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
The VSEPR model of molecular geometry 1031 I ) I, x- 6 X 5″a./6 = 109.5 1 Fig. 13. The mean angle of all six angles in tetrahedral configurations. Fig. 12. The bond arrangement of an AX3B molecule with C2,. symmetry. virtue of the molecular symmetry. For example, the E–P–F angle of the PF3 (i.e. EPF3) molecule can be calculated from the F–P–F bond angle by virtue of the C3,. symmetry of
Ch 4 The shape of molecules 2(14) the structure in which the repulsion among four electron pairs is minimal is not a square with bond angles of 90° but a tetrahedron with bond angles of 109.5 °, definitely larger than 90 °.
Bond angles and other aspects of molecular geometry don’t follow associative rules – you have 3 different molecules, so 3 different structures. You can add a 4th – $ce{H2O}$ – with a bond angle of 104.5$^{circ}$ to extend your comparison.
Six Lewis dot structures can be constructed using one O atom, one F atom, and one N atom. Calculate the formal charges on the atoms in each and use the results to choose the resonance structure …
[PDF] Secl2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle
Molecular Geometry Introduction ThoughtCo
This is used to predict the shapes of simple molecules and ions by considering the repulsions between pairs of electrons (lone pair and bond pair) within the molecule. It states that, “The shape adopted is the one which keeps repulsive forces to a minimum” To determine the shape, count up the number of covalent bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom and work out the shape which
Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding Lewis structures: a review Lewis Theory 3.1 The octet rule All elements except hydrogen ( hydrogen have a duet of electrons) have octet of electrons once
There are three basic steps to determining the bond angles in a molecule: > 1. Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Assume that you must determine the bond angles in “BF”_3. “B” is less electronegative than “F”, so “B” becomes the central atom. If we have three “F” atoms, that means that we are going to use all three electrons from
bond, which is shorter than a single bond. The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently bond molecule.
of bonds. For example, in the structure below, N has 3 charge clouds (2 atoms 1 lone pair), C has 3 charge clouds (3 atoms), and O has 4 charge clouds (2 atoms 2 lone pairs). # of charge # atoms # lp on central atom Hybrid- zation Sketch Molecular Geometry & approx.. bond angle Example 2 2 atoms sp linear bond angle = 180° H–C≡N: 2 1 atom 1 lp sp linear bond angle = N/A :N≡N: 3
The Valence-Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model •The valence-shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) molecular structure of methane. The tetrahedral arrangement of electron pairs produces a tetrahedral arrangement of hydrogen atoms. Predicting Molecular Geometry • The following rules and figures will help discern electron pair arrangements. 1. Draw the Lewis structure 2. Determine how
Molecular shapes College of DuPage – Home
Water Molecule Structure IDC-Online
Name _____ Period ___ Bonding, Nomenclature & Molecular Structure . MOLECULAR GEOMETRY . For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis …
Lewis Structures, Formal Charges, and Molecular Geometry As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry.
The bond angles and bond lengths of a molecule or ion dictate the particular geometry of the species. Lewis structures are two-dimensional representations of a molecule but because molecules are three dimensional, a picture of the molecular geometry must convey …
that the bond angle is in the vicinity of 108”. It looked possible to extend the dilu- It looked possible to extend the dilu- J. Mol. Structure, 10 (1971) 31-38
Since experimental evidence indicates that this molecule is bent (bond angle 120º) and has equal length sulfur : oxygen bonds (1.432 Å), a single formula is inadequate, and the actual structure resembles an average of the two formulas.
electron and molecular geometry, bond angles, and the VBT hybridization. You should find the Figure 2 You should find the Figure 2 and the on the following page to be helpful.
For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4 . We can draw the Lewis structure …
PCL3 Molecular Electron Geometry, Lewis Structure, Bond Angles and Hybridization by Janice Powell · Published February 7, 2018 · Updated March 8, 2018 PCL3 – Phosphorus Trichloride is a chemical formula of phosphorus and chlorine.
The VSEPR model of molecular geometry 1031 I ) I, x- 6 X 5″a./6 = 109.5 1 Fig. 13. The mean angle of all six angles in tetrahedral configurations. Fig. 12. The bond arrangement of an AX3B molecule with C2,. symmetry. virtue of the molecular symmetry. For example, the E–P–F angle of the PF3 (i.e. EPF3) molecule can be calculated from the F–P–F bond angle by virtue of the C3,. symmetry of
Molecular Geometry and Hybrid Orbitals H-C-H bond angle 90o Molecular Geometry Why Should I Care About Molecular Geometry? •Chemical properties:
Bond angle(s) 90° μ (Polarity) 0: Structure of cisplatin, an example of a molecule with the square planar coordination geometry. The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners of a square …
AP Chemistry Chapter 8 Answers – Zumdahl 8.113 The first step always is to draw a valid Lewis structure when predicting molecular structure. When resonance is possible, only one of the possible resonance structures is necessary to predict
Six Lewis dot structures can be constructed using one O atom, one F atom, and one N atom. Calculate the formal charges on the atoms in each and use the results to choose the resonance structure …
The VSEPR theory predicts a see-saw structure with a bond angle of 120 between the S and equatorial F’s and a bond angle of 180 between the S and the axial F’s. The bond angle is actually 102 for the S
Determination of Molecular Structure by MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY Much of what we know about molecular structur e has been learned by observing and analyzing how electromagnetic radiation interacts with matter . Spectroscopy is the observation and analysis of this interaction. Electromagnetic radiation is energy, and when electromagnetic radiation is absorbed by molecules, the molecules gain …
SHAPES OF SIMPLE MOLECULES AND IONS knockhardy.org.uk
[PDF] Secl2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.
The bond angles and bond lengths of a molecule or ion dictate the particular geometry of the species. Lewis structures are two-dimensional representations of a molecule but because molecules are three dimensional, a picture of the molecular geometry must convey …
Molecular geometry or molecular structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is important to be able to predict and understand the molecular structure of a molecule because many of the properties of a substance are determined by its geometry.
The VSEPR model of molecular geometry 1031 I ) I, x- 6 X 5″a./6 = 109.5 1 Fig. 13. The mean angle of all six angles in tetrahedral configurations. Fig. 12. The bond arrangement of an AX3B molecule with C2,. symmetry. virtue of the molecular symmetry. For example, the E–P–F angle of the PF3 (i.e. EPF3) molecule can be calculated from the F–P–F bond angle by virtue of the C3,. symmetry of
electron and molecular geometry, bond angles, and the VBT hybridization. You should find the Figure 2 You should find the Figure 2 and the on the following page to be helpful.
Lewis structure, then the molecular geometry of the molecules. SO 3 SO 2 CH 4 SF4 PCl5 IF5 N H H H O H H H Cl H C Cl Cl Cl C H H O O C O Cl C Cl Cl Cl H H F S F F F F F. 27 Sigma and pi bonds All single bonds are referred to as ‘sigma’ bonds (σ-bonds). The electron density is concentrated along the bond axis. A multiple bond is made up of a combination of sigma and pi bonds (π-bonds
Molecular geometry optimization Calculation for determining the geometry of a molecule that consists in systematically varying the geometric variables (bond lengths, bond angles, dihedral angles) until an energy minimum is reached.
Six Lewis dot structures can be constructed using one O atom, one F atom, and one N atom. Calculate the formal charges on the atoms in each and use the results to choose the resonance structure …
Check if the VSEPR shape of the molecule is correct by going to the database and examining the crystal structure (the refcode for the [PF 6] – structure is WINFAA). Measure the bond angles on the structure comparing them to the ideal VSEPR model angles in the table in the next section. Measure the bond angles on the [PF 6] – structure and and compare them to the ideal bond angles on an
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle.
As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry. Knowing the arrangement of atoms, distribution of electrons, and the shape of the molecule is vastly important in chemistry.
[PDF] Seof2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle
molecular structure Comparision of ONO Bond angle in NO2
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle.
Six Lewis dot structures can be constructed using one O atom, one F atom, and one N atom. Calculate the formal charges on the atoms in each and use the results to choose the resonance structure …
Molecular Geometry Lewis structures are good for figuring out how atoms are bonded to each other within a molecule and where any lone pairs of electrons are. They’re quite flexible in terms of how the atoms can be arranged on the page: bond length and angles between bonds don’t necessarily have to match reality. On the other hand, the information you write down in a Lewis structure is
There are three basic steps to determining the bond angles in a molecule: > 1. Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Assume that you must determine the bond angles in “BF”_3. “B” is less electronegative than “F”, so “B” becomes the central atom. If we have three “F” atoms, that means that we are going to use all three electrons from
Name _____ Period ___ Bonding, Nomenclature & Molecular Structure . MOLECULAR GEOMETRY . For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis …
29/04/2015 · This video shows you how to draw the lewis structure for CH2Cl2. It provides the molecular geometry and bond angle for the CH2Cl2 (dichloromethane) lewis dot structure.
Water Molecule Structure IDC-Online
Bond length Bond Angle Chemical Bonding And Molecular
The molecular structure of 1 is depicted in Fig. 1, and the bond distances and angles are listed in Table 2. The local geometry of the cobalt ion is an octahedral arrangement with two NCS groups in trans position (N(3)–Co–N(3)′=177.1(2)°) and four pyridine units in a basal plane.
Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding Lewis structures: a review Lewis Theory 3.1 The octet rule All elements except hydrogen ( hydrogen have a duet of electrons) have octet of electrons once
PCL3 Molecular Electron Geometry, Lewis Structure, Bond Angles and Hybridization by Janice Powell · Published February 7, 2018 · Updated March 8, 2018 PCL3 – Phosphorus Trichloride is a chemical formula of phosphorus and chlorine.
Bond angle(s) 90° μ (Polarity) 0: Structure of cisplatin, an example of a molecule with the square planar coordination geometry. The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners of a square …
Molecular geometry is the spatial arrangements of atoms that are bonded in a molecule. Several relationships govern geometry including bonding, electron stability, and atomic size. Several relationships govern geometry including bonding, electron stability, and atomic size.
There are three basic steps to determining the bond angles in a molecule: > 1. Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Assume that you must determine the bond angles in “BF”_3. “B” is less electronegative than “F”, so “B” becomes the central atom. If we have three “F” atoms, that means that we are going to use all three electrons from
The bond angle in NO$_2$ is $approx 134^mathrm{o}$ and the NO bond length 120 pm, in $ce{N2O4}$ the N-N bond is very long 175 pm and the angle $approx 126^mathrm{o}$. Nitrogen dioxide is paramagnetic with the odd electron in the $sigma$ bonding sp$^2$ orbital in the ‘third’ lobe as it were with the O atoms occupying the other two.
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space (). A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common
For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4 . We can draw the Lewis structure …
bond, which is shorter than a single bond. The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently bond molecule.
Chapter 7 Practice Worksheet: Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure 1) How are ionic bonds and covalent bonds different? Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another; Covalent bonds result from two atoms sharing electrons. 2) Describe the relationship between the length of a bond and the strength of that bond. Strength of a bond increases as the bond gets shorter
The Lewis structure is drawn with the atoms all in the same plane. As shown in Figure 9.1, however, the actual three-dimensional arrangement has the Cl atoms at the corners of a . tetrahedron, a geometric object with four corners and four faces, each an equilateral triangle. The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles, the angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms
Molecular Geometry and Hybrid Orbitals H-C-H bond angle 90o Molecular Geometry Why Should I Care About Molecular Geometry? •Chemical properties:
3 Molecular structure and bonding Solution Manual & Test
Molecular Geometry Chemistry LibreTexts
The Valence-Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model •The valence-shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) molecular structure of methane. The tetrahedral arrangement of electron pairs produces a tetrahedral arrangement of hydrogen atoms. Predicting Molecular Geometry • The following rules and figures will help discern electron pair arrangements. 1. Draw the Lewis structure 2. Determine how
What would be the molecular structure and bond angle of selenium dioxide? If it satisfies the octet rule..which I think it does…Selenium is in the middle and a double bond to …
For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4 . We can draw the Lewis structure …
Molecular geometry or molecular structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is important to be able to predict and understand the molecular structure of a molecule because many of the properties of a substance are determined by its geometry.
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF NITROGEN TRICHLORIDE AS DETER-
Ch 4 The shape of molecules Soka
Molecular geometry is the spatial arrangements of atoms that are bonded in a molecule. Several relationships govern geometry including bonding, electron stability, and atomic size. Several relationships govern geometry including bonding, electron stability, and atomic size.
As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry. Knowing the arrangement of atoms, distribution of electrons, and the shape of the molecule is vastly important in chemistry.
Liquid and solid water. Ice, like all solids, has a well-defined structure; each water molecule is surrounded by four neighboring H 2 Os. two of these are hydrogen-bonded to the oxygen atom on the central H 2 O molecule, and each of the two hydrogen atoms …
The bond angle in NO$_2$ is $approx 134^mathrm{o}$ and the NO bond length 120 pm, in $ce{N2O4}$ the N-N bond is very long 175 pm and the angle $approx 126^mathrm{o}$. Nitrogen dioxide is paramagnetic with the odd electron in the $sigma$ bonding sp$^2$ orbital in the ‘third’ lobe as it were with the O atoms occupying the other two.
PCL3 Molecular Electron Geometry, Lewis Structure, Bond Angles and Hybridization by Janice Powell · Published February 7, 2018 · Updated March 8, 2018 PCL3 – Phosphorus Trichloride is a chemical formula of phosphorus and chlorine.
The Valence-Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model •The valence-shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) molecular structure of methane. The tetrahedral arrangement of electron pairs produces a tetrahedral arrangement of hydrogen atoms. Predicting Molecular Geometry • The following rules and figures will help discern electron pair arrangements. 1. Draw the Lewis structure 2. Determine how
Name _____ Period ___ Bonding, Nomenclature & Molecular Structure . MOLECULAR GEOMETRY . For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis …
This is used to predict the shapes of simple molecules and ions by considering the repulsions between pairs of electrons (lone pair and bond pair) within the molecule. It states that, “The shape adopted is the one which keeps repulsive forces to a minimum” To determine the shape, count up the number of covalent bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom and work out the shape which
Molecular Geometry PURPOSE A To explore some simple molecular structures. B To explore the relationship between bond order and bond length. C To explore resonance structures. GOALS 1 To compare Lewis structures to three-dimensional models. 2 To visualize the three-dimensional structures of some common molecules. 3 To obtain bond angle, bond length, and hybridization data for …
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle.
a few kelvin, there are considerable oscillations (< ps) in the hydrogen bond length and angles [591]. The potential energy surface [1668] and wagging vibration [1743] of the water dimer have been described and molecular orbitals of the water dimer are shown on another page.
Bond angle(s) 90° μ (Polarity) 0: Structure of cisplatin, an example of a molecule with the square planar coordination geometry. The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners of a square …
The bond angles and bond lengths of a molecule or ion dictate the particular geometry of the species. Lewis structures are two-dimensional representations of a molecule but because molecules are three dimensional, a picture of the molecular geometry must convey …
Chapter 7 Practice Worksheet: Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure 1) How are ionic bonds and covalent bonds different? Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another; Covalent bonds result from two atoms sharing electrons. 2) Describe the relationship between the length of a bond and the strength of that bond. Strength of a bond increases as the bond gets shorter
Lewis structure, then the molecular geometry of the molecules. SO 3 SO 2 CH 4 SF4 PCl5 IF5 N H H H O H H H Cl H C Cl Cl Cl C H H O O C O Cl C Cl Cl Cl H H F S F F F F F. 27 Sigma and pi bonds All single bonds are referred to as ‘sigma’ bonds (σ-bonds). The electron density is concentrated along the bond axis. A multiple bond is made up of a combination of sigma and pi bonds (π-bonds
Bond angle of isothiocyanate. Molecular network of cobalt
Molecular Geometry Worksheet WebAssign
PCL3 Molecular Electron Geometry, Lewis Structure, Bond Angles and Hybridization by Janice Powell · Published February 7, 2018 · Updated March 8, 2018 PCL3 – Phosphorus Trichloride is a chemical formula of phosphorus and chlorine.
There are three basic steps to determining the bond angles in a molecule: > 1. Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Assume that you must determine the bond angles in “BF”_3. “B” is less electronegative than “F”, so “B” becomes the central atom. If we have three “F” atoms, that means that we are going to use all three electrons from
The Lewis structure is drawn with the atoms all in the same plane. As shown in Figure 9.1, however, the actual three-dimensional arrangement has the Cl atoms at the corners of a . tetrahedron, a geometric object with four corners and four faces, each an equilateral triangle. The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles, the angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms
Lewis structure, then the molecular geometry of the molecules. SO 3 SO 2 CH 4 SF4 PCl5 IF5 N H H H O H H H Cl H C Cl Cl Cl C H H O O C O Cl C Cl Cl Cl H H F S F F F F F. 27 Sigma and pi bonds All single bonds are referred to as ‘sigma’ bonds (σ-bonds). The electron density is concentrated along the bond axis. A multiple bond is made up of a combination of sigma and pi bonds (π-bonds
header.jpg Molecular Geometry Worksheet As you work through the steps in the lab procedures, record your experimental values and the results on this worksheet.
As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry. Knowing the arrangement of atoms, distribution of electrons, and the shape of the molecule is vastly important in chemistry.
There are so many things to know about such as molecular geometry, Lewis structure, polarity, hybridization, as well as bond angles, but very little information available online. So in this article, I am going to solve all the confusions regarding of the Sulfur DiFluoride – SF2 molecular geometry .
Bond angle(s) 90° μ (Polarity) 0: Structure of cisplatin, an example of a molecule with the square planar coordination geometry. The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners of a square …
polarity, we need to predict molecular shapes Lewis dot structure provides 2D sketch of the distribution of the valence electrons among bonds between atoms and lone pairs; it provides no information about the shape of the molecule . A hierarchy of models VSEPR Consider the problem in terms of electrostatic repulsion between groups of electrons (charge clouds, domains) Valence bond theory
Secl2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Secl2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory ctlsfasu
Molecular Structure University of Tennessee at Chattanooga
that the bond angle is in the vicinity of 108”. It looked possible to extend the dilu- It looked possible to extend the dilu- J. Mol. Structure, 10 (1971) 31-38
As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry. Knowing the arrangement of atoms, distribution of electrons, and the shape of the molecule is vastly important in chemistry.
a few kelvin, there are considerable oscillations (< ps) in the hydrogen bond length and angles [591]. The potential energy surface [1668] and wagging vibration [1743] of the water dimer have been described and molecular orbitals of the water dimer are shown on another page.
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle.
Ch 4 The shape of molecules 2(14) the structure in which the repulsion among four electron pairs is minimal is not a square with bond angles of 90° but a tetrahedron with bond angles of 109.5 °, definitely larger than 90 °.
Molecular Geometry and Hybrid Orbitals H-C-H bond angle 90o Molecular Geometry Why Should I Care About Molecular Geometry? •Chemical properties:
Since experimental evidence indicates that this molecule is bent (bond angle 120º) and has equal length sulfur : oxygen bonds (1.432 Å), a single formula is inadequate, and the actual structure resembles an average of the two formulas.
Lewis Structures, Formal Charges, and Molecular Geometry As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry.
The Lewis structure is drawn with the atoms all in the same plane. As shown in Figure 9.1, however, the actual three-dimensional arrangement has the Cl atoms at the corners of a . tetrahedron, a geometric object with four corners and four faces, each an equilateral triangle. The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles, the angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms
Check if the VSEPR shape of the molecule is correct by going to the database and examining the crystal structure (the refcode for the [PF 6] – structure is WINFAA). Measure the bond angles on the structure comparing them to the ideal VSEPR model angles in the table in the next section. Measure the bond angles on the [PF 6] – structure and and compare them to the ideal bond angles on an
For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4 . We can draw the Lewis structure …
The VSEPR theory predicts a see-saw structure with a bond angle of 120 between the S and equatorial F’s and a bond angle of 180 between the S and the axial F’s. The bond angle is actually 102 for the S
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory ctlsfasu
Molecular Geometry Chemistry Socratic
The VSEPR theory predicts a see-saw structure with a bond angle of 120 between the S and equatorial F’s and a bond angle of 180 between the S and the axial F’s. The bond angle is actually 102 for the S
Lewis structure, then the molecular geometry of the molecules. SO 3 SO 2 CH 4 SF4 PCl5 IF5 N H H H O H H H Cl H C Cl Cl Cl C H H O O C O Cl C Cl Cl Cl H H F S F F F F F. 27 Sigma and pi bonds All single bonds are referred to as ‘sigma’ bonds (σ-bonds). The electron density is concentrated along the bond axis. A multiple bond is made up of a combination of sigma and pi bonds (π-bonds
For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4 . We can draw the Lewis structure …
What would be the molecular structure and bond angle of selenium dioxide? If it satisfies the octet rule..which I think it does…Selenium is in the middle and a double bond to …
Secl2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Secl2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle.
header.jpg Molecular Geometry Worksheet As you work through the steps in the lab procedures, record your experimental values and the results on this worksheet.
The molecular structure of 1 is depicted in Fig. 1, and the bond distances and angles are listed in Table 2. The local geometry of the cobalt ion is an octahedral arrangement with two NCS groups in trans position (N(3)–Co–N(3)′=177.1(2)°) and four pyridine units in a basal plane.
Chapter 7 Practice Worksheet: Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure 1) How are ionic bonds and covalent bonds different? Ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another; Covalent bonds result from two atoms sharing electrons. 2) Describe the relationship between the length of a bond and the strength of that bond. Strength of a bond increases as the bond gets shorter
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space (). A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common
of bonds. For example, in the structure below, N has 3 charge clouds (2 atoms 1 lone pair), C has 3 charge clouds (3 atoms), and O has 4 charge clouds (2 atoms 2 lone pairs). # of charge # atoms # lp on central atom Hybrid- zation Sketch Molecular Geometry & approx.. bond angle Example 2 2 atoms sp linear bond angle = 180° H–C≡N: 2 1 atom 1 lp sp linear bond angle = N/A :N≡N: 3
Molecular Geometry Lewis structures are good for figuring out how atoms are bonded to each other within a molecule and where any lone pairs of electrons are. They’re quite flexible in terms of how the atoms can be arranged on the page: bond length and angles between bonds don’t necessarily have to match reality. On the other hand, the information you write down in a Lewis structure is
For example, in a molecule such as CH 2 O (AX 3), whose structure is shown below, the double bond repels the single bonds more strongly than the single bonds repel each other. This causes a deviation from ideal geometry (an H–C–H bond angle of 116.5° rather than 120°).
bond, which is shorter than a single bond. The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently bond molecule.
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory ctlsfasu
Water Molecule Structure IDC-Online
There are three basic steps to determining the bond angles in a molecule: > 1. Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Assume that you must determine the bond angles in “BF”_3. “B” is less electronegative than “F”, so “B” becomes the central atom. If we have three “F” atoms, that means that we are going to use all three electrons from
Check if the VSEPR shape of the molecule is correct by going to the database and examining the crystal structure (the refcode for the [PF 6] – structure is WINFAA). Measure the bond angles on the structure comparing them to the ideal VSEPR model angles in the table in the next section. Measure the bond angles on the [PF 6] – structure and and compare them to the ideal bond angles on an
bond, which is shorter than a single bond. The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently The bond angles are also very specific in a covalently bond molecule.
polarity, we need to predict molecular shapes Lewis dot structure provides 2D sketch of the distribution of the valence electrons among bonds between atoms and lone pairs; it provides no information about the shape of the molecule . A hierarchy of models VSEPR Consider the problem in terms of electrostatic repulsion between groups of electrons (charge clouds, domains) Valence bond theory
Molecular Geometry and Hybrid Orbitals H-C-H bond angle 90o Molecular Geometry Why Should I Care About Molecular Geometry? •Chemical properties:
Molecular Structure Topics 3-D structure shape (location of atoms in space) Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbitals Multiple Bonds
Molecular geometry or molecular structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is important to be able to predict and understand the molecular structure of a molecule because many of the properties of a substance are determined by its geometry.
29/04/2015 · This video shows you how to draw the lewis structure for CH2Cl2. It provides the molecular geometry and bond angle for the CH2Cl2 (dichloromethane) lewis dot structure.
Lewis structure, then the molecular geometry of the molecules. SO 3 SO 2 CH 4 SF4 PCl5 IF5 N H H H O H H H Cl H C Cl Cl Cl C H H O O C O Cl C Cl Cl Cl H H F S F F F F F. 27 Sigma and pi bonds All single bonds are referred to as ‘sigma’ bonds (σ-bonds). The electron density is concentrated along the bond axis. A multiple bond is made up of a combination of sigma and pi bonds (π-bonds
The Lewis structure is drawn with the atoms all in the same plane. As shown in Figure 9.1, however, the actual three-dimensional arrangement has the Cl atoms at the corners of a . tetrahedron, a geometric object with four corners and four faces, each an equilateral triangle. The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles, the angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms
a few kelvin, there are considerable oscillations (< ps) in the hydrogen bond length and angles [591]. The potential energy surface [1668] and wagging vibration [1743] of the water dimer have been described and molecular orbitals of the water dimer are shown on another page.
that the bond angle is in the vicinity of 108”. It looked possible to extend the dilu- It looked possible to extend the dilu- J. Mol. Structure, 10 (1971) 31-38
CH2Cl2 lewis structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle
Chem 121 Determination of Molecular Geometry
of bonds. For example, in the structure below, N has 3 charge clouds (2 atoms 1 lone pair), C has 3 charge clouds (3 atoms), and O has 4 charge clouds (2 atoms 2 lone pairs). # of charge # atoms # lp on central atom Hybrid- zation Sketch Molecular Geometry & approx.. bond angle Example 2 2 atoms sp linear bond angle = 180° H–C≡N: 2 1 atom 1 lp sp linear bond angle = N/A :N≡N: 3
In carbene: Electronic configuration and molecular structure. The bond angle for the singlet state, however, is predicted to be larger than that for the triplet state.
C-C bond length in benzene is 140 pm and C-H bond length is 109 pm. The delocalized structure of benzene also accounts for the X-ray data (all C-C bond lengths equal) and the absence of the type of isomerism shown in Fig. 43.1.
As scientists we can predict a lot about how molecules react chemically and their physical properties by looking at Lewis structures and molecular geometry. Knowing the arrangement of atoms, distribution of electrons, and the shape of the molecule is vastly important in chemistry.
10/01/2018 · In this video I explain the following Bond Parameters 1. Bond Length 2. Bond Angle.
Lewis Structures Molecular Geometry Bond Angle and more
Molecular Structure Exercises
Molecular Geometry and Hybrid Orbitals H-C-H bond angle 90o Molecular Geometry Why Should I Care About Molecular Geometry? •Chemical properties:
29/04/2015 · This video shows you how to draw the lewis structure for CH2Cl2. It provides the molecular geometry and bond angle for the CH2Cl2 (dichloromethane) lewis dot structure.
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle.
header.jpg Molecular Geometry Worksheet As you work through the steps in the lab procedures, record your experimental values and the results on this worksheet.
There are so many things to know about such as molecular geometry, Lewis structure, polarity, hybridization, as well as bond angles, but very little information available online. So in this article, I am going to solve all the confusions regarding of the Sulfur DiFluoride – SF2 molecular geometry .
Liquid and solid water. Ice, like all solids, has a well-defined structure; each water molecule is surrounded by four neighboring H 2 Os. two of these are hydrogen-bonded to the oxygen atom on the central H 2 O molecule, and each of the two hydrogen atoms …
What would be the molecular structure and bond angle of selenium dioxide? If it satisfies the octet rule..which I think it does…Selenium is in the middle and a double bond to …
Six Lewis dot structures can be constructed using one O atom, one F atom, and one N atom. Calculate the formal charges on the atoms in each and use the results to choose the resonance structure …
Ch 4 The shape of molecules 2(14) the structure in which the repulsion among four electron pairs is minimal is not a square with bond angles of 90° but a tetrahedron with bond angles of 109.5 °, definitely larger than 90 °.
Bond angle(s) 90° μ (Polarity) 0: Structure of cisplatin, an example of a molecule with the square planar coordination geometry. The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners of a square …
This is used to predict the shapes of simple molecules and ions by considering the repulsions between pairs of electrons (lone pair and bond pair) within the molecule. It states that, “The shape adopted is the one which keeps repulsive forces to a minimum” To determine the shape, count up the number of covalent bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom and work out the shape which
polarity, we need to predict molecular shapes Lewis dot structure provides 2D sketch of the distribution of the valence electrons among bonds between atoms and lone pairs; it provides no information about the shape of the molecule . A hierarchy of models VSEPR Consider the problem in terms of electrostatic repulsion between groups of electrons (charge clouds, domains) Valence bond theory
There are three basic steps to determining the bond angles in a molecule: > 1. Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. Assume that you must determine the bond angles in “BF”_3. “B” is less electronegative than “F”, so “B” becomes the central atom. If we have three “F” atoms, that means that we are going to use all three electrons from
of bonds. For example, in the structure below, N has 3 charge clouds (2 atoms 1 lone pair), C has 3 charge clouds (3 atoms), and O has 4 charge clouds (2 atoms 2 lone pairs). # of charge # atoms # lp on central atom Hybrid- zation Sketch Molecular Geometry & approx.. bond angle Example 2 2 atoms sp linear bond angle = 180° H–C≡N: 2 1 atom 1 lp sp linear bond angle = N/A :N≡N: 3
Seof2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Polar Or Nonpolar. These files are related to Seof2 lewis structure molecular geometry bond angle polar or nonpolar.
molecular structure Comparision of ONO Bond angle in NO2
Molecular Structure and Polarity · Chemistry
In carbene: Electronic configuration and molecular structure. The bond angle for the singlet state, however, is predicted to be larger than that for the triplet state.
Bond angle of isothiocyanate. Molecular network of cobalt